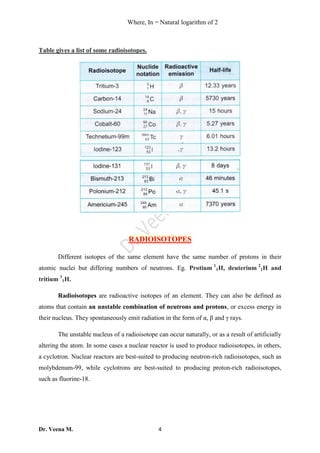
1. Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of unstable atomic nuclei through radioactive decay, releasing energy and radiation. Radioactive materials contain unstable nuclei that emit particles like alpha or beta particles during decay.
2. A Geiger-Müller counter detects ionizing radiation through gas ionization. When radiation enters the GM tube, it causes electrons to be ejected from gas atoms, creating an avalanche effect along the wire that is detected as pulses and counted.
3. Scintillation counting uses scintillator crystals that emit a flash of light when struck by radiation. This light is amplified via photomultiplier tube and counted electronically to measure radiation levels. Autoradiography uses radioactive samples and photographic film