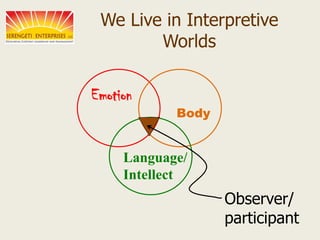
The document discusses applying emotional intelligence as a project manager. It examines emotional intelligence frameworks and identifies three core competencies of high emotional intelligence that are important for project managers - communication, conflict management, and establishing positive relationships. Project managers with high emotional intelligence can enhance communication, reduce conflict, and act as strategic leaders on their projects.