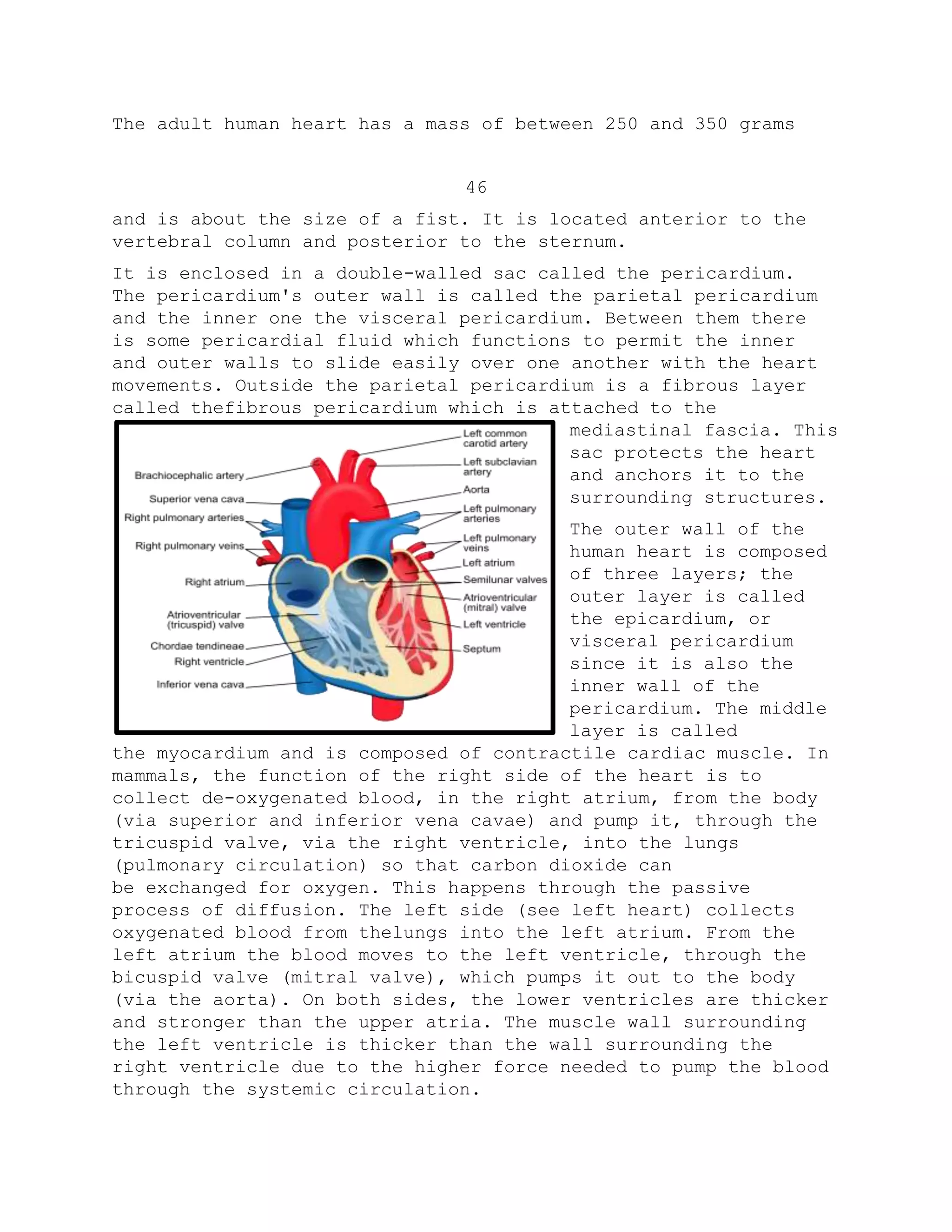
Gamma radiation refers to electromagnetic radiation of extremely high frequency and energy per photon. It is produced by the decay of atomic nuclei and other high-energy processes. Paul Villard discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation from radium, and the term was coined by Ernest Rutherford in 1903. Gamma rays are ionizing radiation and biologically hazardous. Natural sources include naturally occurring radioisotopes and interactions between cosmic rays and the atmosphere.

![bremsstrahlung, inverse Compton scattering and synchrotron
radiation. A large fraction of such
41
astronomical gamma rays are screened by Earth's atmosphere and
can only be detected by spacecraft.
Gamma rays typically have frequencies above 10 exahertz (or >1019
Hz), and therefore have energies above 100 keV and wavelengths
less than 10 picometers (less than the diameter of an atom).
However, this is not a hard and fast definition, but rather only
a rule-of-thumb description for natural processes. Gamma rays
from radioactive decay are defined as gamma rays no matter what
their energy, so that there is no lower limit to gamma energy
derived from radioactive decay. Gamma decay commonly produces
energies of a few hundred keV, and almost always less than 10
MeV. In astronomy, gamma rays are defined by their energy, and
no production process need be specified. The energies of gamma
rays from astronomical sources range over 10 TeV, at a level far
too large to result from radioactive decay. [2]
A notable example
is extremely powerful bursts of high-energy radiation normally
referred to as long duration gamma-ray bursts, which produce
gamma rays by a mechanism not compatible with radioactive decay.
These bursts of gamma rays, thought to be due to the collapse of
stars called hypernovae, are the
most powerful events so far
discovered in the cosmos.
Geiger, Hans Wilhelm
( 1882-1945)
September 30, 1882, Neustadt an de
Haardt, Germany, d. September 24, 1945,
Potsdam. A German physicist and
inventor of the Geiger counter, a type
of particle detector, and for the
Geiger-Marsden experiment which
discovered the atomic nucleus. In 1902
, Geiger started studying physics and
mathematics in the University of Erlangen and was awarded a doctorate
in 1986. In 1907 he began work with Ernest Rutherford at the
Hans Wilhelm "Gengar" Geiger (1928)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volume2withpages-140513115151-phpapp01/75/ENCYCLOPEDIA-Volume-2-2-2048.jpg)




![47
Heat Energy
Heat energy is a form of
energy that results from movement
of atoms, ions or molecules in
solids liquids or gases. It can
be transferred from one object to
another if the two objects have a
temperature difference.
Thermal energy is generated and
measured by heat of any kind. It
is caused by the increased
activity or velocity of molecules in a substance, which in turn
causes temperature to rise accordingly.
There are many natural sources of thermal energy on Earth,
making it an important component of alternative energy.
Heat energy is the type of energy that is emitted from burning
fuel. A unit of heat energy is defined as the amount of heat
required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one
degree Fahrenheit.
Heat energy deals with the transfer of energy of a body or of a
system in the form of heat, or raising temperatures. Raising the
temperature of a substance, raises it's heat energy.
The movement of atoms and molecules create heat energy. It
transfers among particles in a give substance by kinetic energy
which means that the heat is transferred by bouncing particles
bumping into each other.
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (/hiːməːɡloʊbɪn/); also spelled haemoglobin and
abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-
transport metalloproteinase in the red blood cells of
all vertebrates[1]
(with the exception of the fish family](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volume2withpages-140513115151-phpapp01/75/ENCYCLOPEDIA-Volume-2-8-2048.jpg)






![excess glucose from the blood, which otherwise would be toxic.
When blood glucose levels fall below a certain level, the
54
body begins to use stored sugar as an energy source through
glycogenolysis, which breaks down the glycogen stored in the
liver and muscles into glucose, which can then be utilized as an
energy source. As a central metabolic control mechanism, its
status is also used as a control signal to other body systems
(such as amino acid uptake by body cells). In addition, it has
several other anabolic effects throughout the body.
When control of insulin levels fails, diabetes mellitus can
result. As a consequence, insulin is used medically to treat
some forms of diabetes mellitus. Patients with type 1 diabetes
depend on external insulin (most commonly injected
subcutaneously) for their survival because the hormone is no
longer produced internally.[2]
Patients with type 2 diabetes are
often insulin resistant and, because of such resistance, may
suffer from a "relative" insulin deficiency. Some patients with
type 2 diabetes may eventually require insulin if other
medications fail to control blood glucose levels adequately.
Over 40% of those with Type 2 diabetes require insulin as part
of their diabetes management plan.
The human insulin protein is composed of 51 amino acids, and has
a molecular weight of 5808 Da. It is a dimer of an A-chain and a
B-chain, which are linked together by disulfide bonds.
Insulin's name is derived from the Latin insula for "island".
Insulin's structure varies slightly between species of animals.
Insulin from animal sources differs somewhat in "strength" (in
carbohydrate metabolism control effects) from that in humans
because of those variations. Porcine insulin is especially close
to the human version.
Synthesis
Insulin is proIn mammals, insulin is synthesized in the pancreas
within the β-cells of the islets of Langerhans. One million to
three million islets of Langerhans (pancreatic islets) form the
endocrine part of the pancreas, which is primarily an exocrine
gland. The endocrine portion accounts for only 2% of the total
mass of the pancreas. Within the islets of Langerhans, beta
cells constitute 65–80% of all the cells.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volume2withpages-140513115151-phpapp01/75/ENCYCLOPEDIA-Volume-2-15-2048.jpg)
![Insulin consists of two polypeptide chains, the A- and B-
chains, linked together by disulfide bonds. It is however first
synthesized as a single polypeptide called preproinsulin in
55
pancreatic β-cells. Preproinsulin contains a 24-residue signal
peptide which directs the nascent polypeptide chain to the rough
endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The signal peptide is cleaved as
the polypeptide is translocated into lumen of the RER, forming
proinsulin.[13]
In the RER the proinsulin folds into the correct
conformation and 3 disulfide bonds are formed. About 5–10 min
after its assembly in the endoplasmic reticulum, proinsulin is
transported to the trans-Golgi network (TGN) where immature
granules are formed. Transport to the TGN may take about 30 min.
In the posttranslational modifications insulin and its related
proteins have been shown to be produced inside the brain, and
reduced levels of these proteins are linked to Alzheimer's
disease.
duced in the pancreas and released when any of several stimuli
are detected. These stimuli include ingested protein and glucose
in the blood produced from digested food. Carbohydrates can be
polymers of simple sugars or the simple sugars themselves. If
the carbohydrates include glucose, then that glucose will be
absorbed into the bloodstream and blood glucose level will begin
to rise. In target cells, insulin initiates a signal
transduction, which has the effect of increasing glucose uptake
and storage. Finally, insulin is degraded, terminating the
response.
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the
symbol Fe (from Latin: ferrum) and
atomic number 26. It is a metal in
the first transition series. It by
mass is the most common element on
Earth, forming much of Earth's outer
and inner core. It is the fourth most
1lustrous metallic with a grayish
tinge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volume2withpages-140513115151-phpapp01/75/ENCYCLOPEDIA-Volume-2-16-2048.jpg)

![compounds are common oxygen transport proteins in vertebrates.
Iron is also the metal used at the active site of many important
redox enzymes dealing with cellular respiration and oxidation
and reduction in plants and animals.
57
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers (/ːaɪsəmərz/; from Greek ἰ ζομερής,
isomerès; isos = "equal", méros = "part") are molecules with the
same molecular formula but different chemical structures. That
is, isomers contain the same number of atoms of each element,
but have different arrangements of their atoms in space.[1][2]
Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they
also have the same functional groups. There are many different
classes of isomers, like positional isomers, cis-trans isomers
and enantiomers, etc. (see chart below). There are two main
forms of isomerism: structural isomerism and stereoisomerism
(spatial isomerism)
Structural isomers
In structural isomers, sometimes referred to as constitutional
isomers, the atoms and functional groups are joined together in
different ways. Structural isomers have different IUPAC names
and may or may not belong to the same functional group.[3]
This
group includes chain isomerism whereby hydrocarbon chains have
variable amounts of branching; position isomerism, which deals
with the position of a functional group on a chain; and](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volume2withpages-140513115151-phpapp01/75/ENCYCLOPEDIA-Volume-2-18-2048.jpg)
![functional group isomerism, in which one functional group is
split up into different ones.
For example, two position isomers would be 2-fluoropropane and
1-fluoropropane, illustrated on the left side of the diagram
above.
58
In skeletal isomers the main carbon chain is different between
the two isomers. This type of isomerism is most identifiable in
secondary and tertiary alcohol isomers.
Tautomers are structural isomers of the same chemical substance
that spontaneously interconvert with each other, even when pure.
They have different chemical properties and, as a consequence,
distinct reactions characteristic to each form are observed. If
the interconversion reaction is fast enough, tautomers cannot be
isolated from each other. An example is when they differ by the
position of a proton, such as in keto/enol tautomerism, where
the proton is alternately on the carbon or oxygen.
Stereoisomer In stereoisomers the bond structure is the same,
but the geometrical positioning of atoms and functional groups
in space differs. This class includes enantiomers, which are
non-superimposable mirror-images of each other, and
diastereomers, which are not. Enantiomers always contain chiral
centres and diastereomers often do, but there are some
diastereomers that neither are chiral nor contain chiral
centers.[4]
Another type of isomer, conformational isomers
(conformers), may be rotamers, diastereomers, or enantiomers
depending on the exact compound. For example, ortho- position-
locked biphenyl systems have enantiomers.
E/Z isomers, which have restricted rotation within the molecule,
to be specific isomers containing a double bond, are
configurational isomers. They are classified as diastereomers,
whether or not they contain any chiral centres.[4]
E/Z notation
depicts absolute stereochemistry, which is an unambiguous
descriptor based on CIP priorities.
"Cis–trans isomers" are used to describe any molecules with
restricted rotation in the molecule. However, these descriptors
describe relative stereochemistry only based on group bulkiness
or principal carbon chain, so can be ambiguous. This is
especially problematic for double bonds that have more than two
substituents. An obsolete term for cis–trans isomerism is](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volume2withpages-140513115151-phpapp01/75/ENCYCLOPEDIA-Volume-2-19-2048.jpg)
!["geometric isomerism".[5]
For alkenes with more than two
substituents, E-Z notation is used instead of cis and trans. If
possible, E and Z (written in italic type) is also preferred in
compounds with two substituents.[6]
In octahedral coordination compounds, facial–meridional
isomerism occurs. The isomers can be fac- (with facial ligands)
59
or mer- (with meridional ligands).
Note that, although conformers can be referred to as
stereoisomers, they are not stable isomers, since bonds in
conformers can easily rotate, thus converting one conformer to
another, which can be either diastereomeric or enantiomeric to
the original one.
While structural isomers typically have different chemical
properties, stereoisomers behave identically in most chemical
reactions, except in their reaction with other stereoisomers.
Enzymes, however, can distinguish between different enantiomers
of a compound, and organisms often prefer one isomer over the
other. Some stereoisomers also differ in the way they rotate
polarized light.
Isomerization
Isomerization is the process by which one molecule is
transformed into another molecule that has exactly the same
atoms, but the atoms are rearranged.[7]
In some molecules and
under some conditions, isomerization occurs spontaneously. Many
isomers are equal or roughly equal in bond energy, and so exist
in roughly equal amounts, provided that they can interconvert
relatively freely, that is the energy barrier between the two
isomers is not too high. When the isomerization occurs
intramolecularly, it is considered a rearrangement reaction.
An example of an organometallic isomerization is the production
of decaphenylferrocene, [(η5
-C5Ph5)2Fe] from its linkage
isomer.[8][9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volume2withpages-140513115151-phpapp01/75/ENCYCLOPEDIA-Volume-2-20-2048.jpg)
![matrix. A high pressure
clinopyroxene that is frequently
carved and polished as a
gemstone. Jadeite is
a pyroxene mineral with
composition NaAlSi2O6. It
is monoclinic. It has a Mohs
hardness of about 6.5 to 7.0
61
depending on the composition. The
mineral is dense, with a specific gravity of about 3.4. Jadeite
forms solid solutions with other pyroxene endmembers such
asaugite and diopside (CaMg-rich endmembers), aegirine (NaFe
endmember), and kosmochlor (NaCr endmember). Pyroxenes rich in
both the jadeite and augite endmembers are known as omphacite.
Jasper
A variety of colored chert,
typically red or green and often
found in association with iron
ores. Jasper is frequently used as
a gemstone or in the production of
ornaments.
The name means "spotted or speckled
stone", and is derived via Old
French jaspre (variant of Anglo-Norman jaspe) and Latin iaspidem
(nom. iaspis)) from Greek ἴ αζπις iaspis, (feminine noun)[5]
from
a Semitic language (cf. Hebrew יושפהyushphah, Akkadian
yashupu).
Green jasper was used to make bow drills in Mehrgarh between 4th
and 5th millennium BC. Jasper is known to have been a favorite
gem in the ancient world; its name can be traced back in Arabic,
Persian, Hebrew, Assyrian, Greek and Latin. On Minoan Crete,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volume2withpages-140513115151-phpapp01/75/ENCYCLOPEDIA-Volume-2-22-2048.jpg)





![Kinetics
The cars of a roller coaster reach their maximum kinetic energy
when at the bottom of their path. When they start rising, the
kinetic energy begins to be converted to gravitational potential
energy. The sum of kinetic and potential energy in the system
remains constant, ignoring losses to friction.
Common symbol(s): KE, Ek, or T SI unit: joule (J)
Derivations from other quantities: Ek = ½mv2 Ek = Et+Er
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it
possesses due to its motion.[1] It is defined as the work needed
to
67
accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated
velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the
body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes. The
same amount of work is done by the body in decelerating from its
current speed to a state of rest.
In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a non-rotating
object of mass m traveling at a speed v is ½ mv². In
relativistic mechanics, this
is only a good approximation
when v is much less than the
speed of light.
K- Potassium
Potassium is a chemical
element with symbol K (from
Neo-Latin kalium) and atomic
number 19. Elemental
potassium is a soft silvery-
white alkali metal that
oxidizes rapidly in air and
is very reactive with water,
generating sufficient heat
to ignite the hydrogen
emitted in the reaction and burning with a lilac flame.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volume2withpages-140513115151-phpapp01/75/ENCYCLOPEDIA-Volume-2-28-2048.jpg)

![Krypton is characterized by several sharp emission lines
(spectral signatures) the strongest being green and yellow.[9]
It
is one of the products of uranium fission.[10]
Solidified krypton
is white and crystalline with a face-centered cubic crystal
structure, which is a common property of all noble gases (except
helium, with a hexagonal close-packed crystal structure)
69](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volume2withpages-140513115151-phpapp01/75/ENCYCLOPEDIA-Volume-2-30-2048.jpg)




![73
to thermodynamics, photochemistry, and isotope separation, and
is also known for his concept of acids and bases.
G. N. Lewis was born in 1875 in Weymouth, Massachusetts. After
receiving his PhD in chemistry from Harvard University and
studying abroad in Germany and the Philippines, Lewis moved
to California to teach chemistry at the University of
California, Berkeley. Several years later, he became the Dean of
the college of Chemistry at Berkeley, where he spent the rest of
his life. As a professor, he incorporated thermodynamic
principles into the chemistry curriculum and reformed chemical
thermodynamics in a mathematically rigorous manner accessible to
ordinary chemists. He began measuring the free energy values
related to several chemical processes, both organic and
inorganic.
In 1916, he also proposed his theory of bonding and added
information about electrons in the periodic table of
the elements. In 1933, he started his research on isotope
separation. Lewis worked with hydrogen and managed to purify a
sample of heavy water. He then came up with his theory of acids
and bases, and did work in photochemistry during the last years
of his life. In 1926, Lewis coined the term "photon" for the
smallest unit of radiant energy. He was a brother in Alpha Chi
Sigma, the professional chemistry fraternity.
Though he was nominated 35 times, G. N. Lewis never won
the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. On March 23, 1946, Lewis was found
dead in his Berkeley laboratory where he had been working
with hydrogen cyanide; many postulated that the cause of his
death was suicide. After Lewis' death, his children followed
their father's career in chemistry.
Most of Lewis’ lasting interests originated during his Harvard
years. The most important was thermodynamics, a subject in which
Richards was very active at that time. Although most of the
important thermodynamic relations were known by 1895, they were
seen as isolated equations, and had not yet been rationalized as
a logical system, from which, given one relation, the rest could
be derived. Moreover, these relations were inexact, applying
only to ideal chemical systems. These were two outstanding
problems of theoretical thermodynamics. In two long and
ambitious theoretical papers in 1900 and 1901, Lewis tried to
provide a solution. Lewis introduced the thermodynamic concept
of activity and coined the term "fugacity".[5]
His new idea of
fugacity, or "escaping tendency", was a function with the
dimensions of pressure which expressed the tendency of a
74](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volume2withpages-140513115151-phpapp01/75/ENCYCLOPEDIA-Volume-2-35-2048.jpg)

![grow in the Netherlands, particularly Lecanora
tartarea and Roccella tinctorum. Litmus turns red in acidic
solutions and blue in alkaline solutions and is the oldest and
most commonly used indicator of whether a substance is
an acid or a base.
Treatment of the lichens with ammonia, potash, and lime in the
presence of air produces the various coloured components of
litmus. By 1840 litmus had been partially separated into several
substances named azolitmin, erythrolitmin, spaniolitmin, and
erythrolein. These are apparently mixtures of closely related
compounds that were identified.
Logic gate
A logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing
a Boolean function, that is,
it performs a logical
operation on one or more
logical inputs, and produces a
single logical output.
Depending on the context, the
term may refer to an ideal
logic gate, one that has for
instance zero rise time and
unlimited fan-out, or it may
refer to a non-ideal physical
device[1]
(see Ideal and real
op-amps for comparison).
Logic gates are primarily
implemented
using diodes or transistors acting as electronic switches, but
can also be constructed using electromagnetic relays (relay
logic), fluidic logic, pneumatic logic, optics, molecules, or
even mechanical elements. With amplification, logic gates can be
cascaded in the same way that Boolean functions can be composed,
allowing the construction of a physical model of all of Boolean
logic, and therefore, all of the algorithms and mathematics that
can be described with Boolean logic. Logic circuits include such
devices as multiplexers, registers, arithmetic logic
units (ALUs), and computer memory, all the way up through
complete microprocessors, which may contain more than 100
million gates.
76](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volume2withpages-140513115151-phpapp01/75/ENCYCLOPEDIA-Volume-2-37-2048.jpg)
