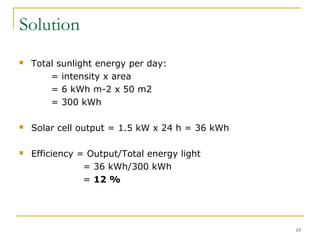
The document discusses photovoltaic (solar) cells and their efficiency. It explains that efficiency is the most important characteristic and is defined as the fraction of incident light energy converted to electrical energy. The efficiency depends on factors like the semiconductor material, device structure, temperature, and sun spectrum. It also notes that cost and lifetime are important beyond just efficiency alone. The document then examines I-V characteristics of solar cells and how efficiency is calculated using measurements of short circuit current, open circuit voltage, and maximum power point from the I-V curve. It provides an example calculation of efficiency for a specific solar cell operating under a resistive load.