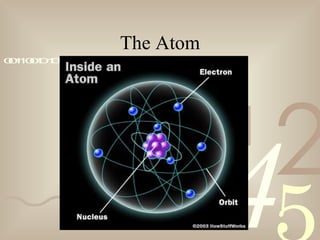
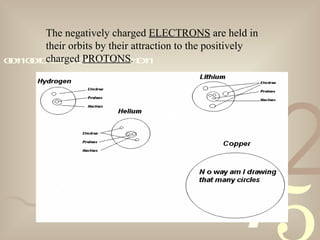
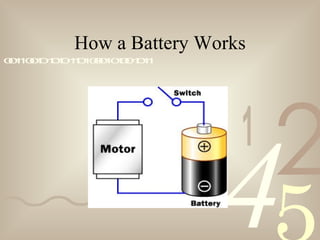
The document discusses electron theory and static electricity. It defines key terms like matter, energy, atoms, ions, conductors, and insulators. It explains that atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons, and that static electricity occurs when electrons are transferred between materials that are rubbed together, resulting in one material gaining a positive charge and the other a negative charge. It also provides examples of static electricity like rubbing a balloon on wool to make it stick to a wall.