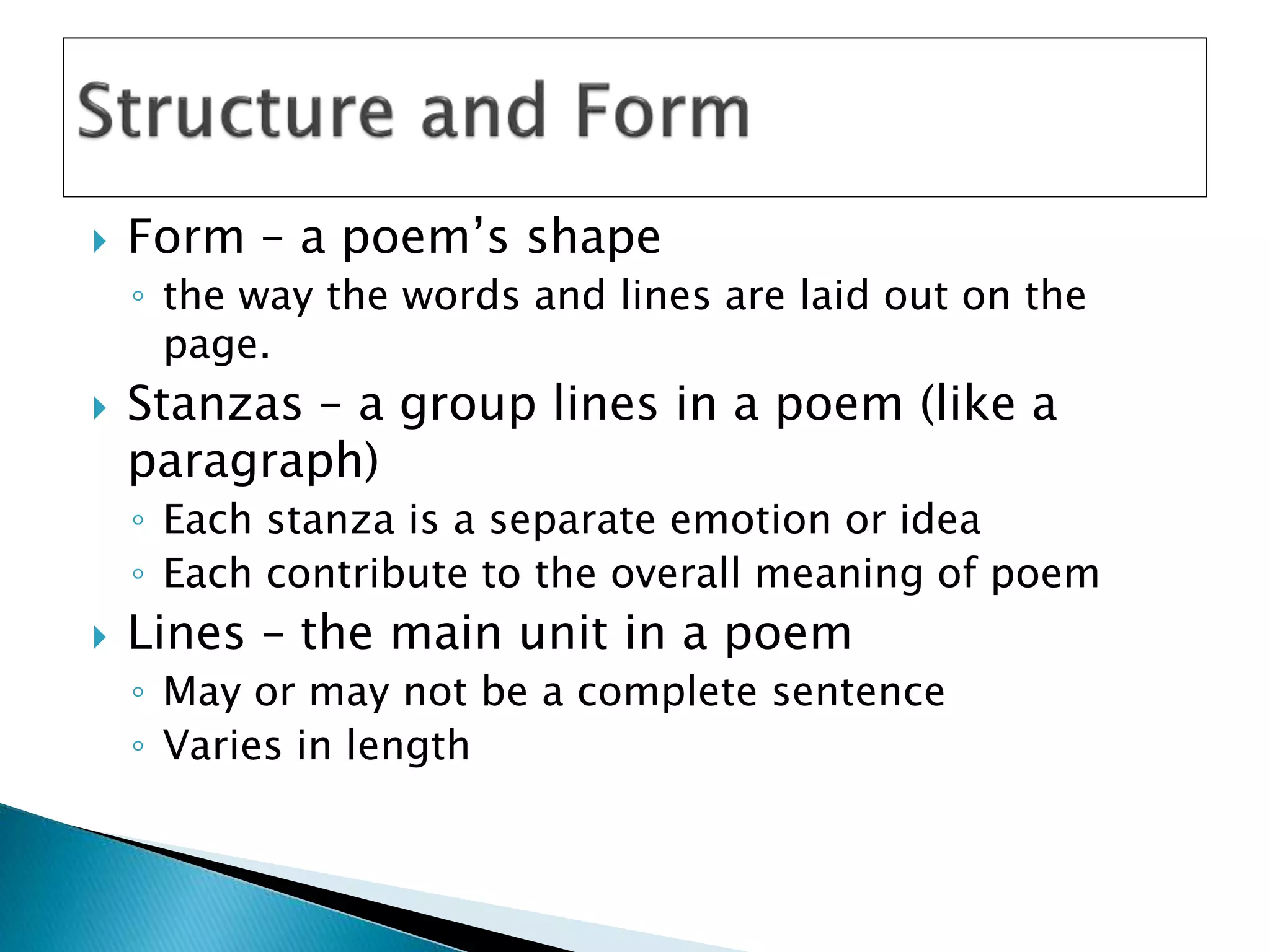
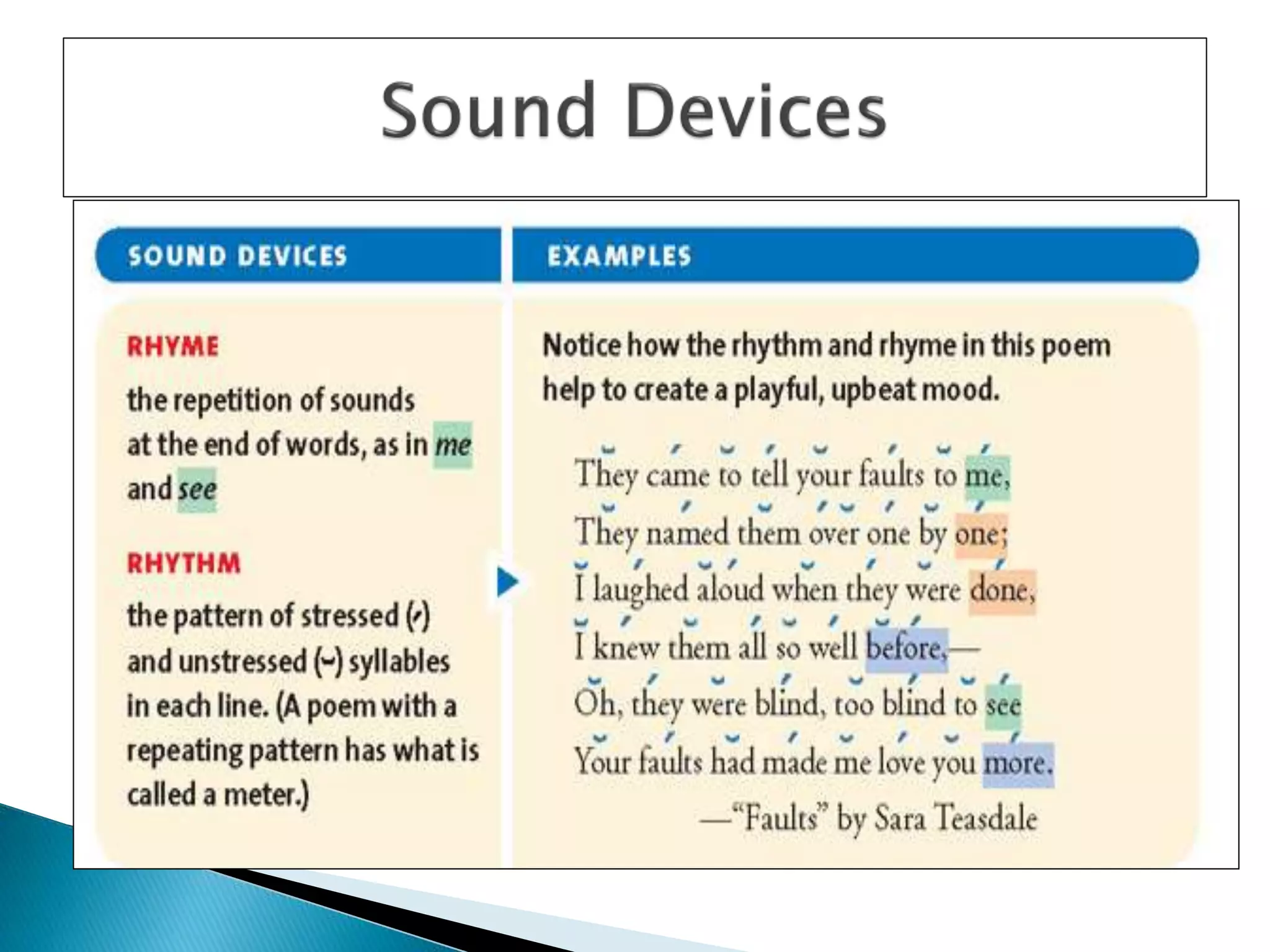
The document discusses various elements of poetry such as stanzas, lines, rhythm, rhyme, imagery and different forms of poetry including free verse, haikus, and limericks. It provides examples of different rhyme schemes and describes how various literary devices such as metaphor, simile and personification are used in poems to appeal to different senses and create vivid pictures and emotions for the reader.