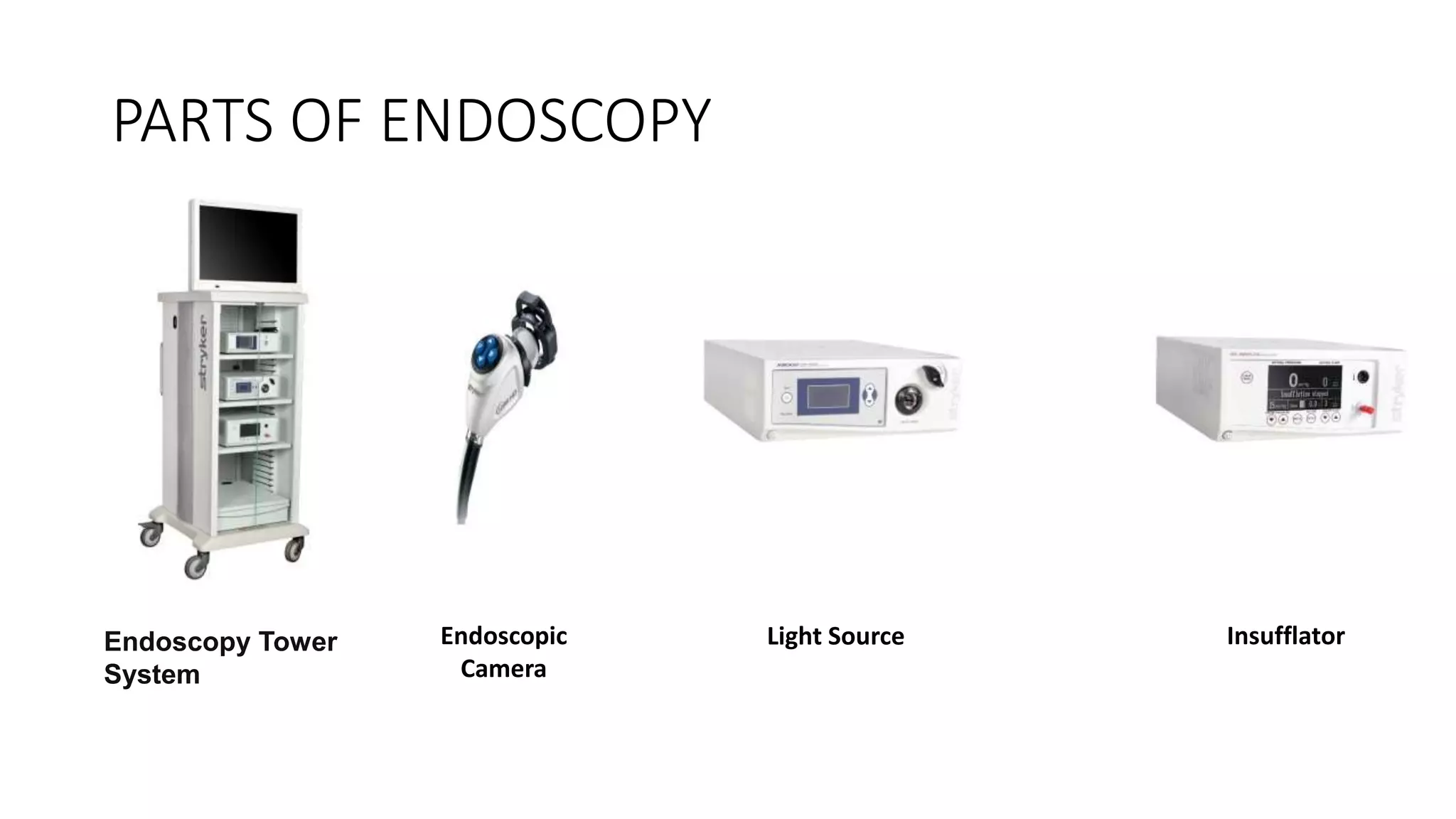
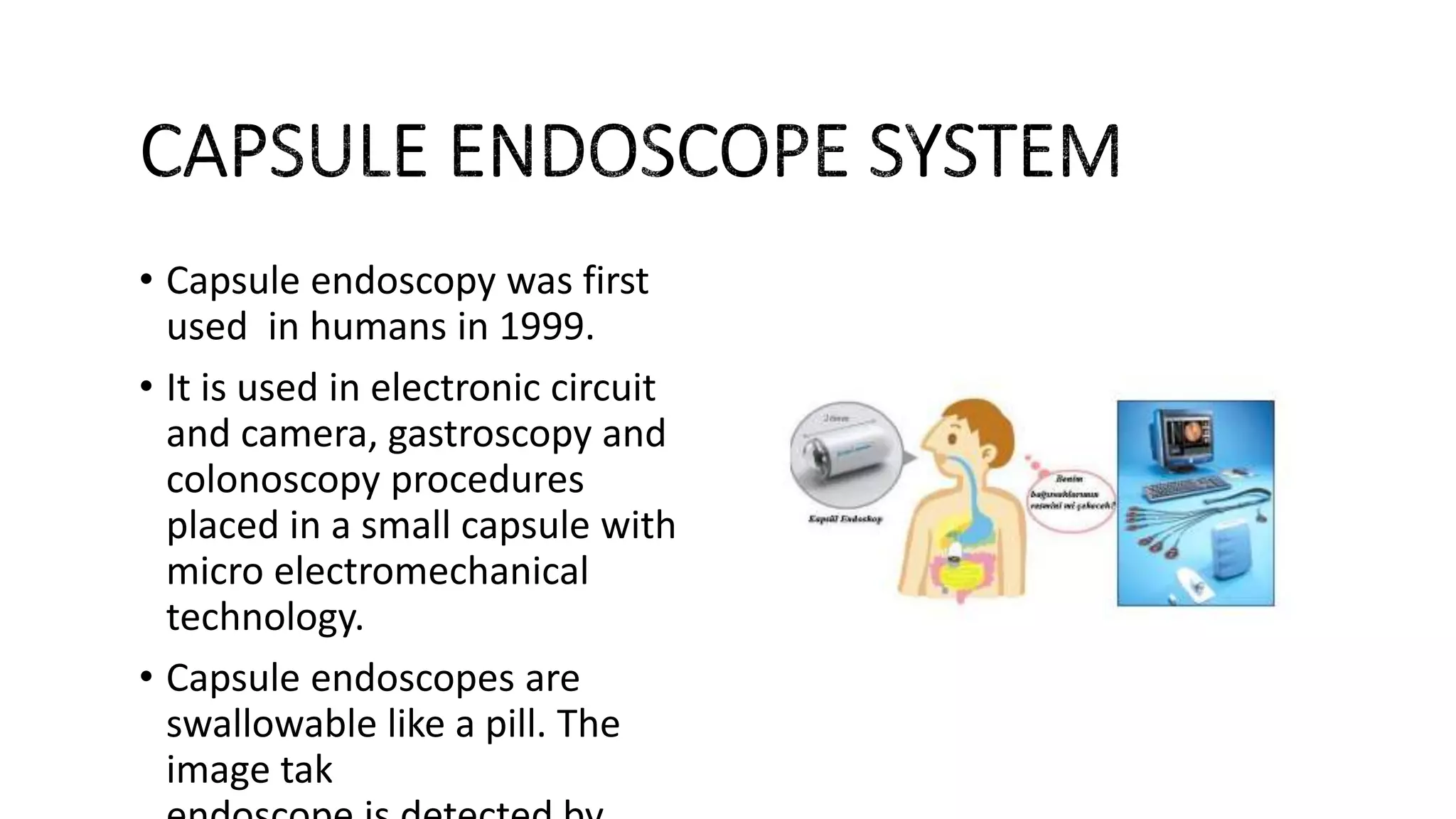
This document provides an overview of endoscopy. It begins with definitions and a brief history, noting that endoscopy allows doctors to view and operate on internal organs using specialized instruments. It describes the typical components of an endoscopy system, including the endoscopic camera, light source, insufflator, and endoscopy tower. The document outlines different types of endoscopy based on the part of the body being examined and describes the process, risks, and future trends of endoscopy, including capsule endoscopy and robotic systems like da Vinci.