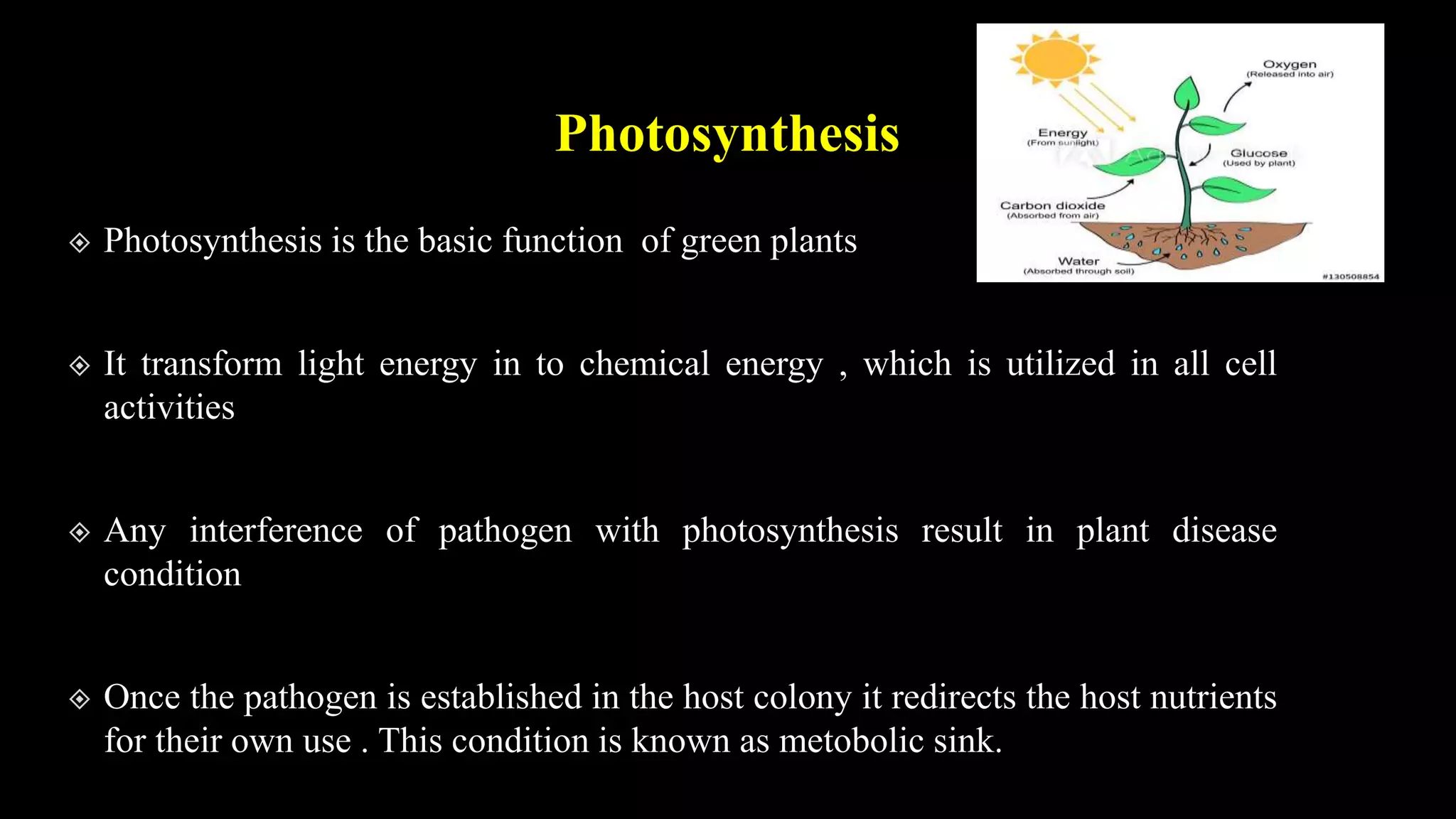
This document discusses the effects of virus, bacterial, and fungal infections on plant physiology. It summarizes that virus infections can reduce chloroplast numbers and chlorophyll content, as well as stimulation of early CO2 incorporation but decline after several days of infection. Bacterial infections can decrease chloroplast stroma and destroy chloroplast integrity, suppressing CO2 fixation. Fungal infections can reduce chloroplast content and inhibit processes like photophosphorylation and electron transport, suppressing CO2 fixation. It also discusses the process of plant respiration and how respiration rates increase in diseased plants as they use reserve carbohydrates faster than healthy tissues.