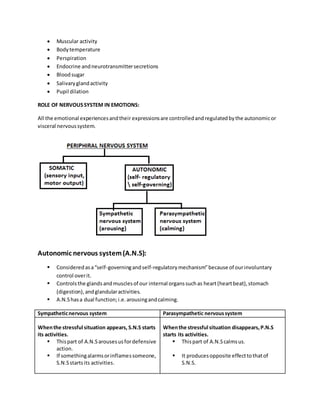
Emotions involve psychological arousal, expression of feelings, and behavior influenced by conscious experiences. They motivate individuals and involve changes in heart rate, breathing, gland activity and more. Emotions have cognitive, psychological, and behavioral components and are expressed through facial expressions and vocal tones. The autonomic nervous system regulates emotional experiences through the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, which control internal organs and arousal levels. Key areas of the brain involved in emotions include the cerebral cortex, sub-cortical structures, and autonomic nervous system.