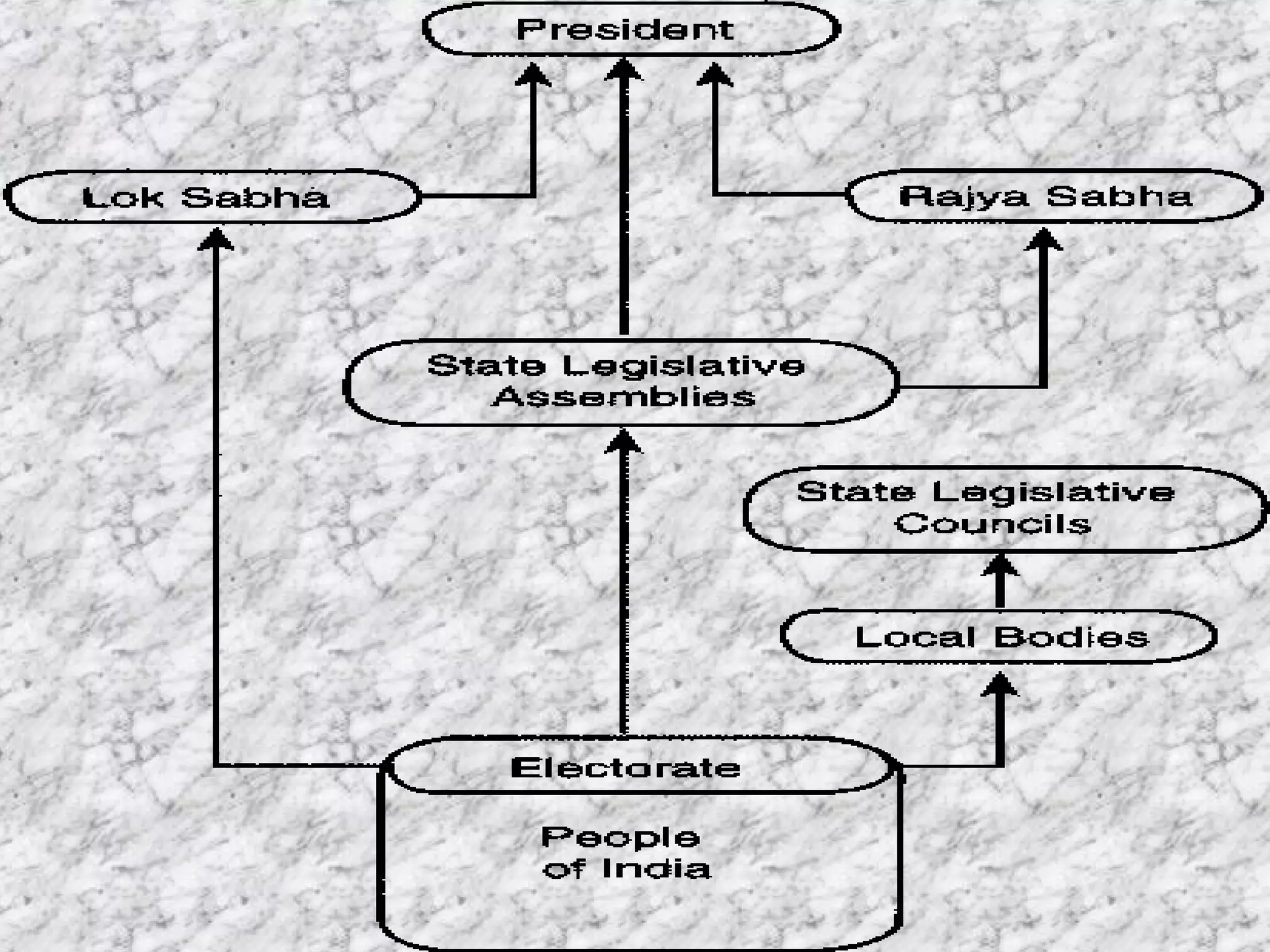
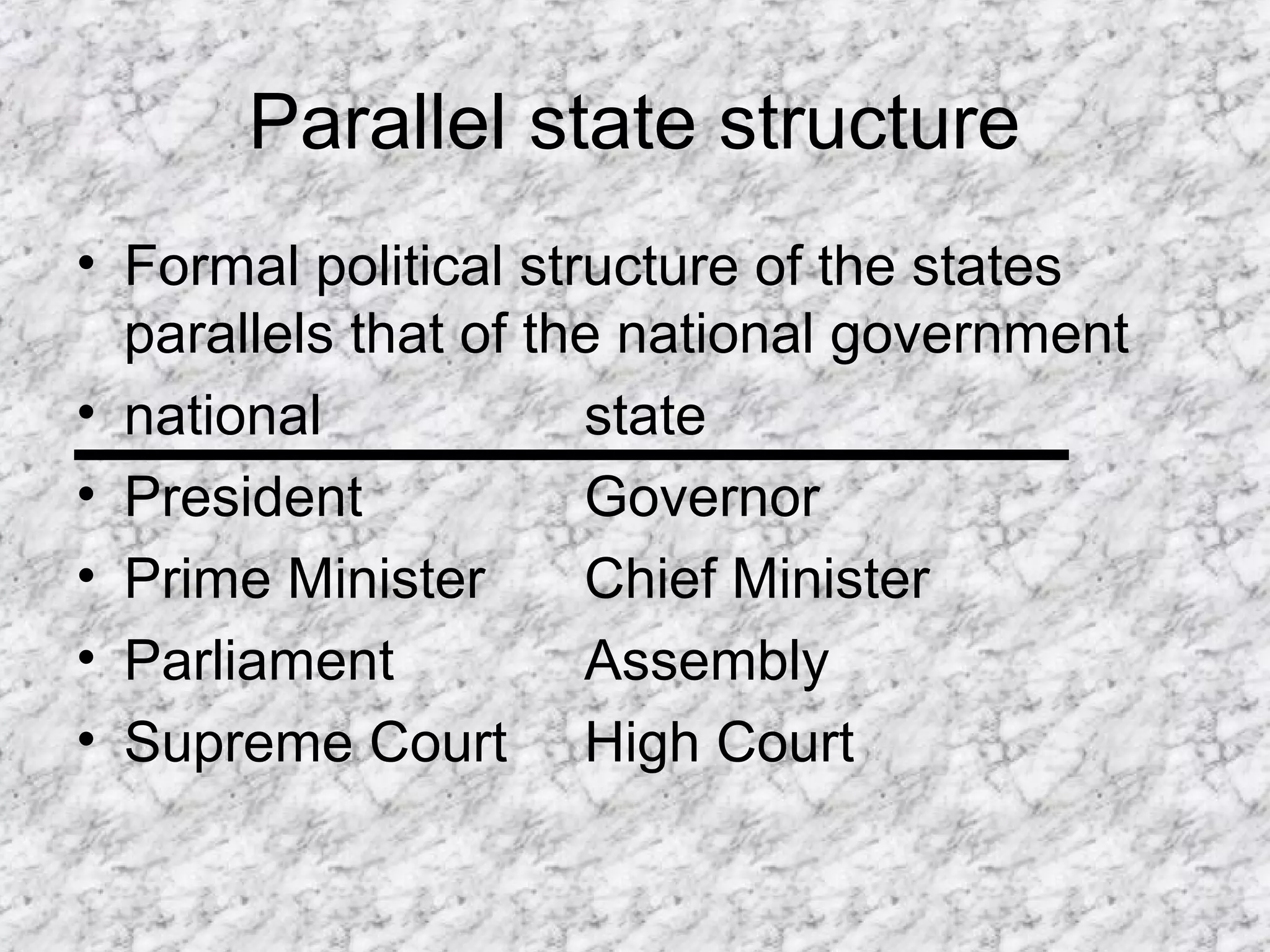
The document summarizes key aspects of electoral politics and government in India. It describes India as a federal parliamentary republic with 28 states and 7 union territories. Power is shared between the central and state governments, though the central government maintains control over key areas like defense, foreign policy, taxation, and economic planning. It also outlines the structure of India's parliamentary democracy, with the Lok Sabha (lower house) and Rajya Sabha (upper house) comprising the bicameral parliament. The leader of the majority party in the Lok Sabha becomes the Prime Minister.