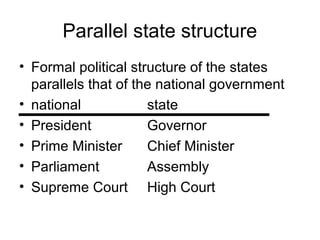
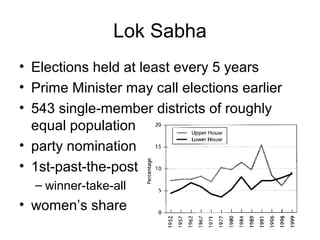
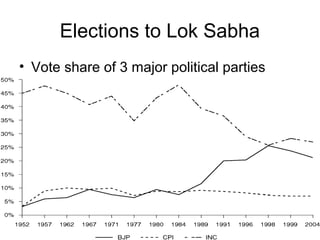
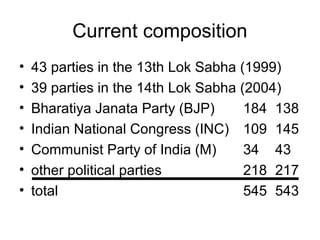
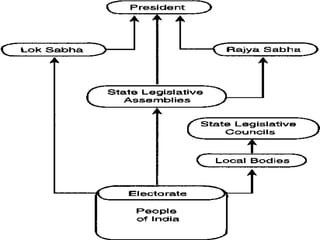
India has a federal parliamentary democratic republic system of government. Power is shared between the central government and 26 states and 6 union territories. The central government has authority over key areas like defense, foreign policy, taxation and economic planning. States have powers over agriculture, education and law and order. The legislature is bicameral, consisting of the Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha. The leader of the majority party in the Lok Sabha becomes Prime Minister. The President is the ceremonial head of state. The judiciary balances parliamentary sovereignty with judicial review of legislation.