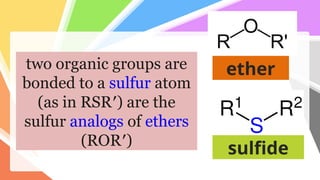
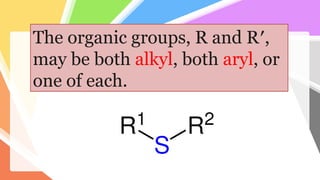
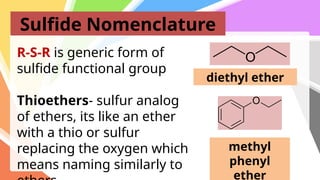
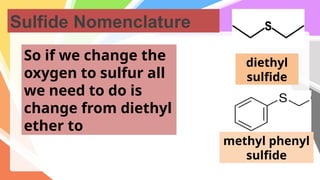
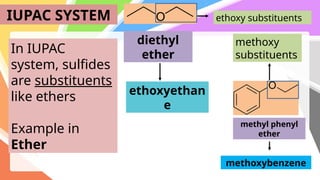
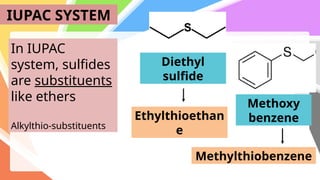
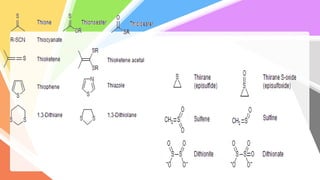
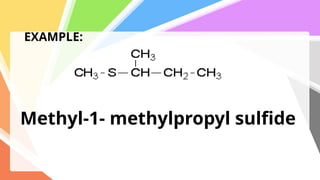
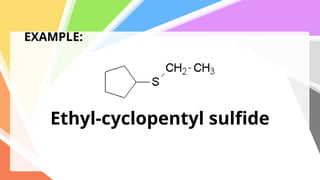
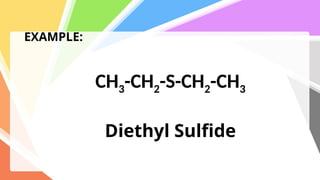
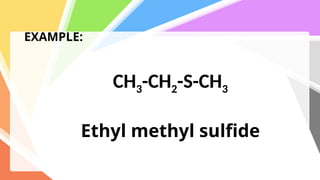
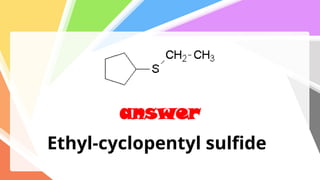
Sulfides are chemical compounds containing sulfur, categorized into inorganic, organic, and phosphine sulfides. Inorganic sulfides consist of ionic compounds with the sulfide ion, while organic sulfides contain sulfur bonded to organic groups, resembling ethers in structure. Sulfides have various industrial applications, can release toxic hydrogen sulfide, possess strong odors, and have both beneficial health properties and hazards due to their flammability.