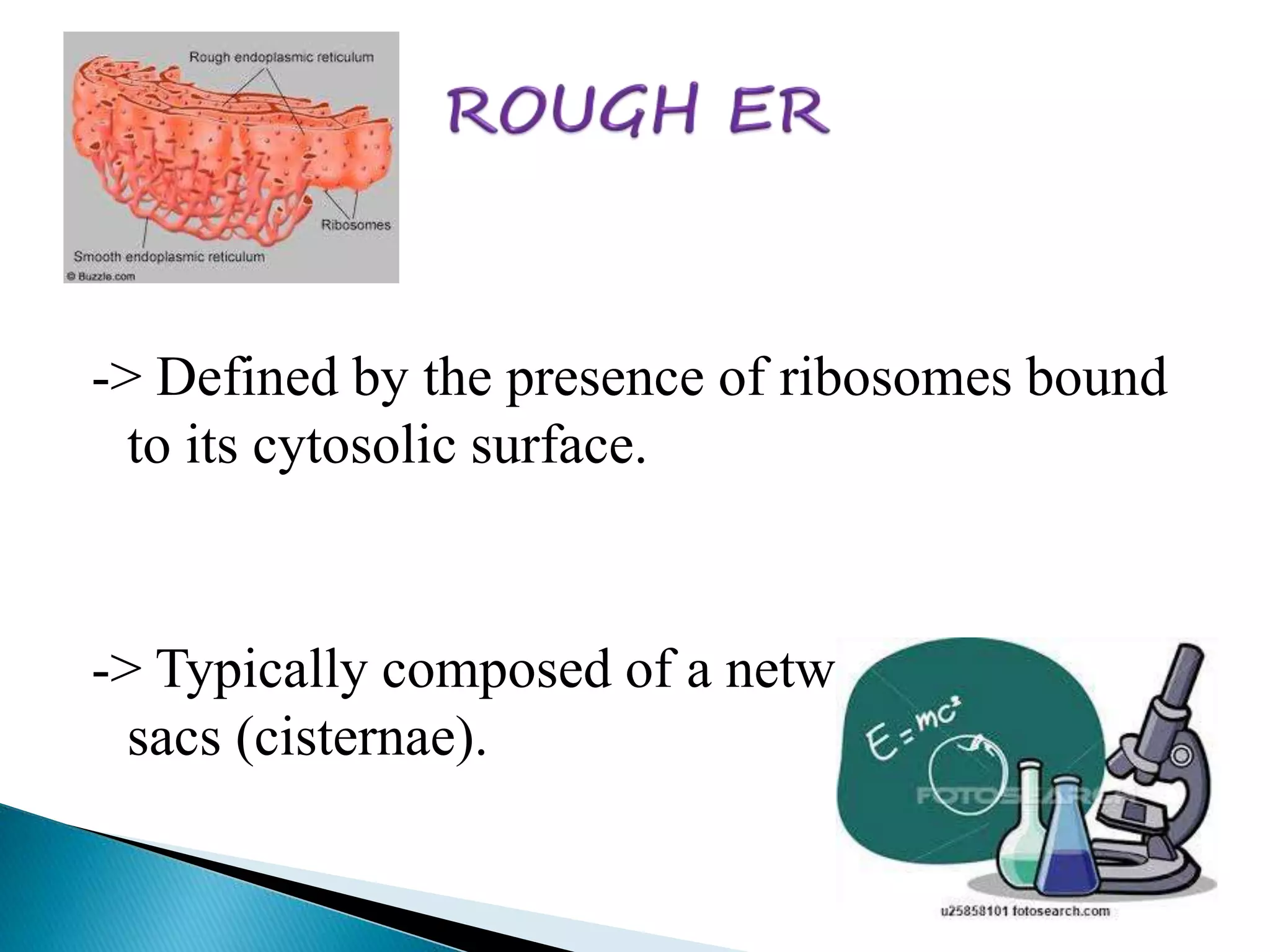
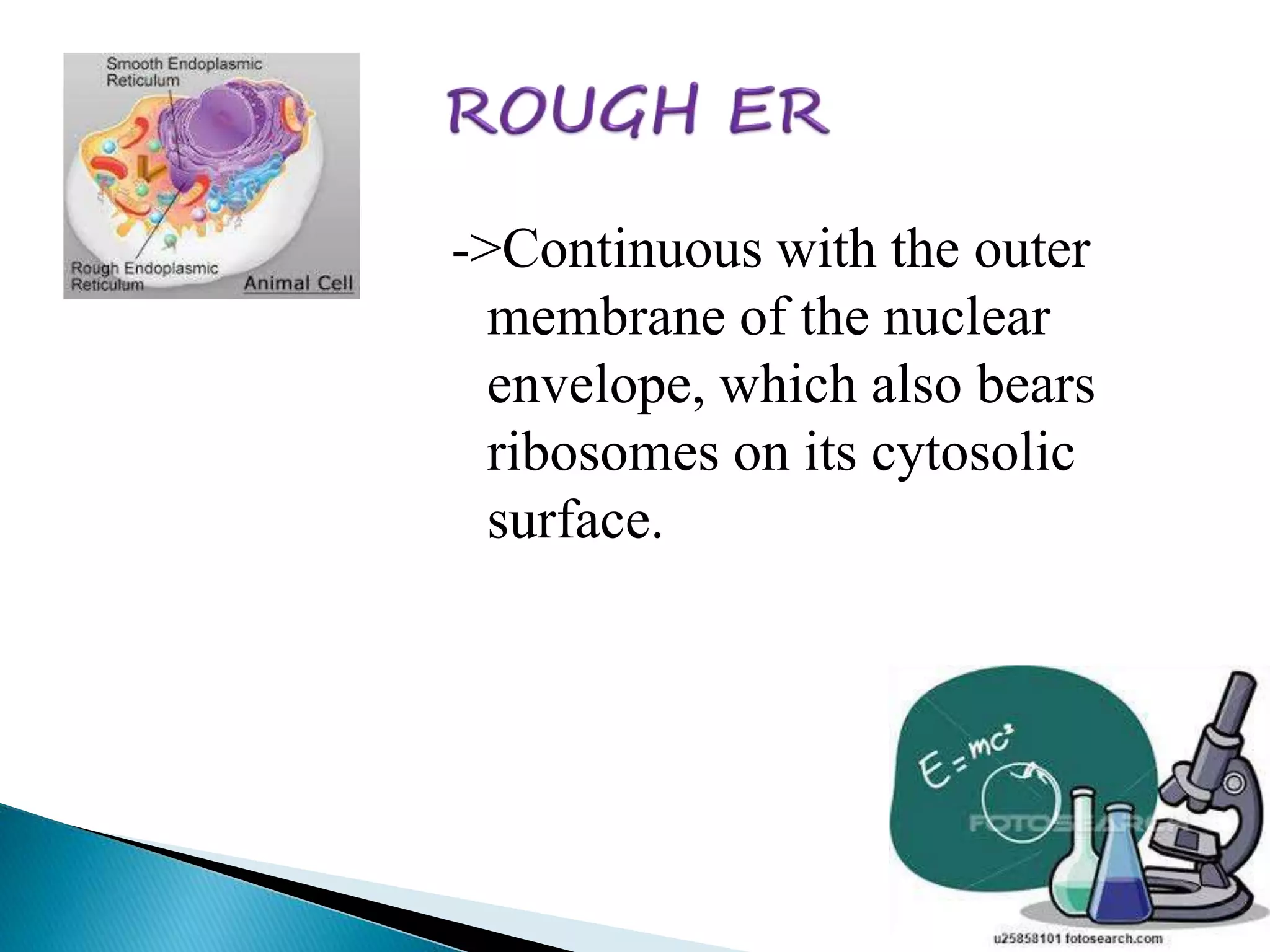
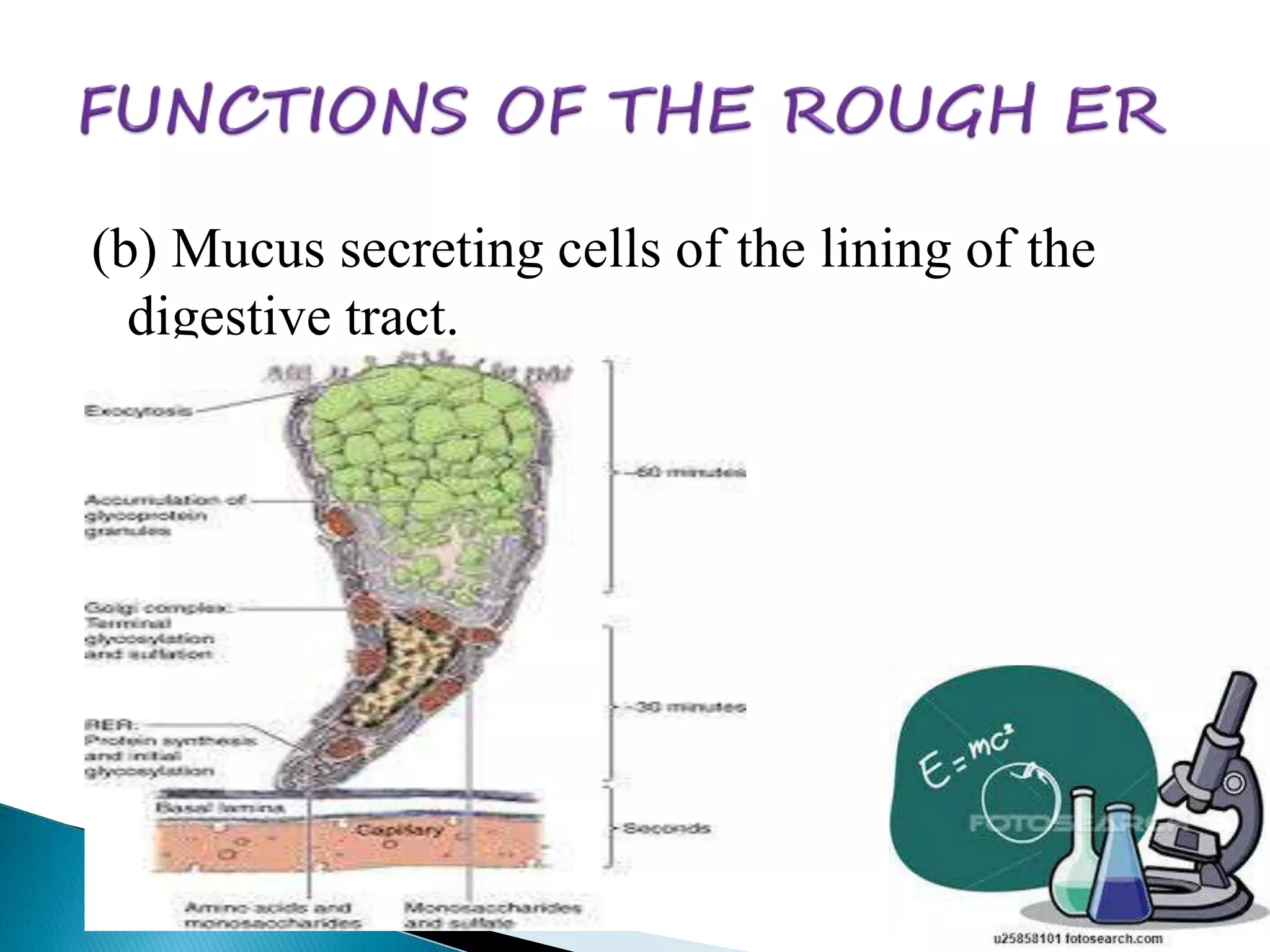
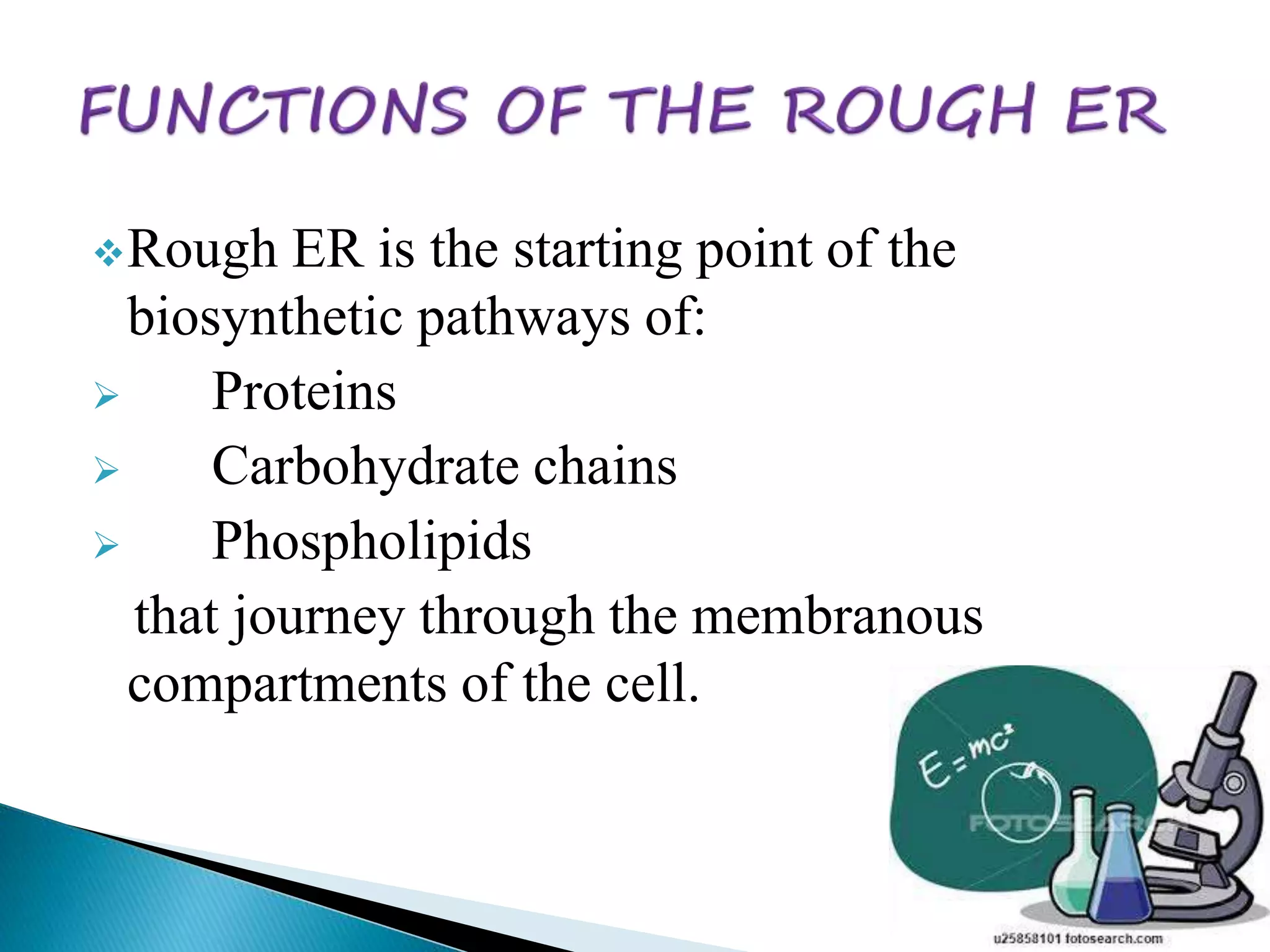
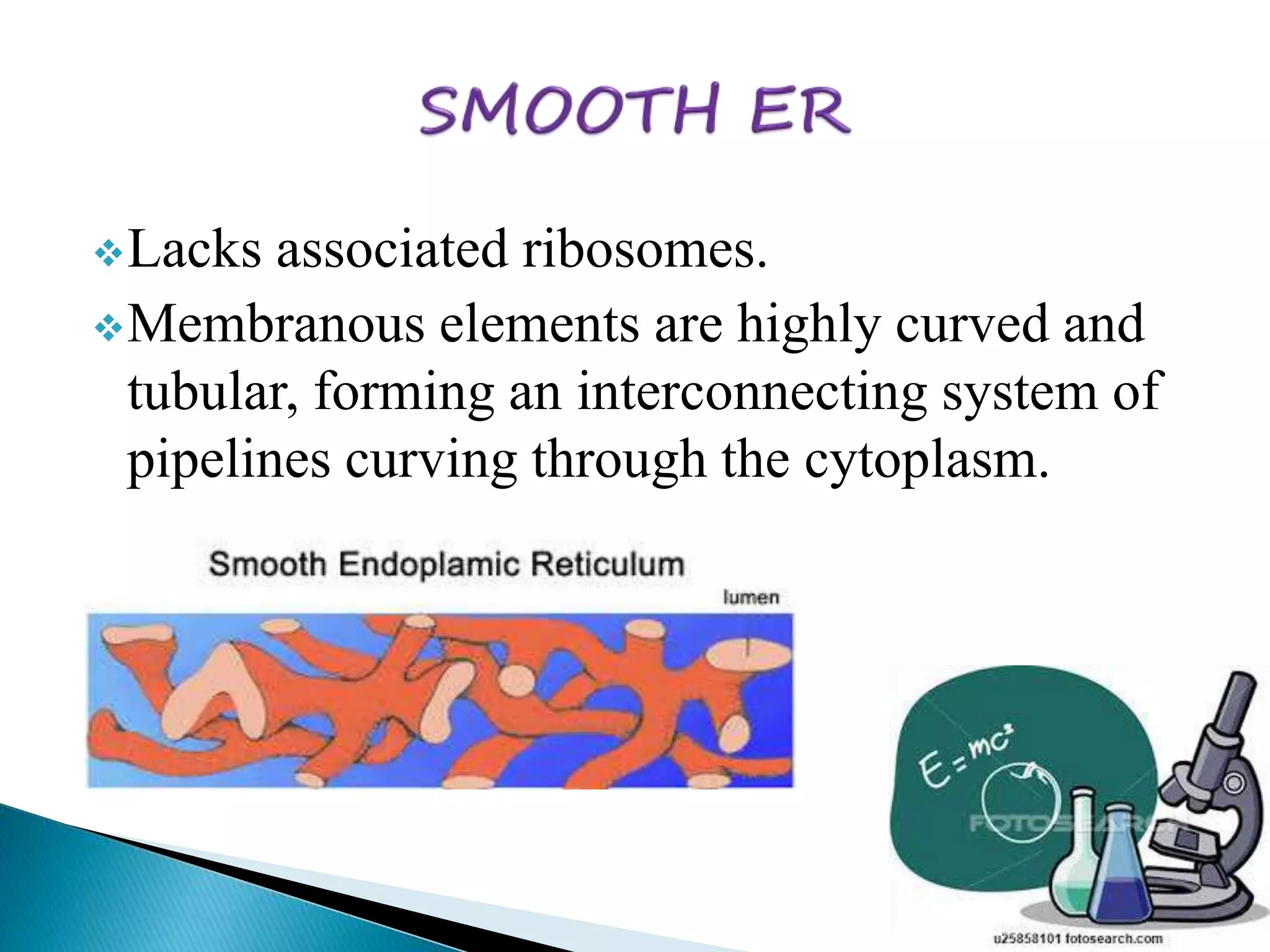
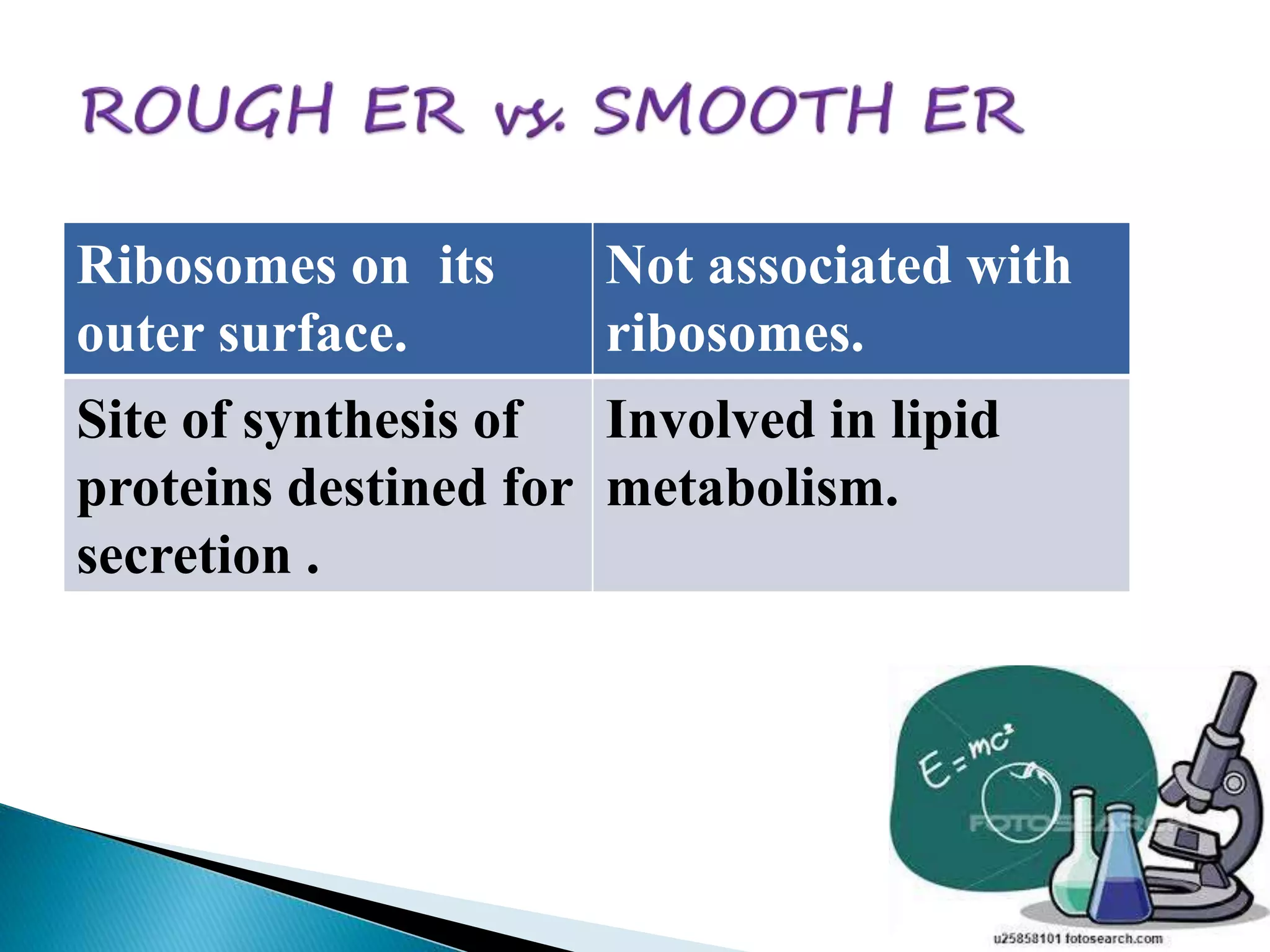
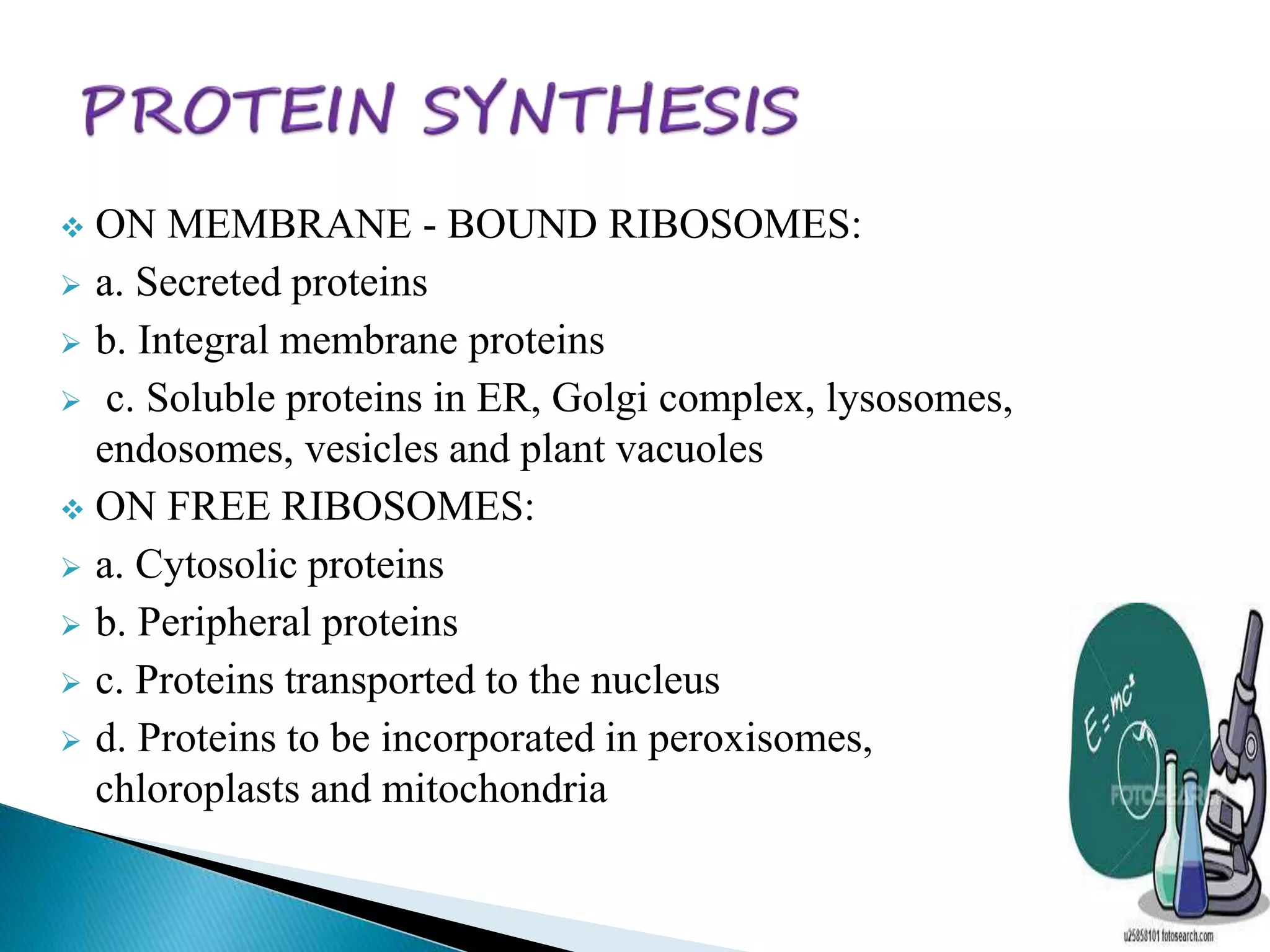
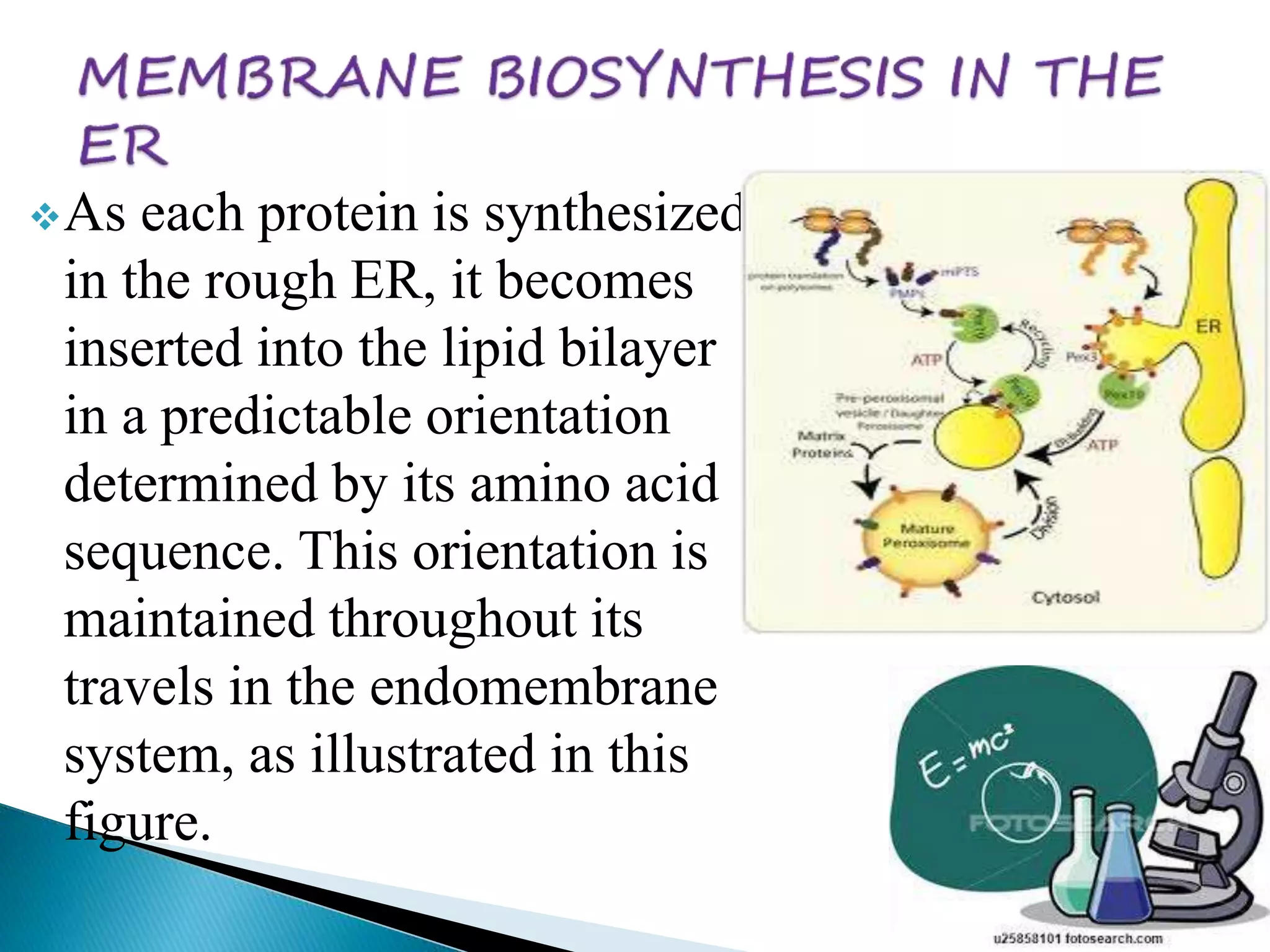
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes found throughout the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. It was first observed in 1945 by Albert Claude using an electron microscope. The endoplasmic reticulum is divided into two subcompartments: the rough endoplasmic reticulum, which is studded with ribosomes, and the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, which lacks ribosomes. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is the site of protein synthesis and transports proteins throughout the cell, while the smooth endoplasmic reticulum is involved in lipid and steroid metabolism.