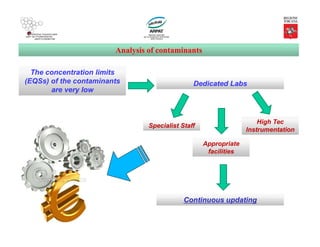
This document discusses emerging contaminants and the precautionary principle in relation to water quality standards. It provides background on the Water Framework Directive and its goals of protecting and improving water resources in the EU. Priority substances are identified, and environmental quality standards (EQS) are established with very low limits to regulate the concentration of pollutants in water. The document also examines the watch list established to monitor emerging contaminants and the challenges of detecting contaminants that may pose risks to the environment and human health at trace levels.











![20
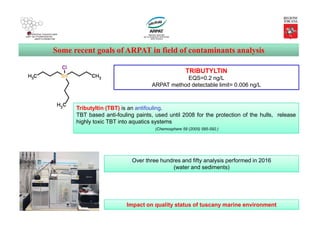
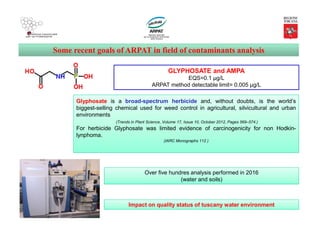
Emerging contaminants: Watch List
{2-[(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetic acid
DICLOFENAC
{2-[(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetic acid
Diclofenac is a widely used pharmaceutical that was reported as the
causal agent of outbreaks in populations of three species of vultures
(Gyps bengalensis, Gyps indicus, and Gyps tenuirostris), that have
declined by more than 97 % and are now classified as critically
endangered .
This example might will be the worst ever case of poisoning of wildlife
by a chemical (Sumpter, 2010).
The most direct entry of diclofenac to aquatic environments is through discharges of sewage treatment plants
(STPs) effluents.
Removal rates in STPs are highly variable (between 0-80%) (Jiskra, 2008)
The two major sinks identified for diclofenac are photodegradation and biodegradation (Santos et. Al 2010)
PEC
(µg/L)
MEC (µg/L) PNEC
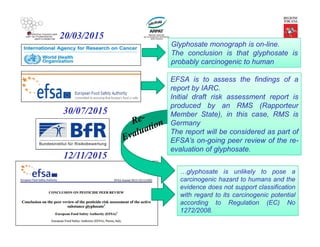
(µg/L)
PEC/PNEC
0.05 0.08-1.4 0.01 5
A risk is expected because
PEC/PNEC > 1
Advanced oxidation processes
by means of combining
different highly oxidizing
agents, such as H2O2/ozone or
UV/ozone, can provide the best
removal rate for diclofenac
(99,9%).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dott-171020091613/85/Emerging-contaminants-and-precautionary-principle-20-320.jpg)
![21
Emerging contaminants: Watch List
{2-[(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetic acid
17-Beta-estradiol
(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3,17-diol
Natural Hormone
Ethinylestradiol
(8R,9S,13S,14S,17R)-17-Ethinyl-13-methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3,17-diol
Synthetic Hormone
Active substance in contraceptive pills
What are endocrine disruptors?
"An endocrine disruptor is an exogenous substance or
mixture that alters function(s) of the endocrine system
and consequently causes adverse health effects in an
intact organism, or its progeny, or (sub)populations"
ENDOCRINE DISRUPTORS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dott-171020091613/85/Emerging-contaminants-and-precautionary-principle-21-320.jpg)
![22
Emerging contaminants: Watch List
{2-[(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetic acid
OXADIAZON
{-(2,4-Dichloro-5-(1-methylethoxy)phenyl)-5-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2(3H)-one (9CI)
Oxadiazon is an oxadiazole herbicide used for pre-emergent control of grasses,
broadleaves, vines, brambles, bushes, and trees.
Oxadiazon inhibits the plant enzyme protoporphyrinogen oxidase.
Effect on soil fertility (beneficial soil microorganisms)
Reduction of the number of mycorrhizal
fungal spores
(Moorman, 1989)
Aquatic Non-target organisms
In one study, oxadiazon was found to
severely reduce algae growth.
(Ambrosi et al., 1978).
Non-target organisms
The herbicide oxadiazon is also toxic to
bees, which are pollinators.
(Washington State Department of Transportation, 1993).
Interdisc Toxicol. 2009; Vol. 2(1): 1–12.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dott-171020091613/85/Emerging-contaminants-and-precautionary-principle-22-320.jpg)
![23
Emerging contaminants: Watch List
{2-[(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetic acid
METHIOCARB
3,5-Dimethyl-4-(methylsulfanyl)phenyl methylcarbamate
Methiocarb is an acaricides (carbamate acaricides), bird repellents, insecticides
(phenyl methylcarbamate insecticides)
(http://www.alanwood.net/pesticides/index_cn_frame.html)
Hazards to non-target invertebrates
Formulated methiocarb has been found to
be toxic to a wide range of polyphagous
predators
Hazards to aquatic non-target organisms
Aquatic invertebrates appear to be more
sensitive to methiocarb than fish with
acute toxicity (96h-LC50) ranging between
0.0054 and 8.8 mg/L for a range of
species
(Marking and Chandler, 1981).
A. M.Giacomello et al. Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, Wallingford 2006](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dott-171020091613/85/Emerging-contaminants-and-precautionary-principle-23-320.jpg)
![24
Emerging contaminants: Watch List
{2-[(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetic acid
2,6-DITERT-BUTYL-4-METHYLPHENOL
Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT)
BHT is an antioxidant.
European and U.S. regulations allow small amounts to be used as a food
additive (E321) . In addition to this use, BHT is widely used to prevent oxidation
in fluids (e.g. fuel, oil) and other materials where free radicals must be
controlled.
(other informations in EFSA Journal 2012;10(3):2588
Triallate is an herbicides (thiocarbamate herbicides)
(http://www.alanwood.net/pesticides/index_cn_frame.html)
TRIALLATE
S-2,3,3-trichloroallyl diisopropyl(thiocarbamate)
Based on the available studies, tri-allate was considered very toxic to aquatic organisms.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dott-171020091613/85/Emerging-contaminants-and-precautionary-principle-24-320.jpg)
![25
Emerging contaminants: Watch List
{2-[(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetic acid
Imidacloprid, Thiacloprid, Thiamethoxam, Clothianidin, Acetamiprid
NEONICOTINOIDS INSECTICIDES
Example: Imidacloprid (E)-1-(6-chloro-3-pyridylmethyl)-N-nitroimidazolidin-2-
ylideneamine is an insecticide (nitroguanidine neonicotinoid insecticides;
pyridylmethylamine neonicotinoid insecticides)
(http://www.alanwood.net/pesticides/index_cn_frame.html)
Hazards to honeybees
Synergism in honeybees has also been reported with
neonicotinoids when combined with EBI fungicides
(ergosterol biosynthesis inhibitors) (Iwasa et al. 2004).
In one example, the toxicity of thiachloprid was reported to
have increased by up to several hundred-fold in the
presence of an EBI.
C. Walker “Ecotoxicology” 2014 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC
Honeybees sub lethal effects
This type of insecticide is neurotoxic, and it is well
documented that they can have sublethal effects on bees,
including effects upon behavior (Thompson 2003).
Wagtail dance and navigation are negatively influenced
(Henry et al. 2012)
ARPAT: Over one thousand of analysis performed in 2016
(water)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dott-171020091613/85/Emerging-contaminants-and-precautionary-principle-25-320.jpg)
![26
Emerging contaminants: Watch List
{2-[(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetic acid
Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Azithromycin
MACROLIDES ANTIBIOTICS
Example: Erythromycin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of
bacterial infections](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dott-171020091613/85/Emerging-contaminants-and-precautionary-principle-26-320.jpg)
![27
Emerging contaminants: Watch List
{2-[(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl}acetic acid
2-ETHYLHEXYL-4-METHOXYCINNAMATE
2-Ethylhexyl 4-methoxycinnamate is used as a light stabiliser in plastics (Ashford 1994), and as a UV-filter in a
wide variety of cosmetic products including sun-care, skin-care and hair-care products (Household Products
Database)
2-Ethylhexyl 4-methoxycinnamate is unlikely to meet the
EU PBT or vPvB criteria since it is predicted to be readily
biodegradable.
It should be noted, however, that the substance appears to
meet the bioaccumulative, very bioaccumulative and toxic
screening criteria (based on predicted data).
Based on this analysis, ethylhexyl ethoxycinnamate is a high
priority for further work
“UV-filters in cosmetics –prioritisation for environmental assessment”,
Environment Agency December 2008, www.environment-agency.gov.uk
Journal of Investigative Dermatology
Volume 113, Issue 4, October 1999, Pages 547-553](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dott-171020091613/85/Emerging-contaminants-and-precautionary-principle-27-320.jpg)