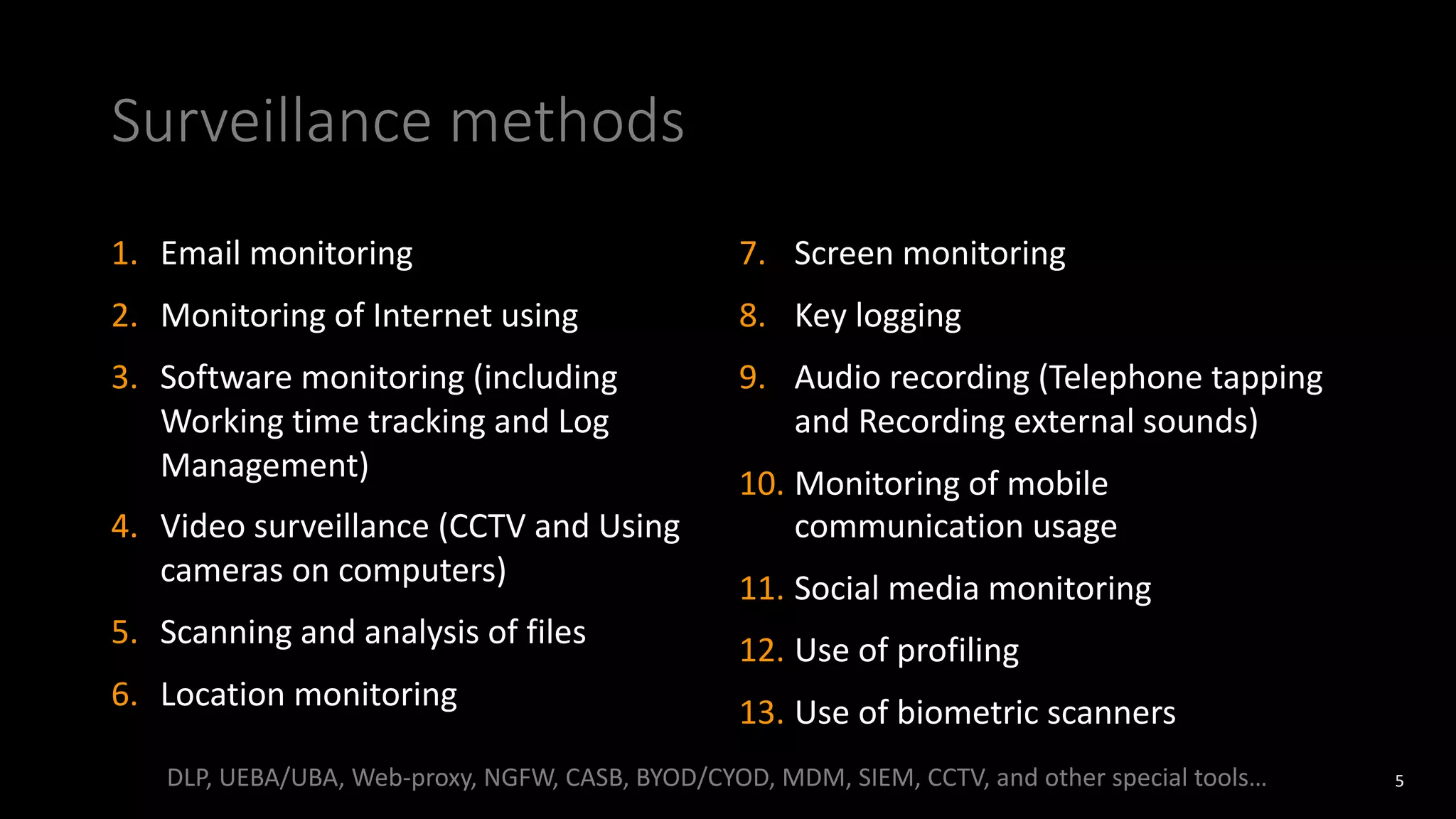
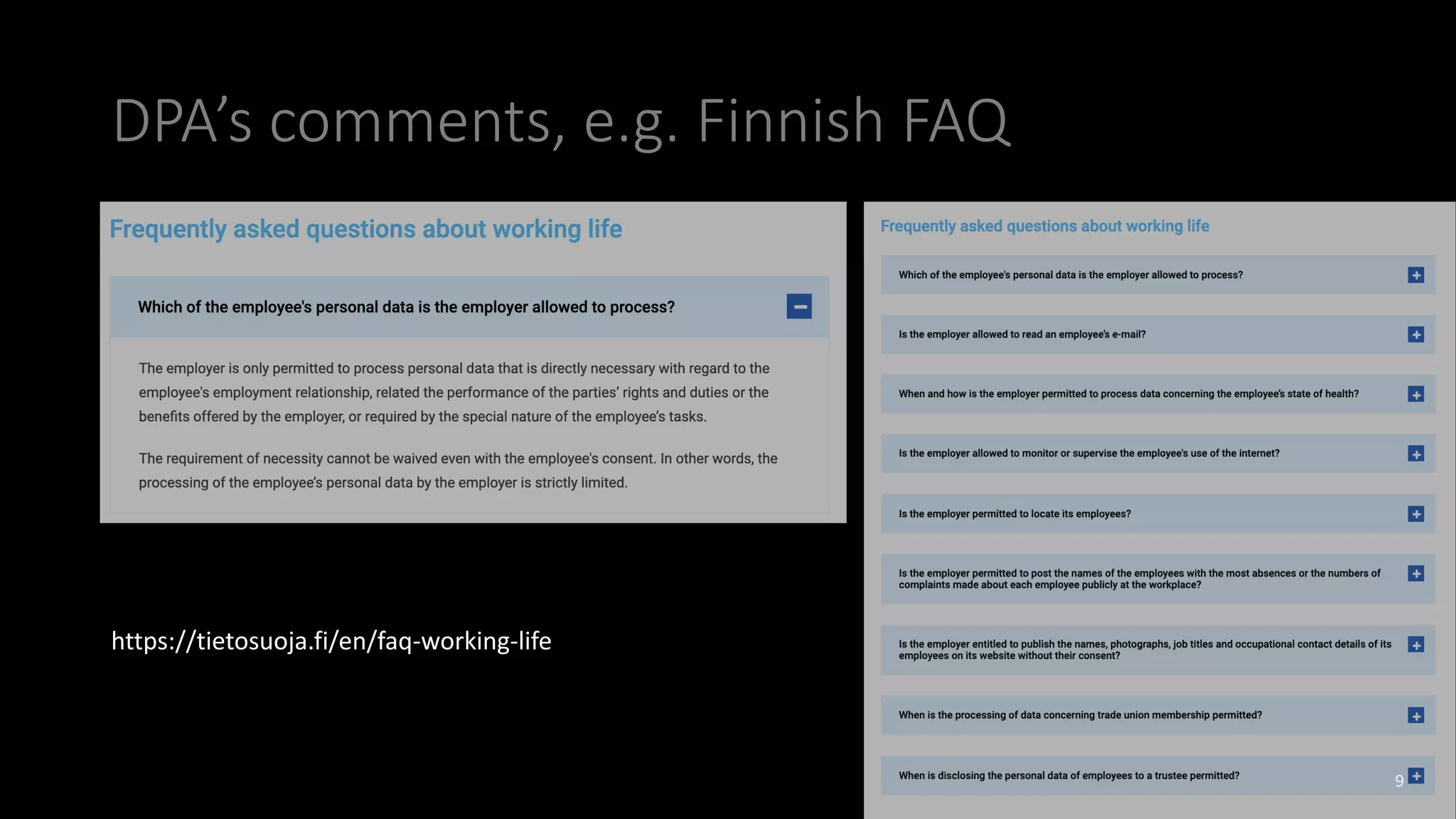
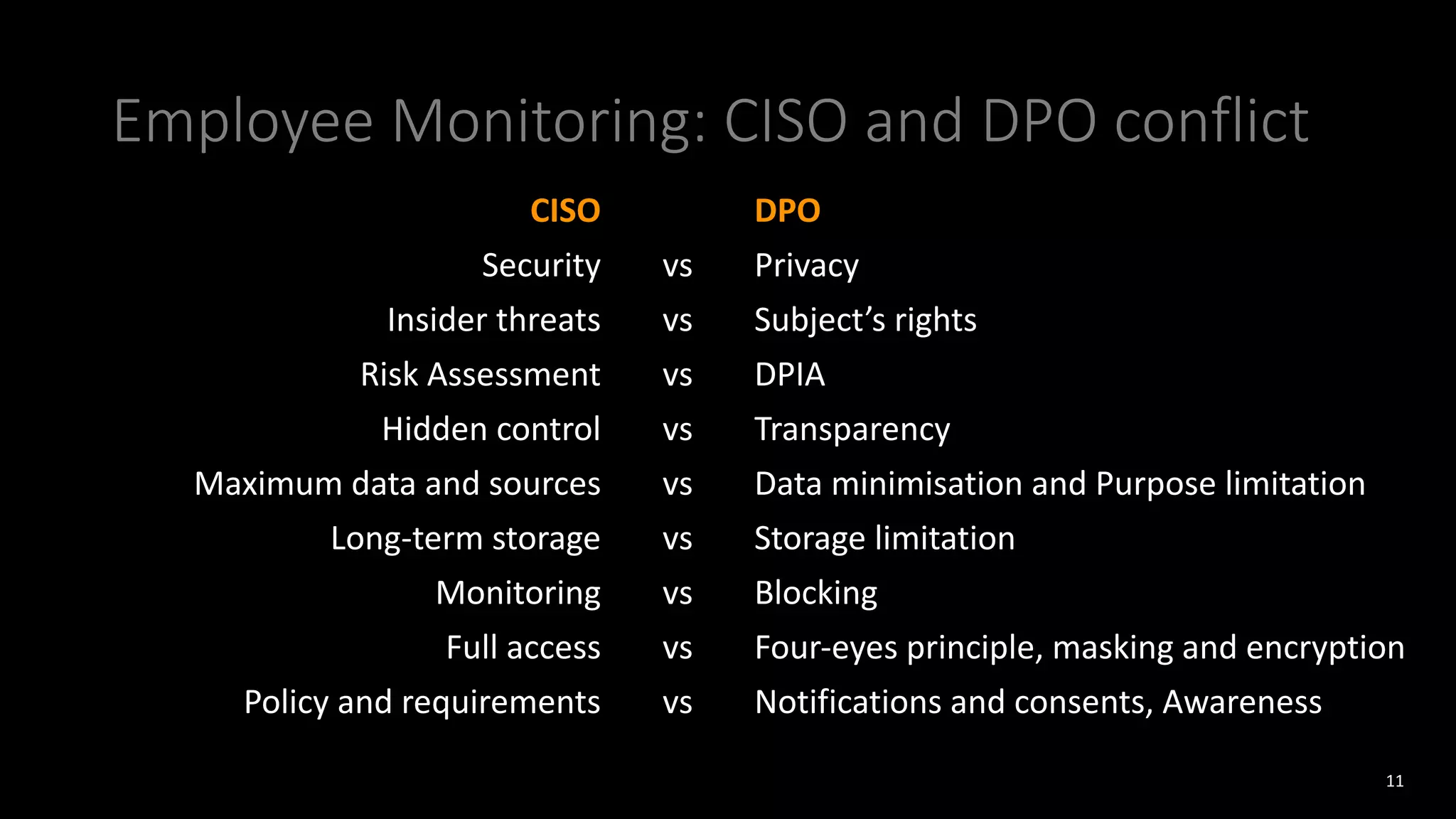
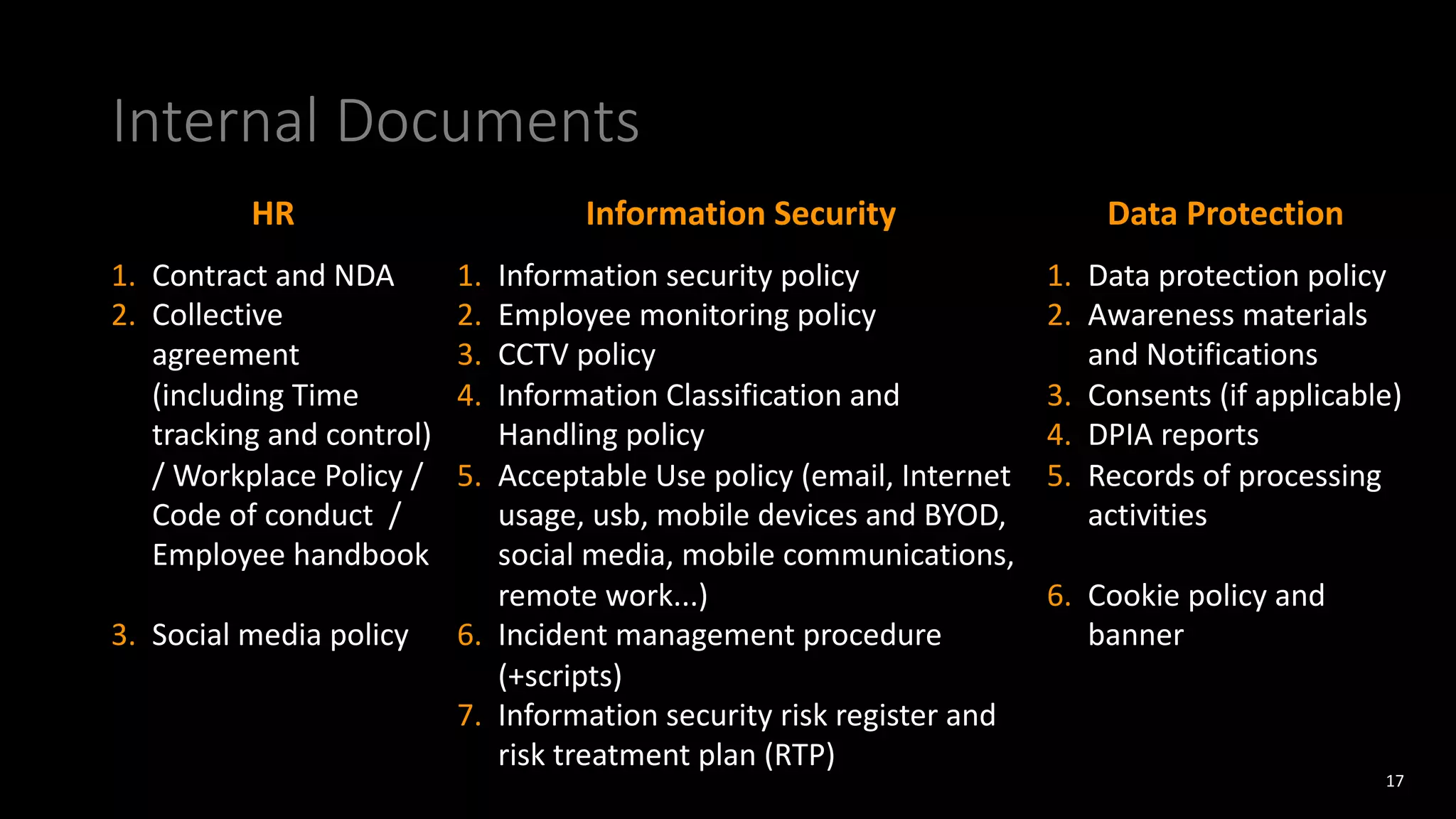
The document discusses employee monitoring and privacy. It covers surveillance methods used by organizations to monitor employees, including email, internet, software, video, and location monitoring. Specific considerations for remote work are outlined. Legal requirements for employee monitoring from the GDPR, local data protection and labor laws are examined. The document also discusses balancing security and privacy as seen from the perspectives of a CISO and DPO. Risks of inadequate monitoring and examples of GDPR fines for violations are provided. Principles for lawful employee monitoring and recommendations for internal policies are presented.