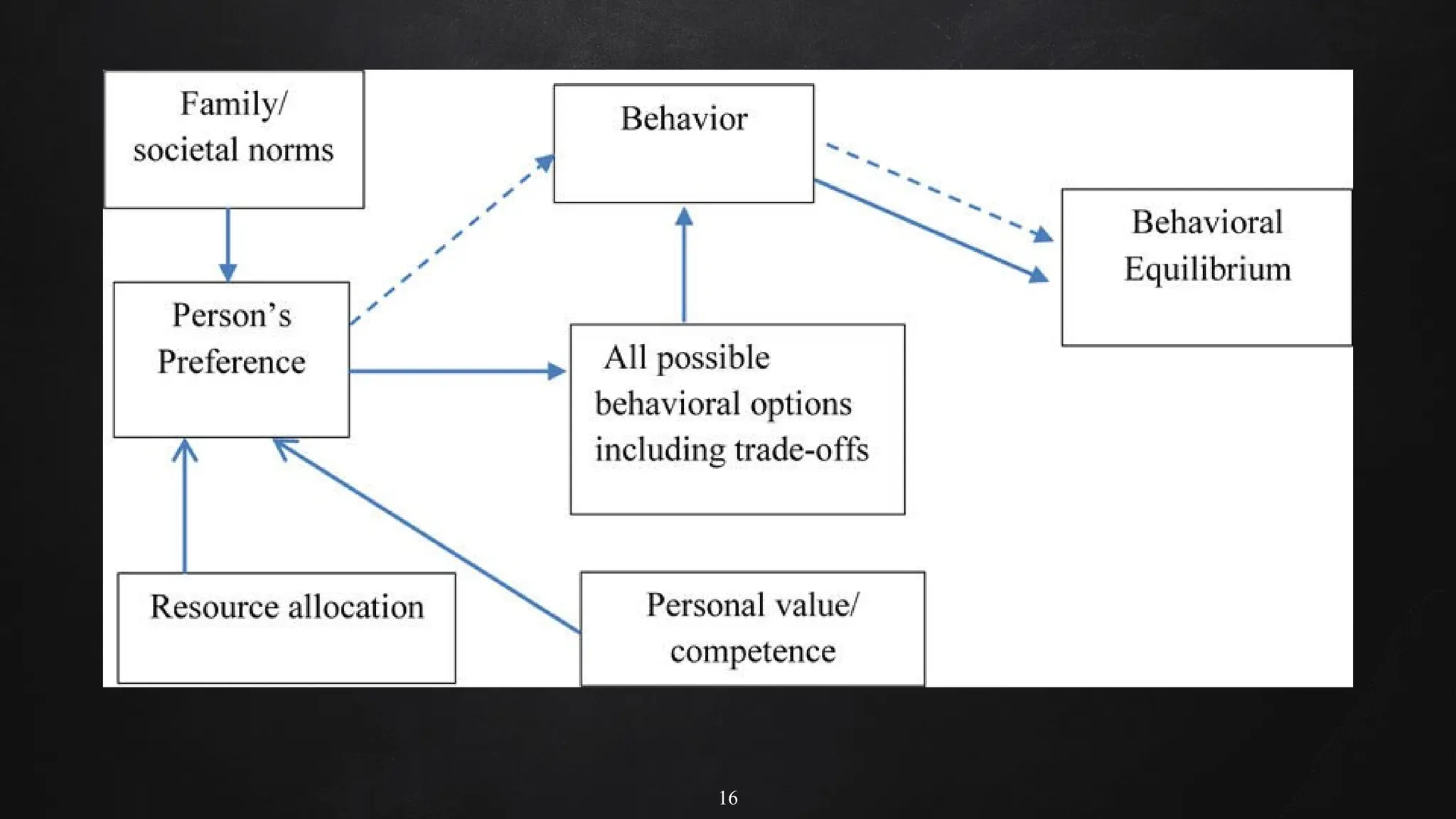
Rational choice theory proposes that people act rationally by weighing costs and benefits to make choices that provide the greatest personal benefit. It assumes individuals are self-interested and aim to maximize rewards. Choices are based on individual preferences and what people believe will serve their interests best, even if choices seem irrational to others. While it helps explain behavior and promote understanding, rational choice theory is limited by not accounting for intuitive decision-making or non-rational influences on behavior.