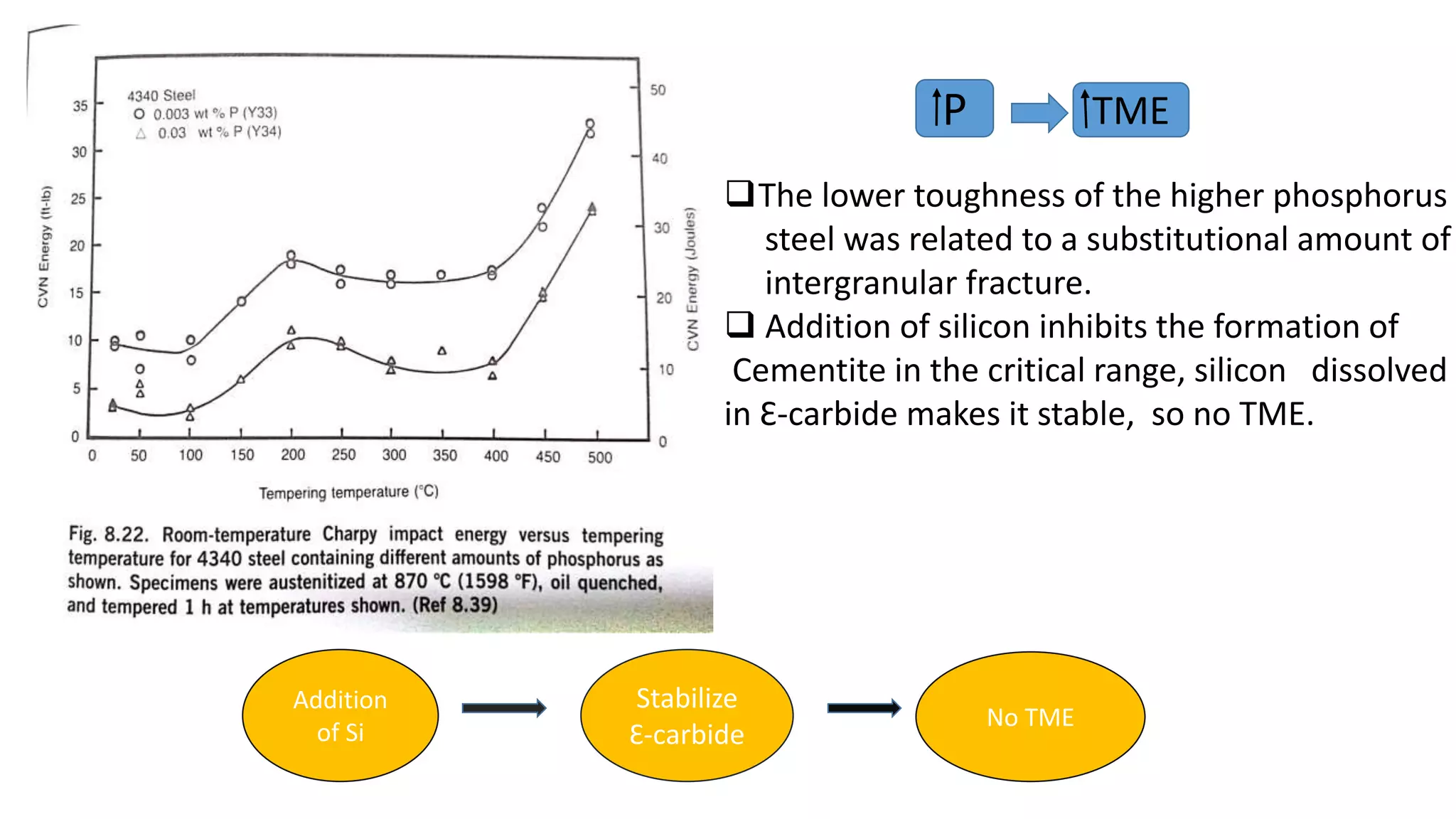
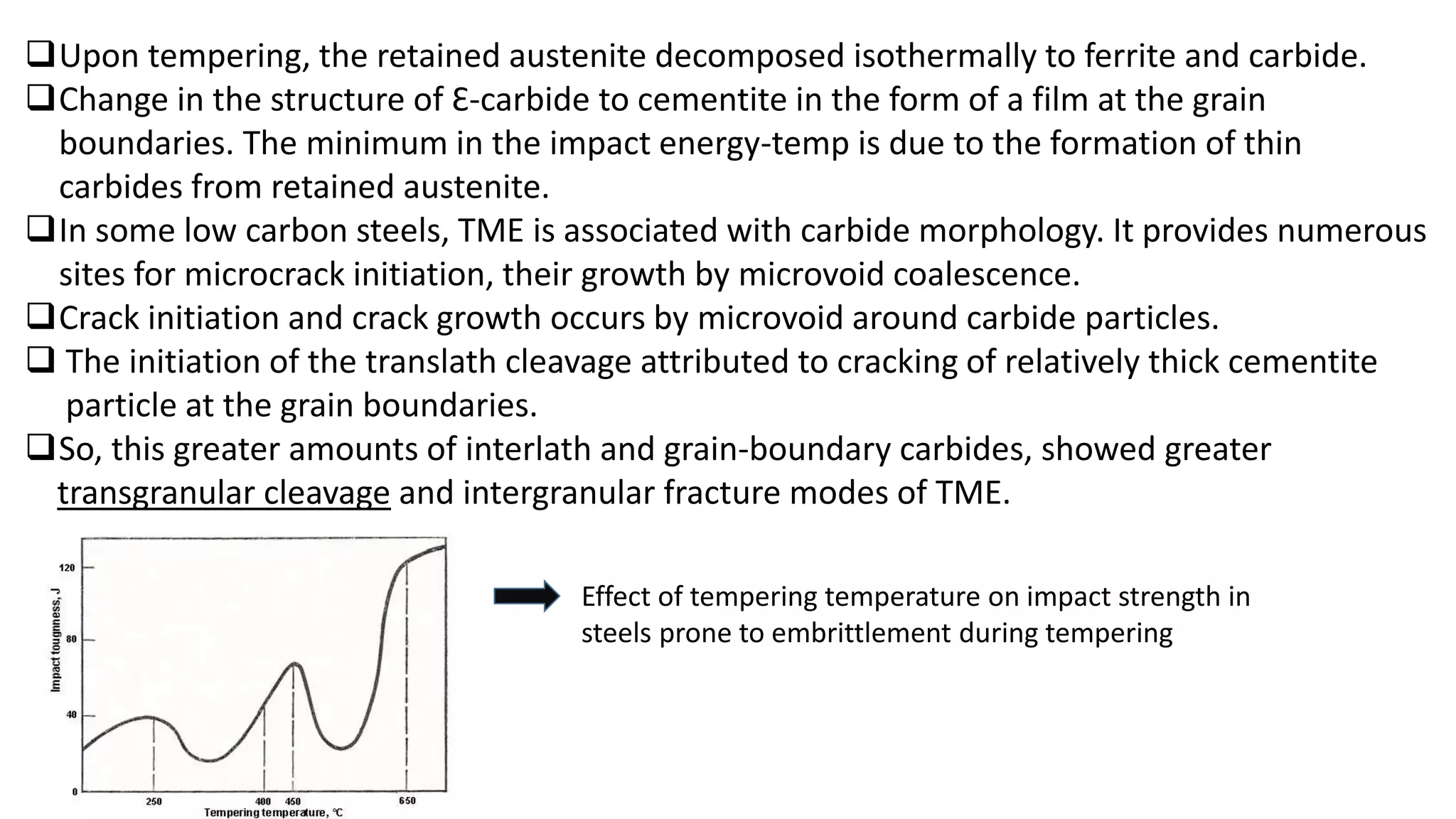
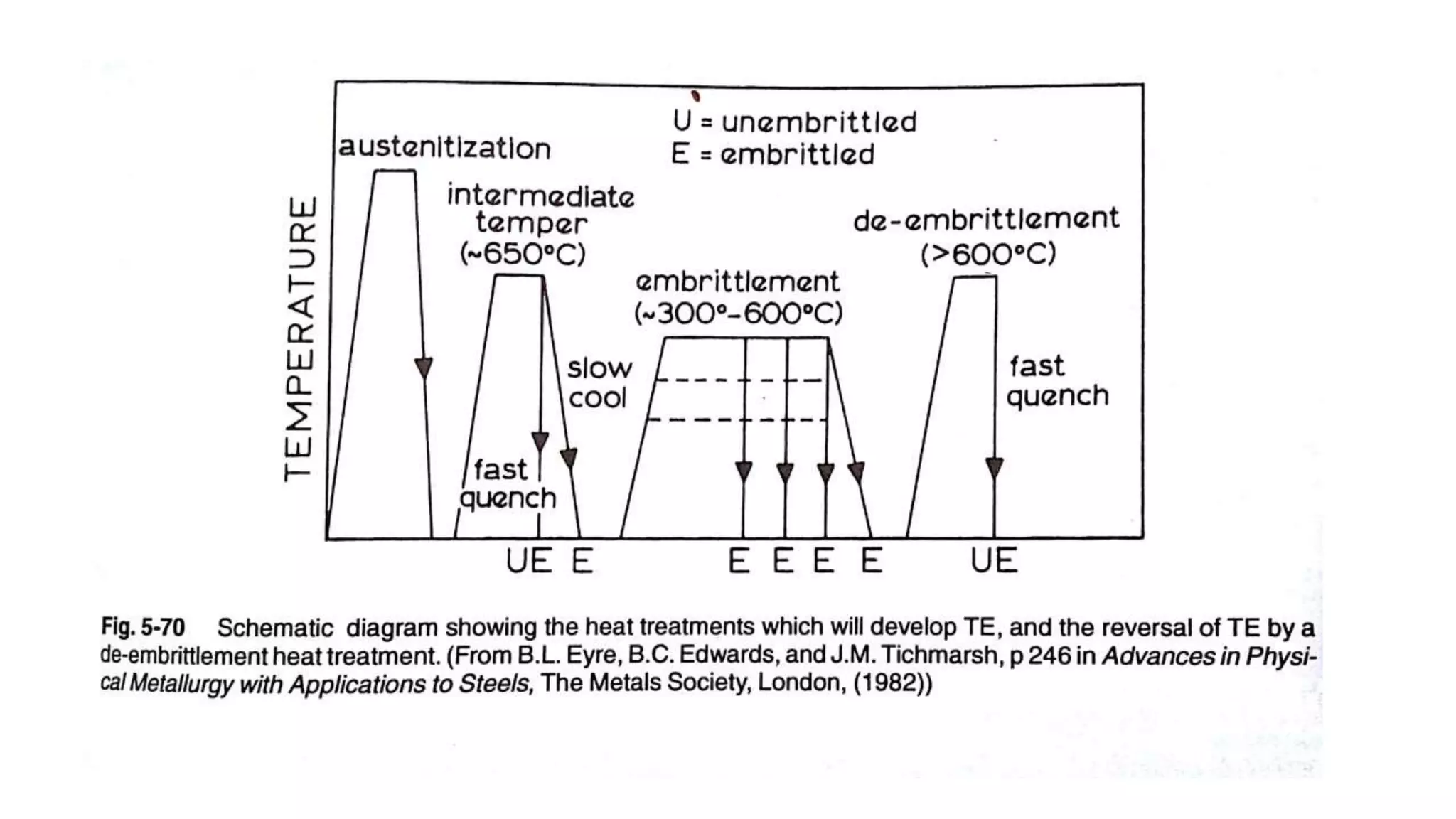
The document discusses various types of embrittlement mechanisms during the tempering of steel, including temper embrittlement and tempered martensite embrittlement, which result from structural changes and environmental interactions. It highlights the conditions and structural features that lead to embrittlement, such as segregation of minor elements and the formation of cementite, which weaken grain boundaries and initiate cracking. Additionally, it mentions how alloy compositions and tempering temperatures influence the toughness and ductility of steel.