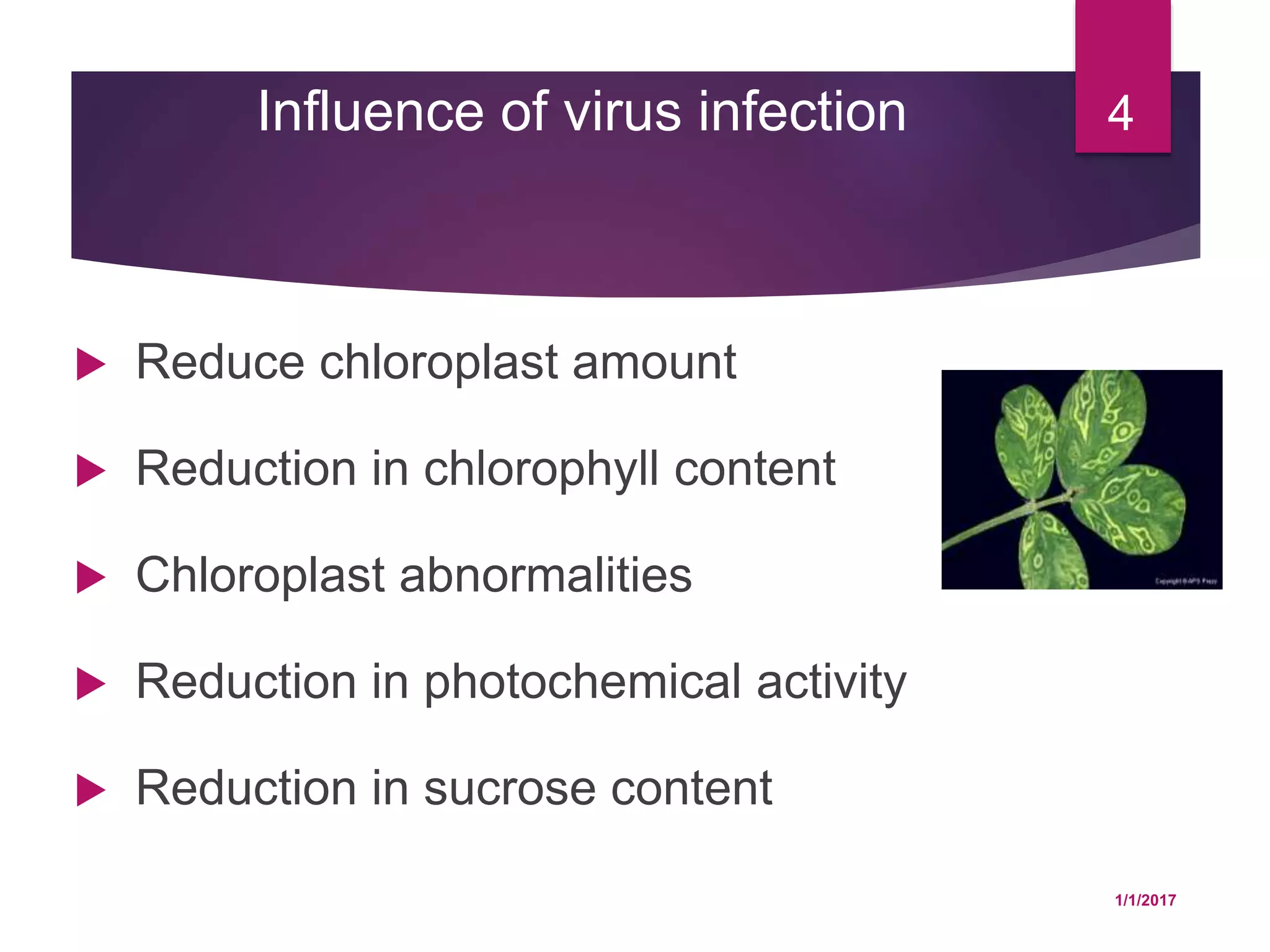
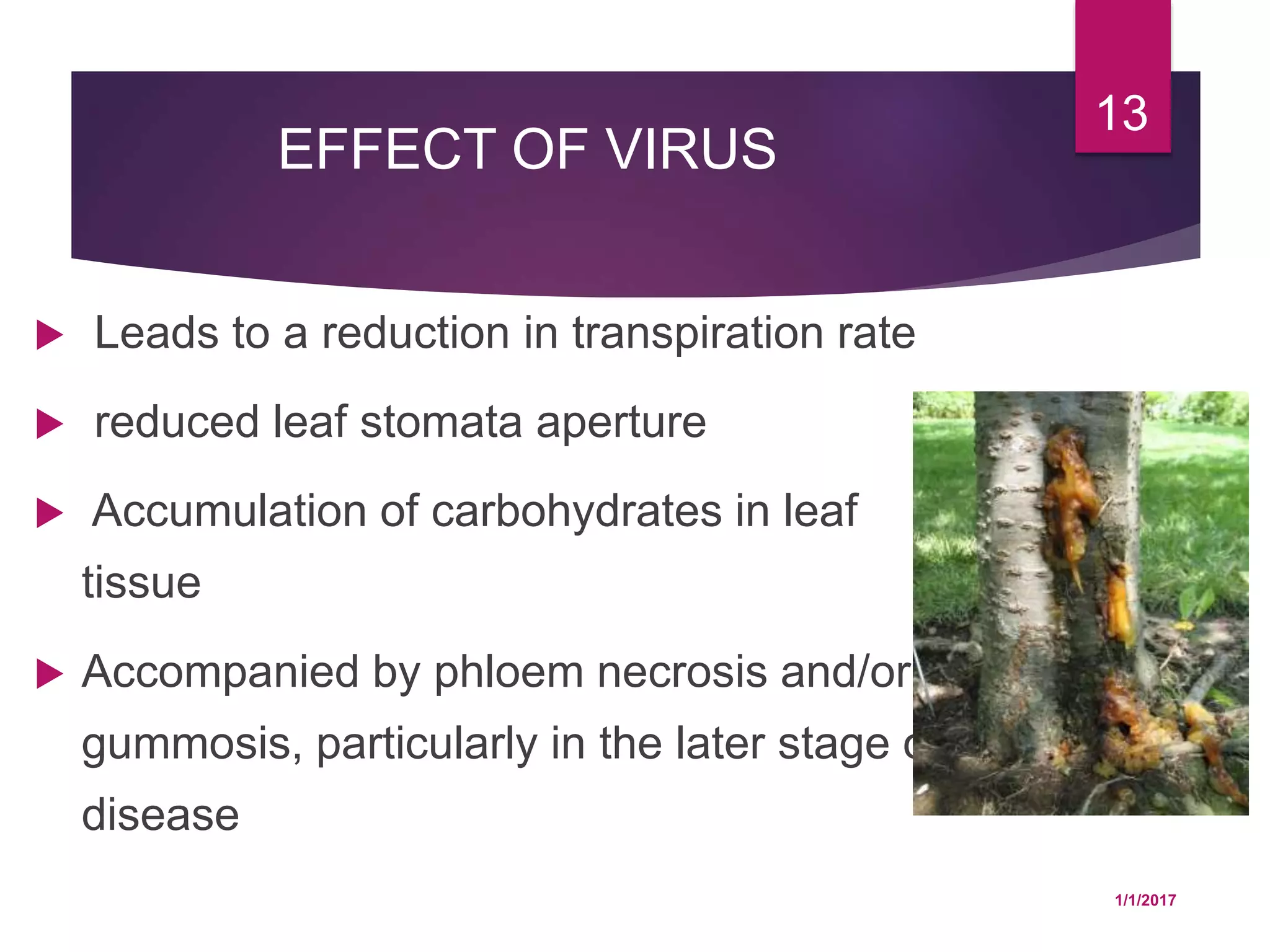
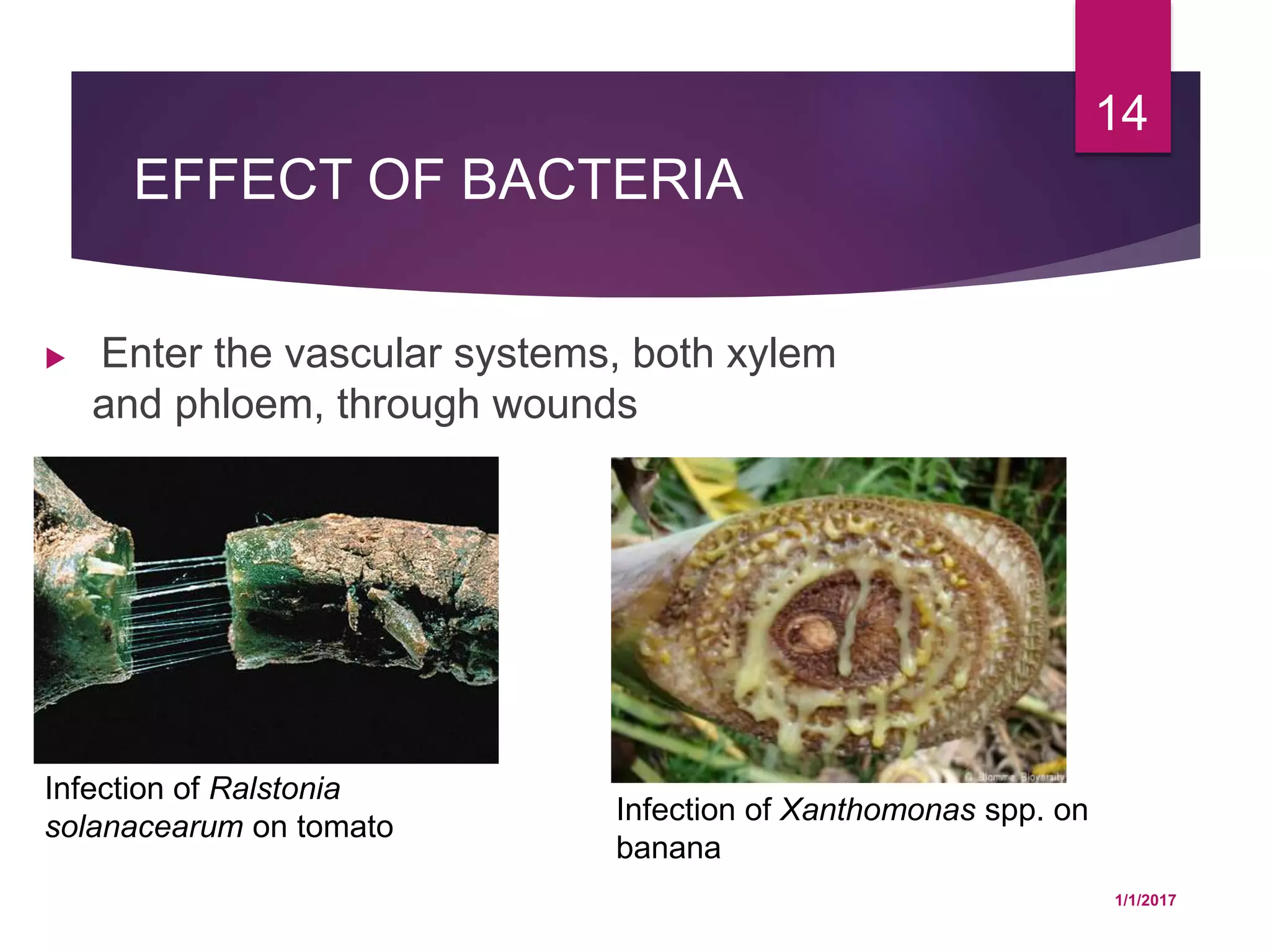
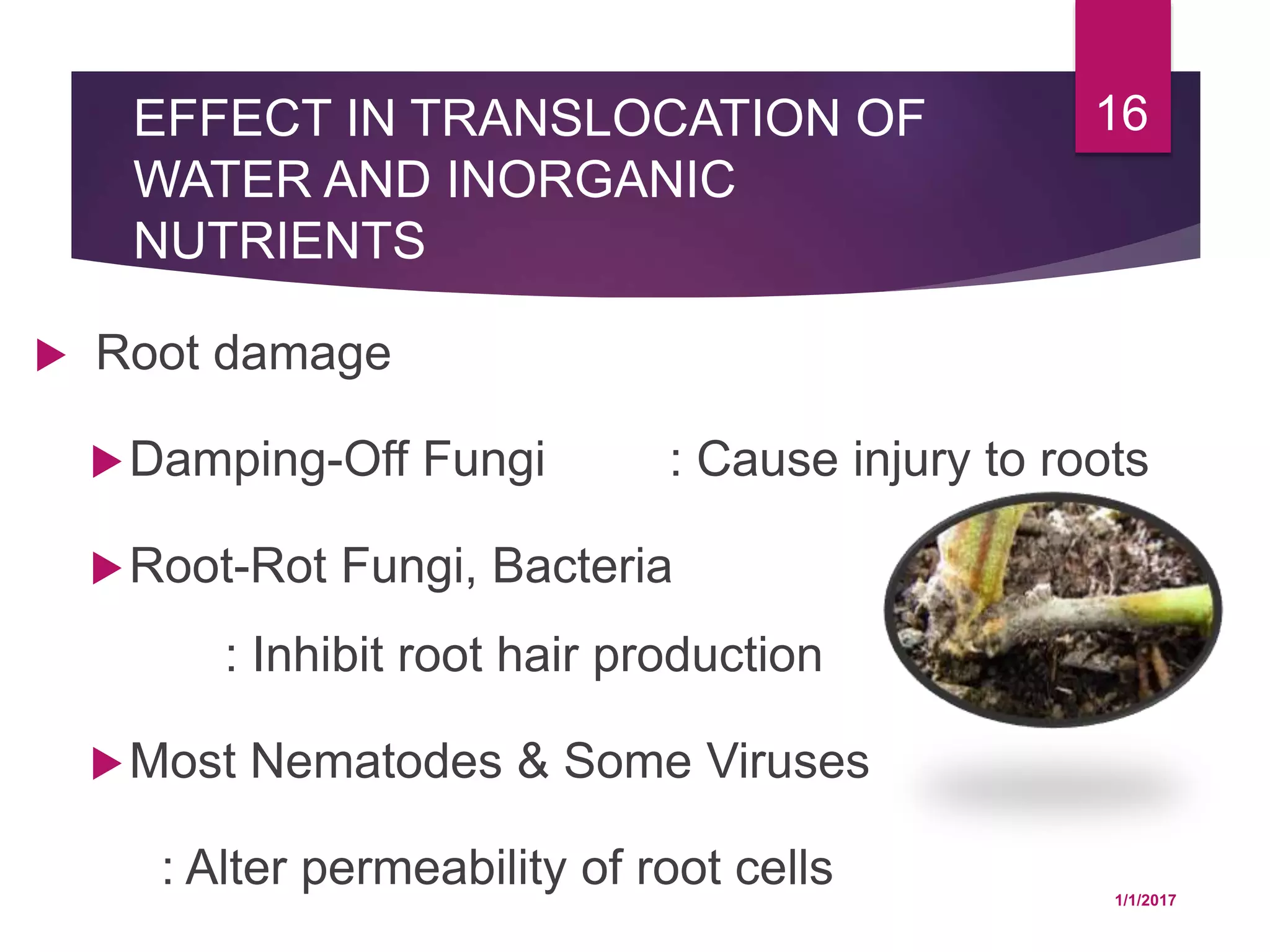
The document discusses how various plant pathogens like viruses, bacteria, and fungi can interfere with key physiological functions in plants such as photosynthesis, respiration, membrane permeability, translocation of water and nutrients, and transcription and translation. Pathogens are shown to reduce chloroplast function, chlorophyll content, and carbon fixation, while increasing respiration rates. They also impact membrane permeability, block translocation through vascular systems, and alter transcription and translation processes in the plant.