Embed presentation
Downloaded 10 times





Embedded systems are computer systems designed for a specific function within a larger mechanical or electrical system. They are typically based on microcontrollers for low power consumption and fixed time constraints. Embedded systems are designed to perform specific tasks, have real-time operation, limited size and cost, and prioritize reliability and safety over flexibility. Common examples include digital watches, traffic lights, MP3 players, appliances, phones, engine controllers, medical devices, and defense technologies. Key components are processors and memory, while programming is typically done in languages like C/C++ using compilers and simulators.
Presented by Md. Nahid Hasan, this slide introduces the topic of embedded systems with author details.
An embedded system combines hardware and software for a specific function, often using microcontrollers.
Highlights the key differences: general purpose is versatile, while embedded systems are task-specific and economical.
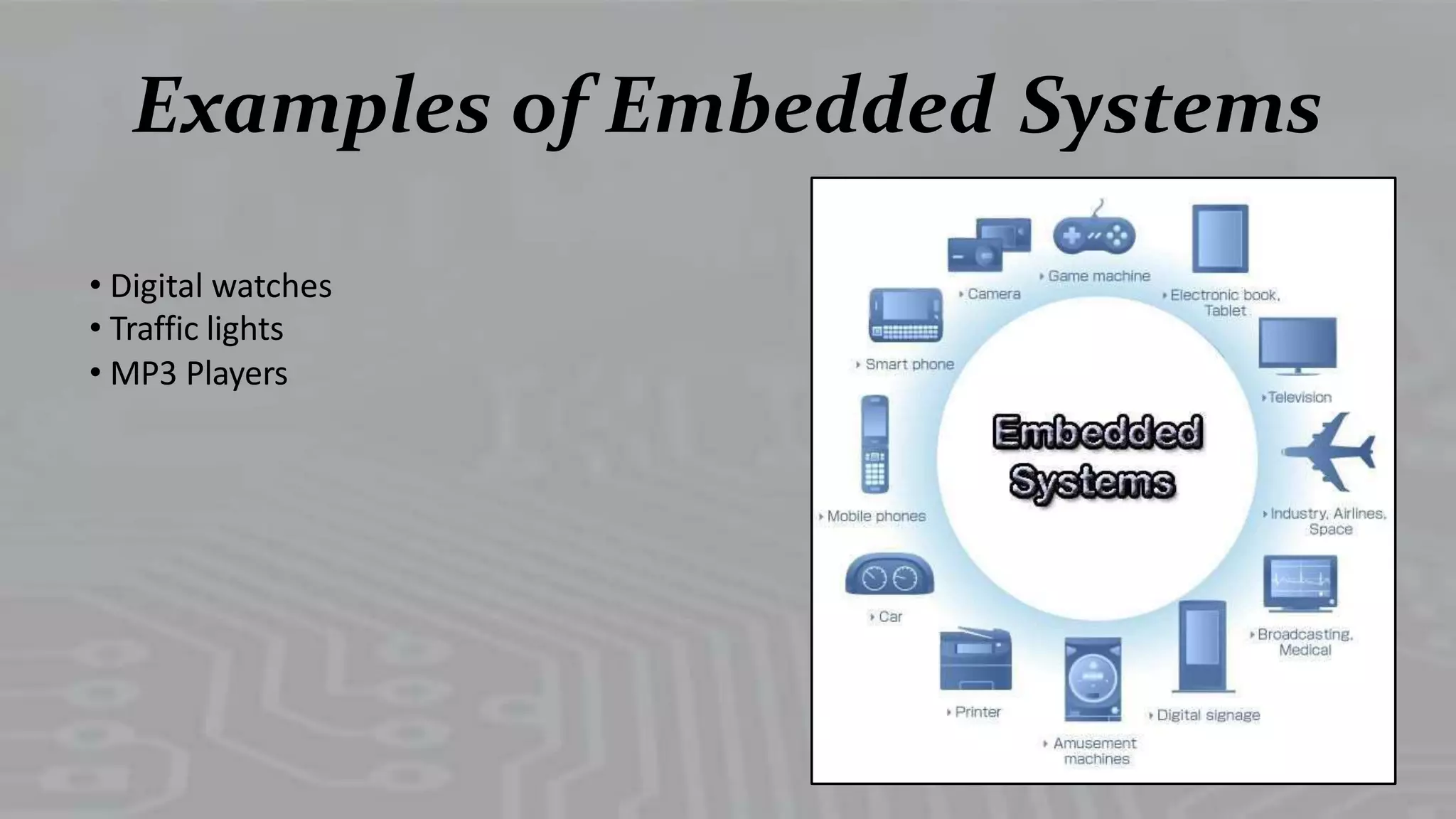
Lists examples like digital watches, traffic lights, and MP3 players illustrating everyday embedded systems.
Discusses features like real-time operation, size, cost, reliability, safety, and energy efficiency.
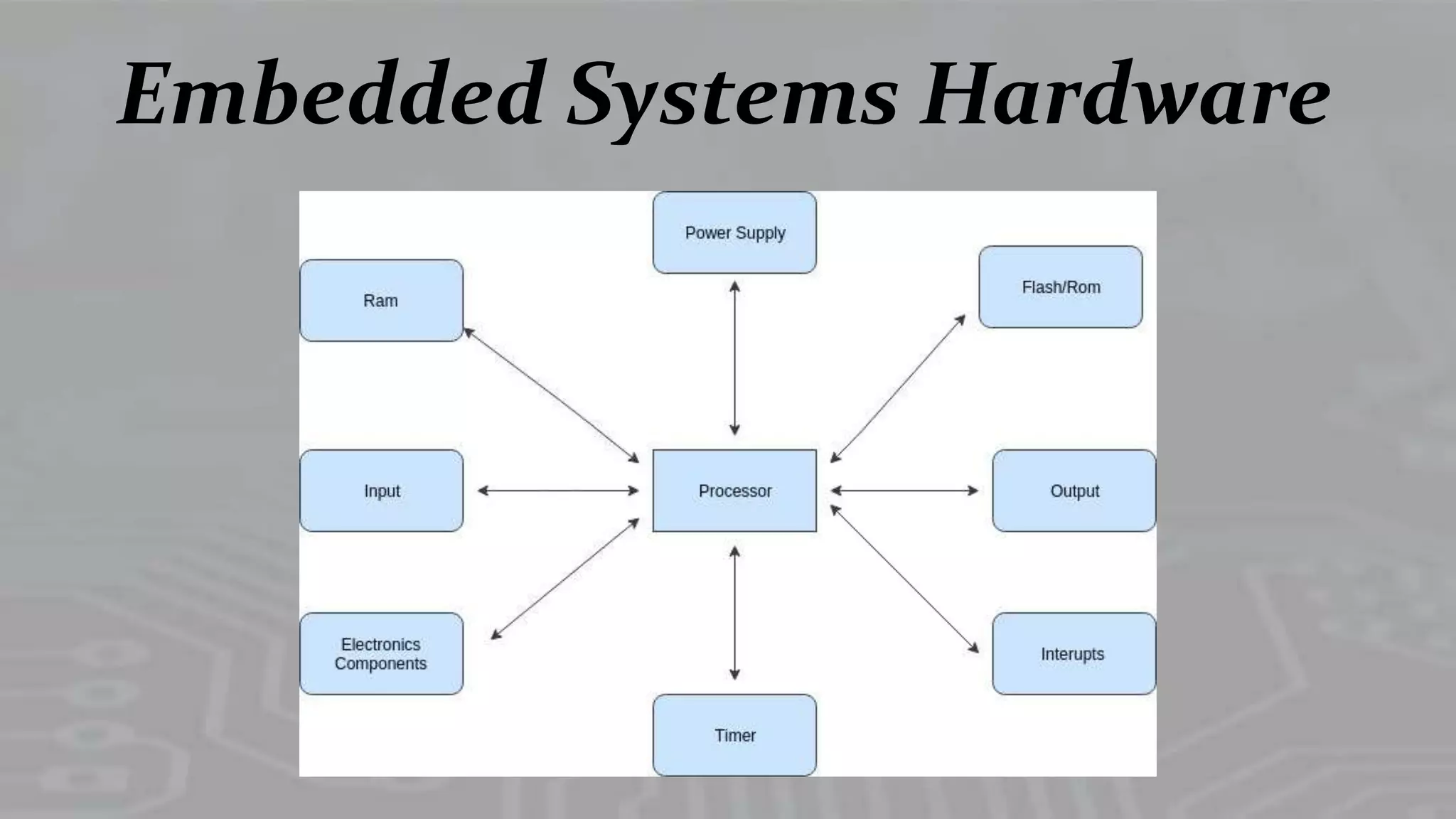
Brief mention of embedded systems hardware, indicating it plays a crucial role in the system's functionality.
Identifies two main components: processors and memory essential for embedded systems.
Outlines programming languages and tools like Masm, C, C++, and simulators relevant to embedded systems.
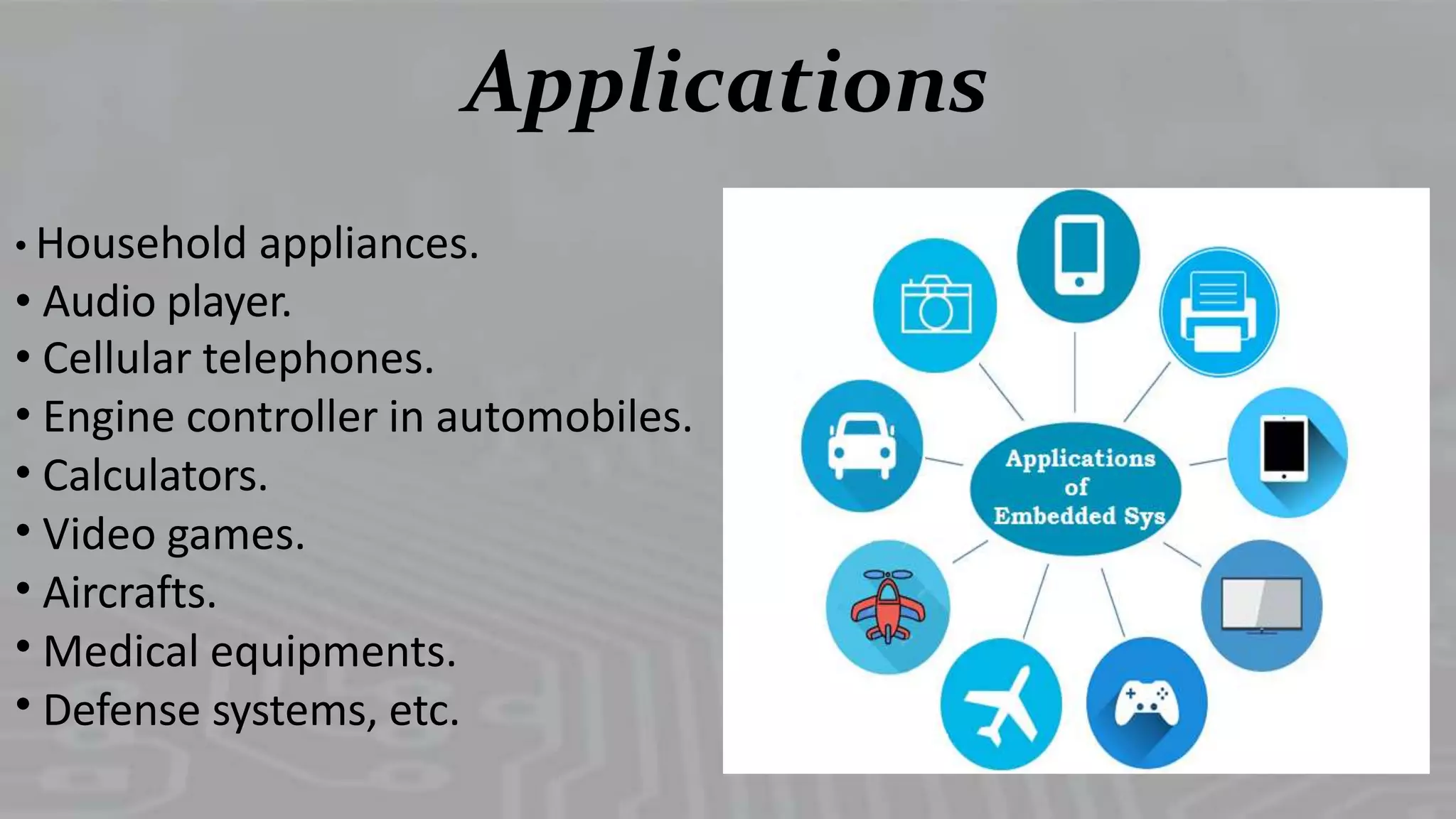
Describes diverse applications ranging from household appliances to medical equipment and defense systems.
A simple thank you slide, closing the presentation on embedded systems.









