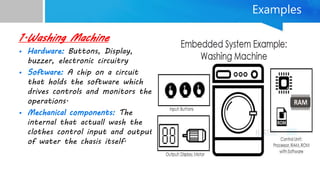
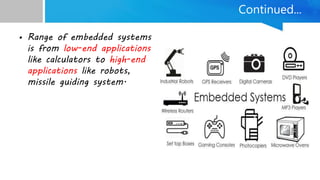
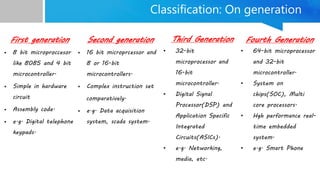
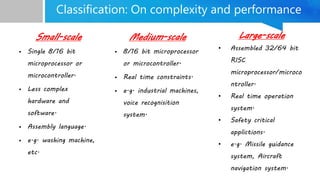
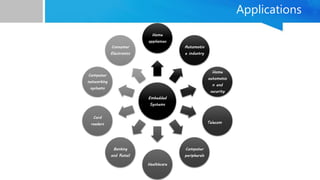
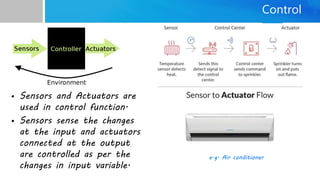
Embedded systems are specialized computing systems designed for dedicated functions within larger systems, differing significantly from general-purpose computers. They comprise both hardware and software components and are classified based on generation, complexity, performance, and triggering behaviors. With applications ranging from simple household appliances to complex industrial and military systems, the evolution of embedded technologies is expected to enhance the standard of living in the future.