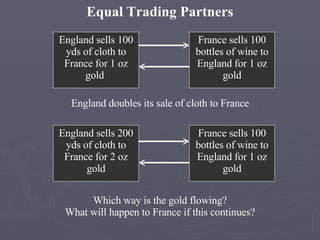
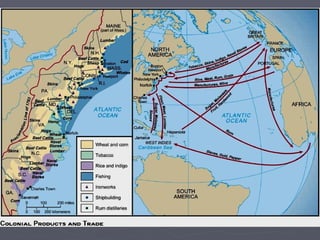
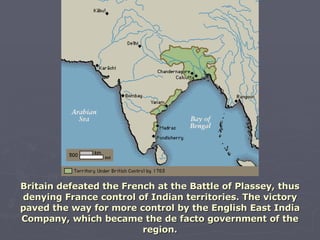
The document discusses the 18th century European empires and their colonial ambitions. It describes how empires used mercantilism to promote their economic interests and gain control over trade. This led to increasing tensions and rivalry over colonies in North America and India between France and Britain. The Seven Years' War from 1756-1763 resulted in major territorial changes that strengthened Britain's hold on North America and India at the expense of France and Spain.