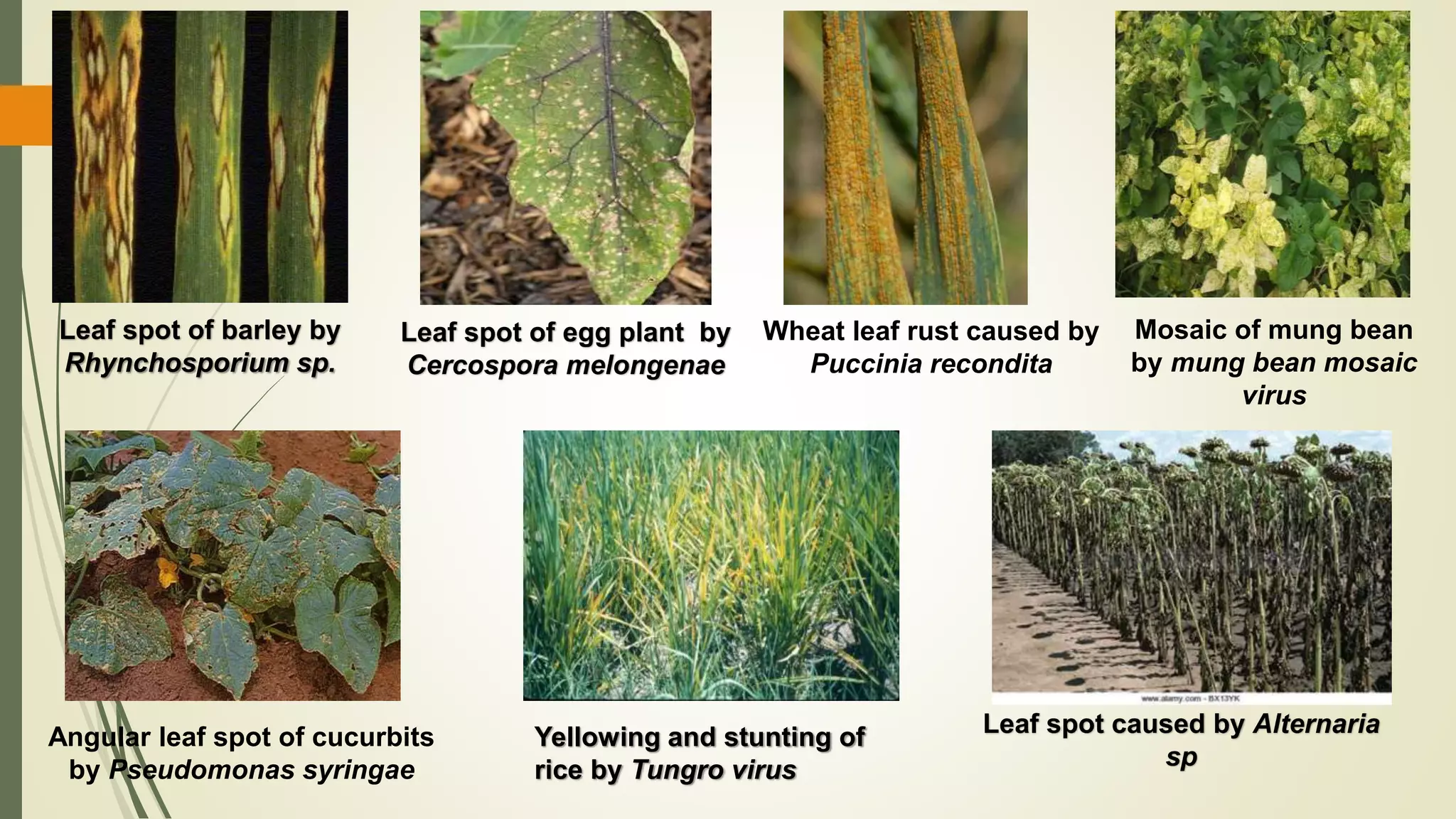
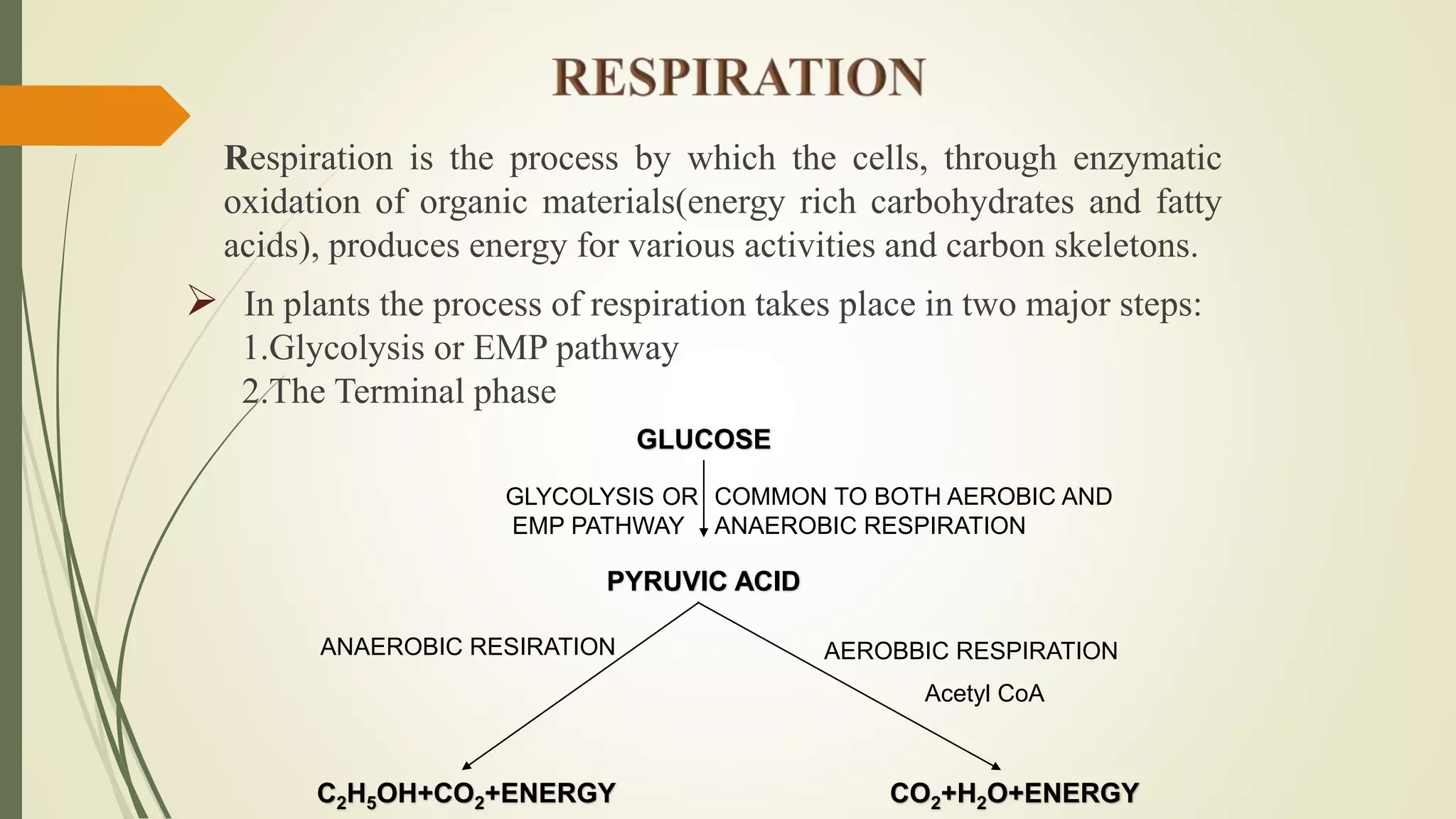
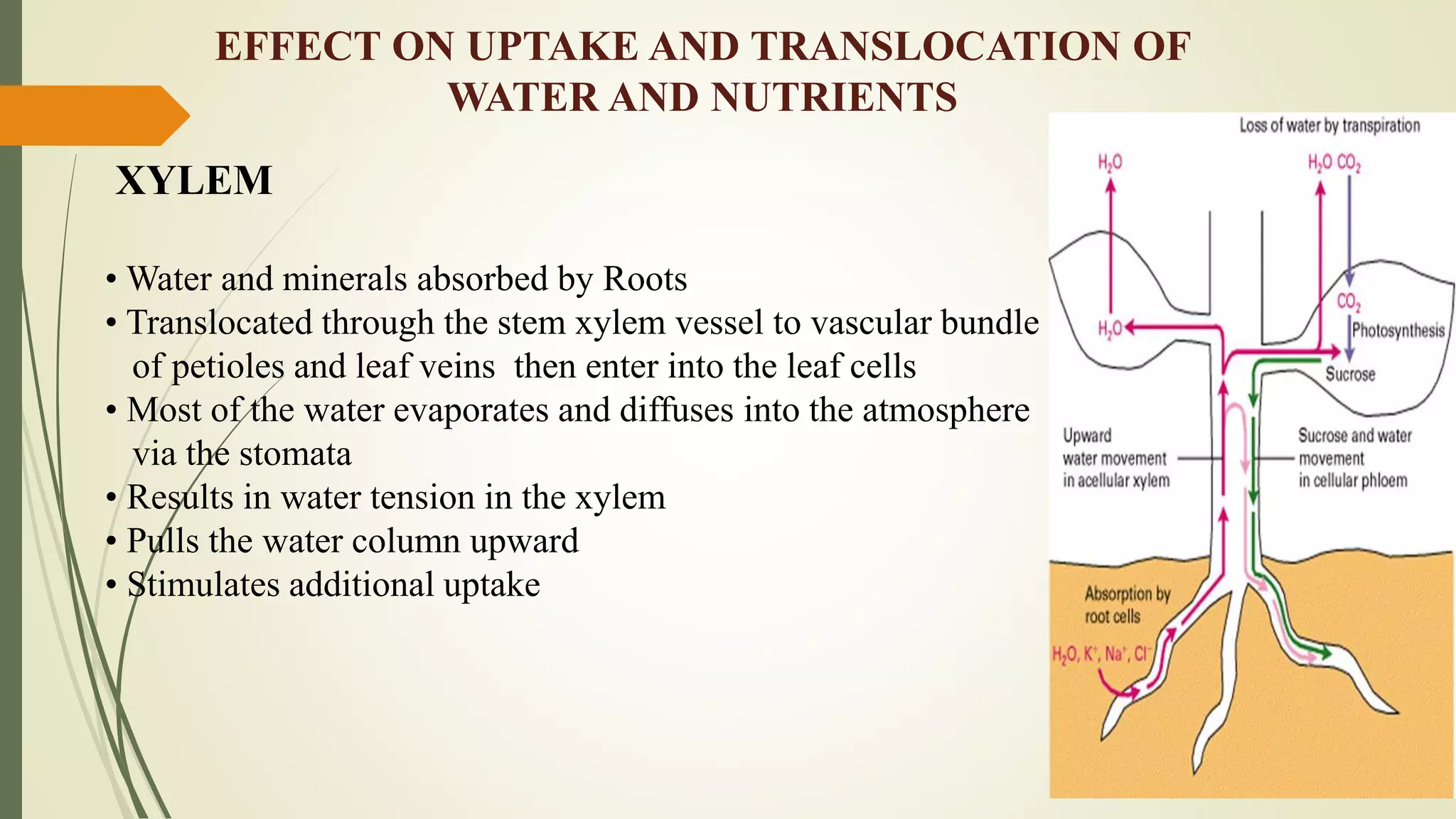
Plant pathogens can interfere with key plant physiological functions such as photosynthesis, respiration, transpiration, nutrient transport, and cellular processes. This document discusses how pathogens disrupt these functions through tissue damage, toxin production, and cellular changes. Specifically, it notes that pathogens reduce photosynthesis by destroying chlorophyll or inhibiting related enzymes. They also increase plant respiration and interfere with nutrient transport through the xylem and phloem.