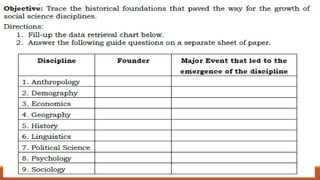
Anthropology emerged in Europe during the Era of Imperialism. Key figures in the early development of anthropology include Charles Darwin, who proposed the theory of evolution; Edward Tylor, who argued that all societies progressed through the same stages of cultural evolution; and Franz Boas, who rejected the idea that genetic differences explained cultural variation. Henry Otley Beyer is considered the Father of Philippine Anthropology and introduced the Migration Theory.