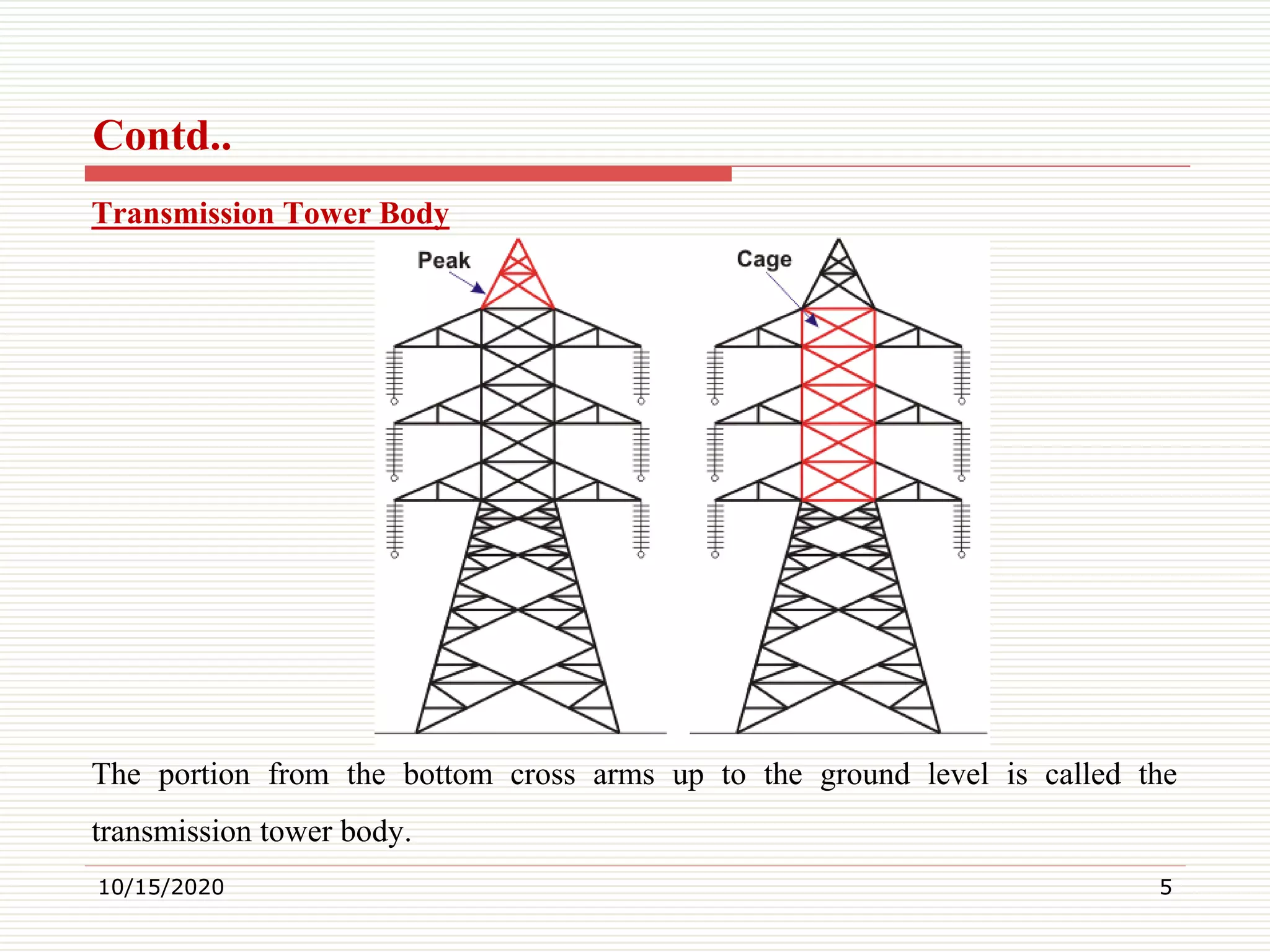
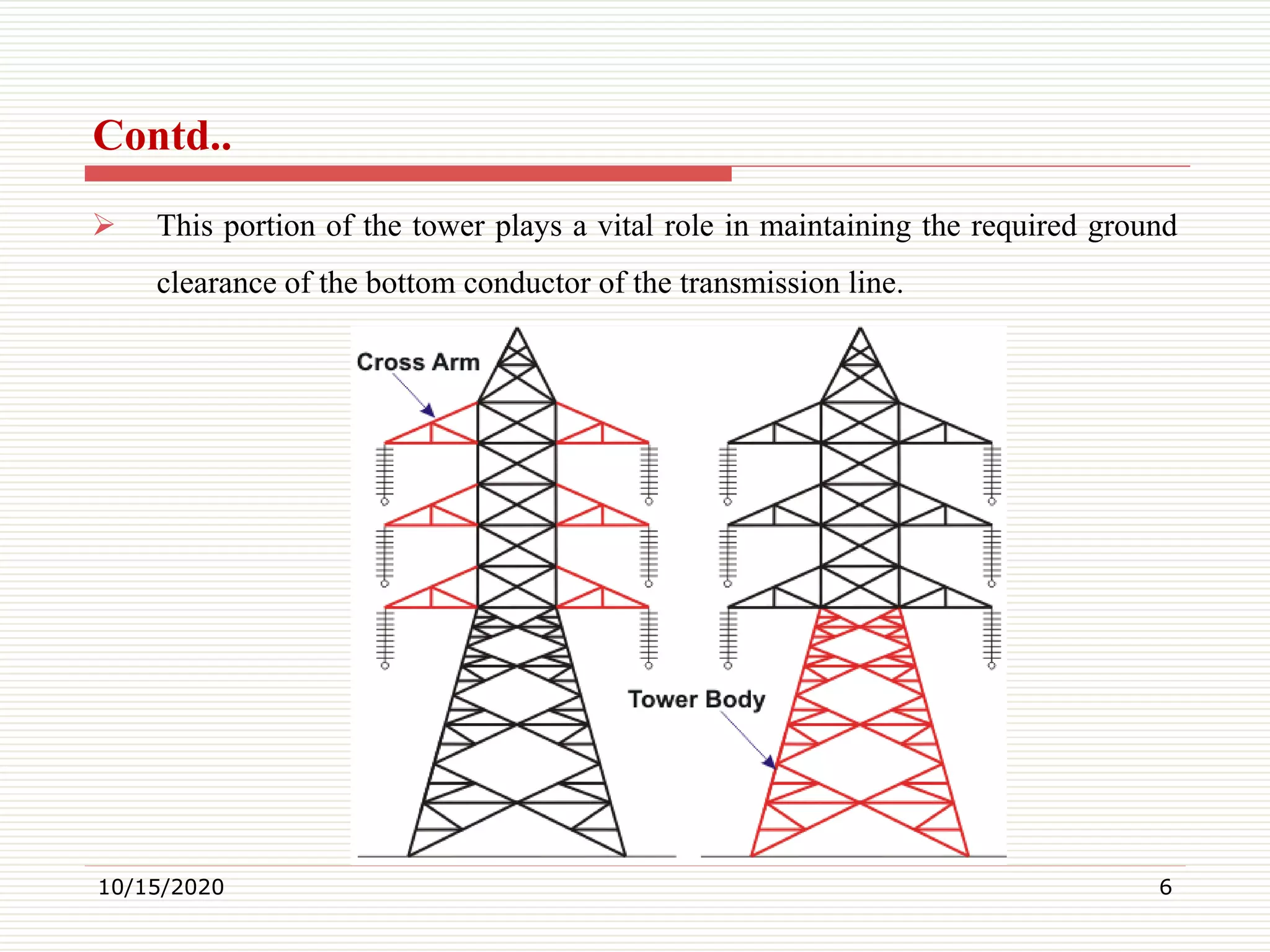
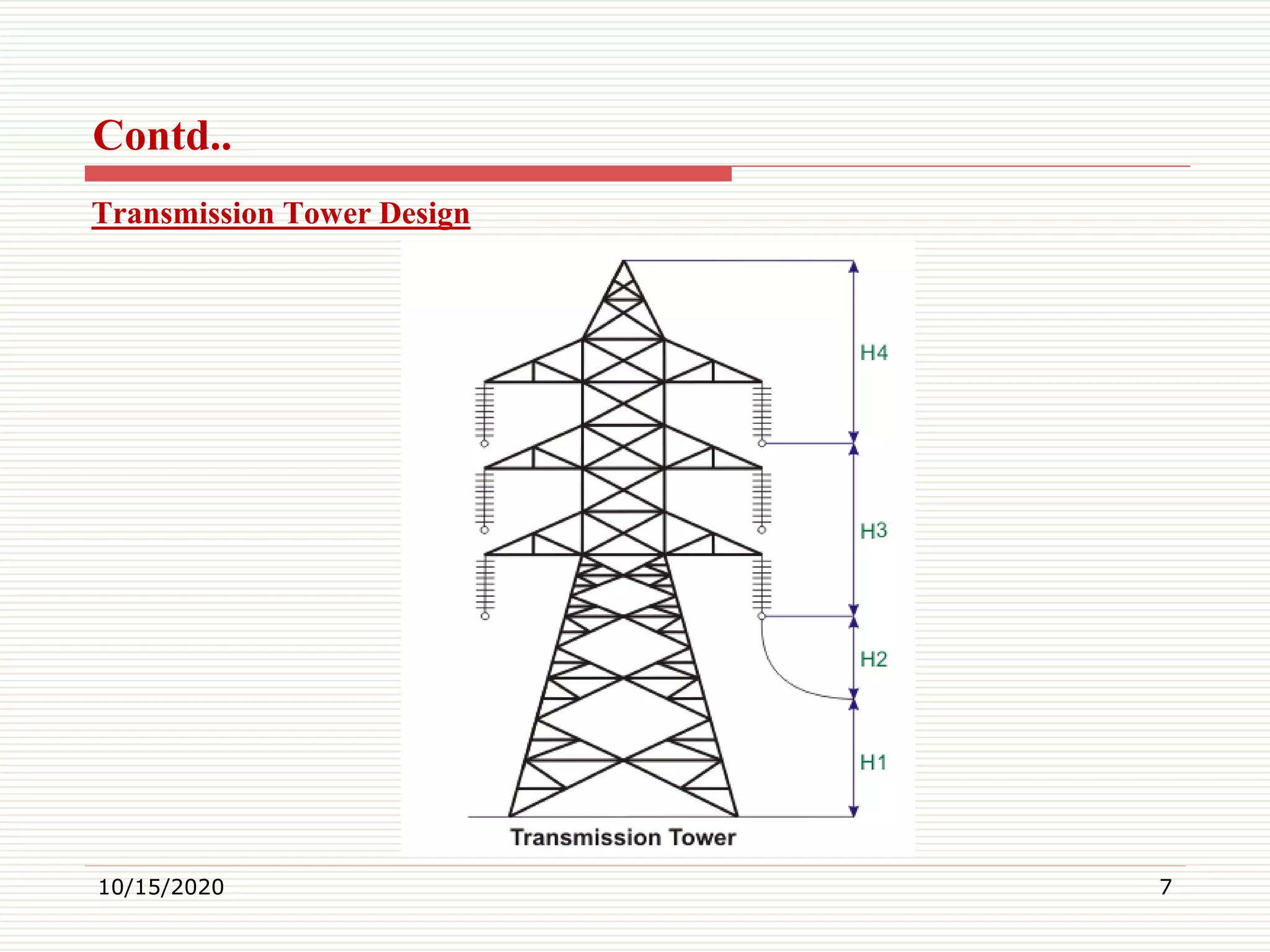
This document discusses electrical transmission towers, including their purpose, parts, design considerations, and types. It notes that transmission towers carry high voltage power lines from generating stations to substations and must sustain heavy conductors and natural calamities. The key parts of a transmission tower are identified as the peak, cross arms, boom, cage, body, legs, and baseplate assembly. Design considerations include ground clearance, insulator length, conductor spacing and clearance, and midspan clearance. Towers are classified by angle of deviation as A, B, C, or D type and by force application as tangent suspension or angle towers. Special towers include those for river, railway, or highway crossings and transposition.