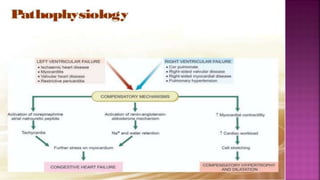
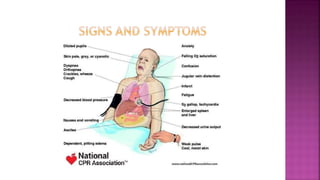
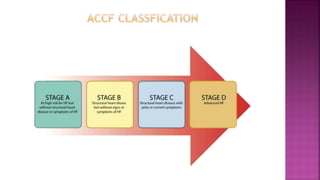
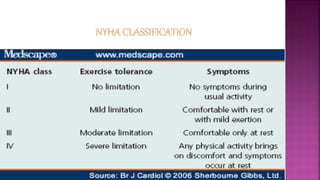
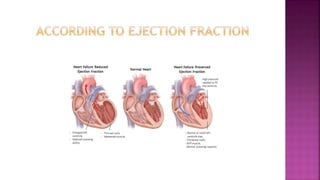
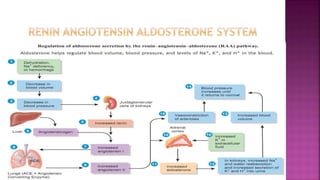
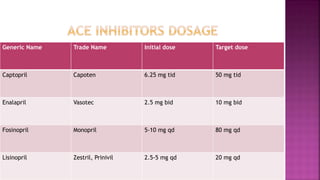
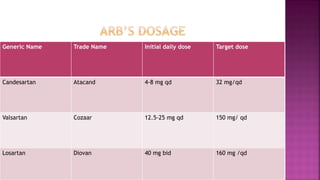
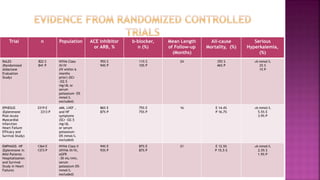
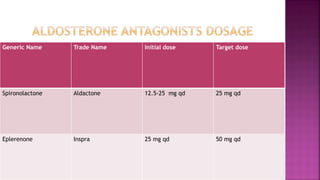
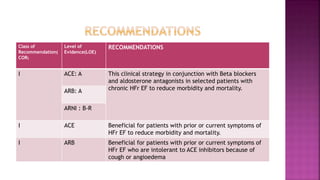
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a syndrome resulting from various cardiac and systemic conditions that lead to reduced heart function and increased aldosterone production, which facilitates inflammation and fibrosis. Treatment strategies include ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and aldosterone antagonists, each with specific indications and side effects, particularly in patients unable to tolerate ACE inhibitors. Newer agents like angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs) have shown promise in reducing cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization, alongside established therapies.