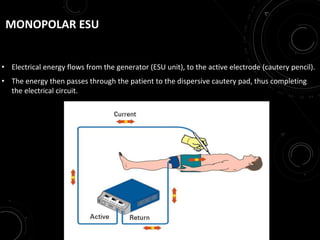
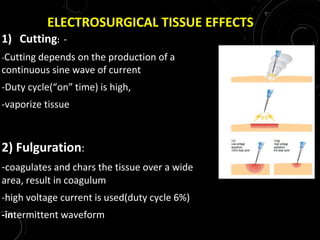
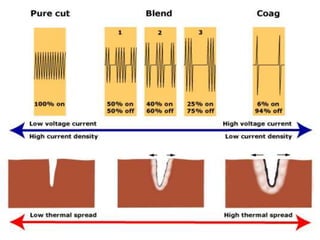
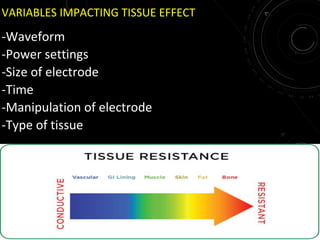
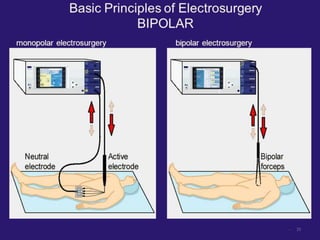
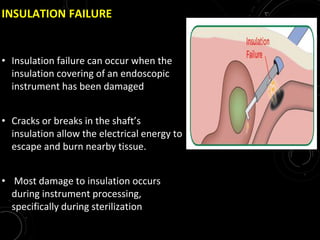
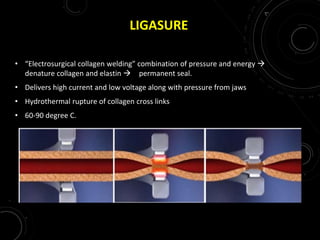
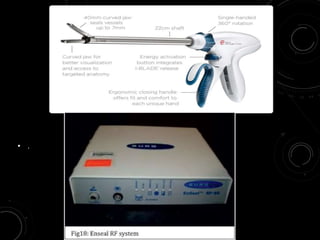
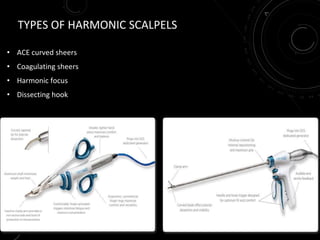
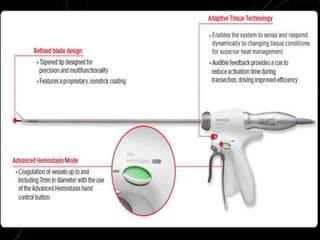
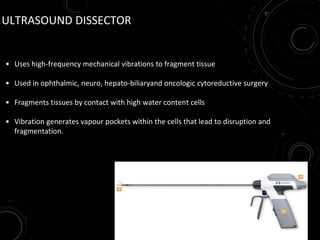
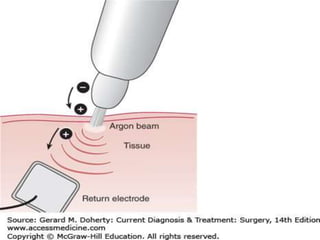
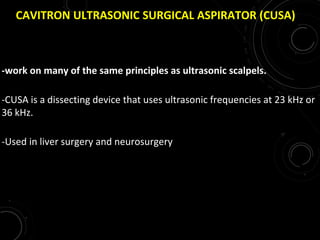
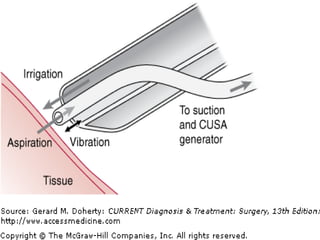
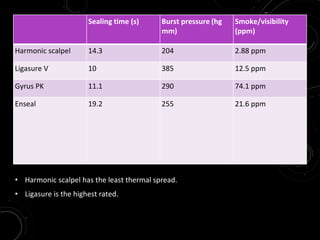
The document discusses various energy sources used in surgery including electrical, ultrasonic, argon beam, and laser energies. It provides details on electrosurgery modalities like electrocautery and electrosurgery. Newer advanced bipolar devices like Ligasure, Gyrus ACMI, and Enseal are described which provide vessel sealing through thermal coagulation. Ultrasonic devices like Harmonic scalpel use high frequency vibrations for vessel sealing and precise dissection. Other technologies discussed include argon beam coagulation, CUSA, microwave ablation, and radiosurgery. Patient safety considerations are highlighted for different energy sources.