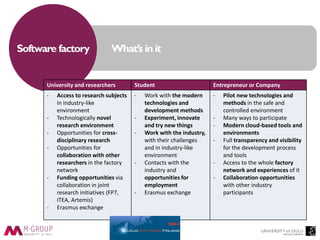
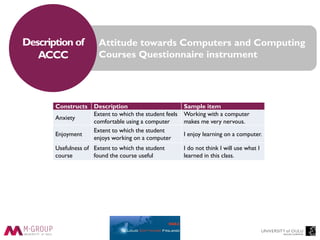
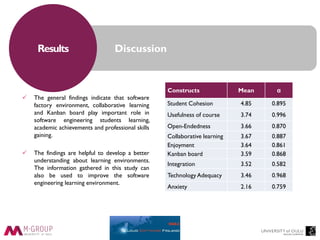
This document discusses the perceptions and attitudes of software engineering students towards a software factory created at the University of Oulu to enhance practical learning experiences. The study reveals that elements such as collaborative learning, the use of Kanban boards, and an industry-like environment positively influence student confidence, skills, and overall learning outcomes. Future research is suggested to expand on these findings with larger sample sizes and further exploration of the factors affecting student learning.