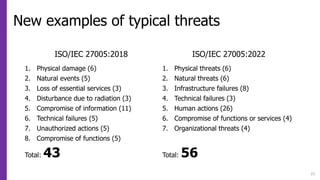
This document provides an overview of changes between the 2018 and 2022 versions of ISO 27005, which provides guidance on managing information security risks. Some key changes include aligning terminology with ISO 31000:2018, adjusting the structure to match ISO 27001:2022, introducing risk scenario concepts, revising and restructuring annexes, and providing additional examples and models. The 2022 version contains 62 pages compared to 56 pages previously and has undergone terminology, process, and content updates to align with updated ISO standards and better support organizations in performing information security risk management.