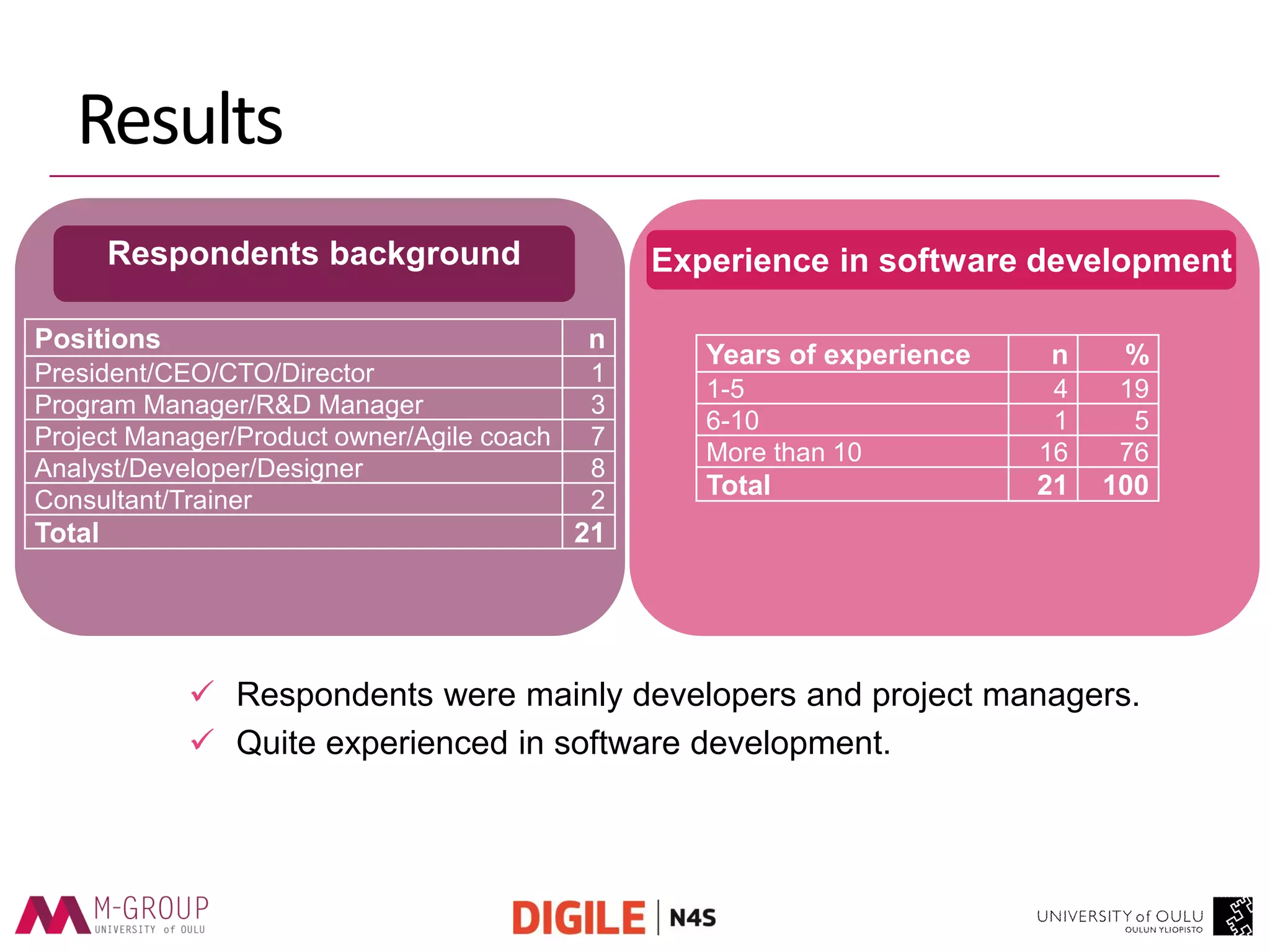
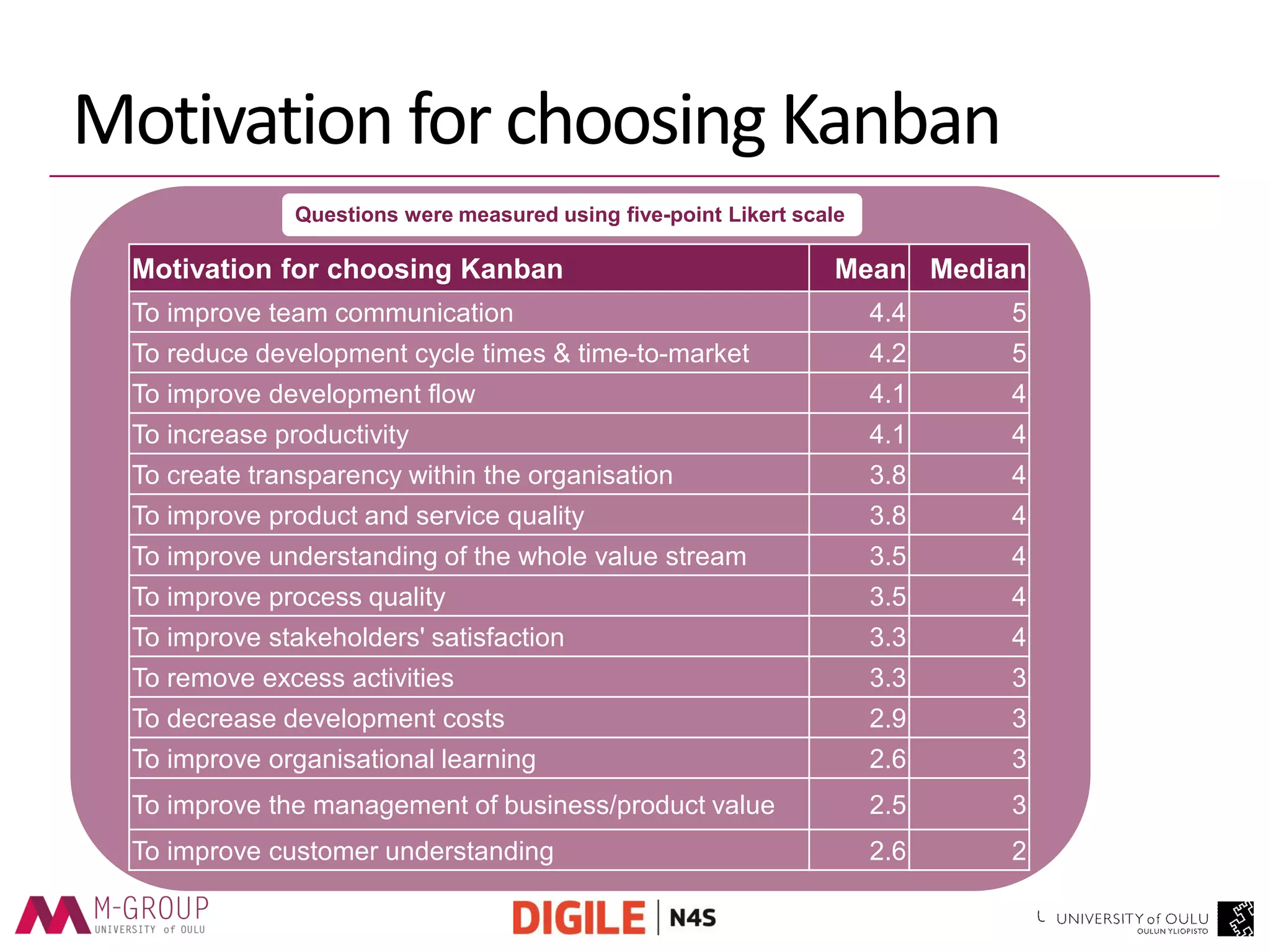
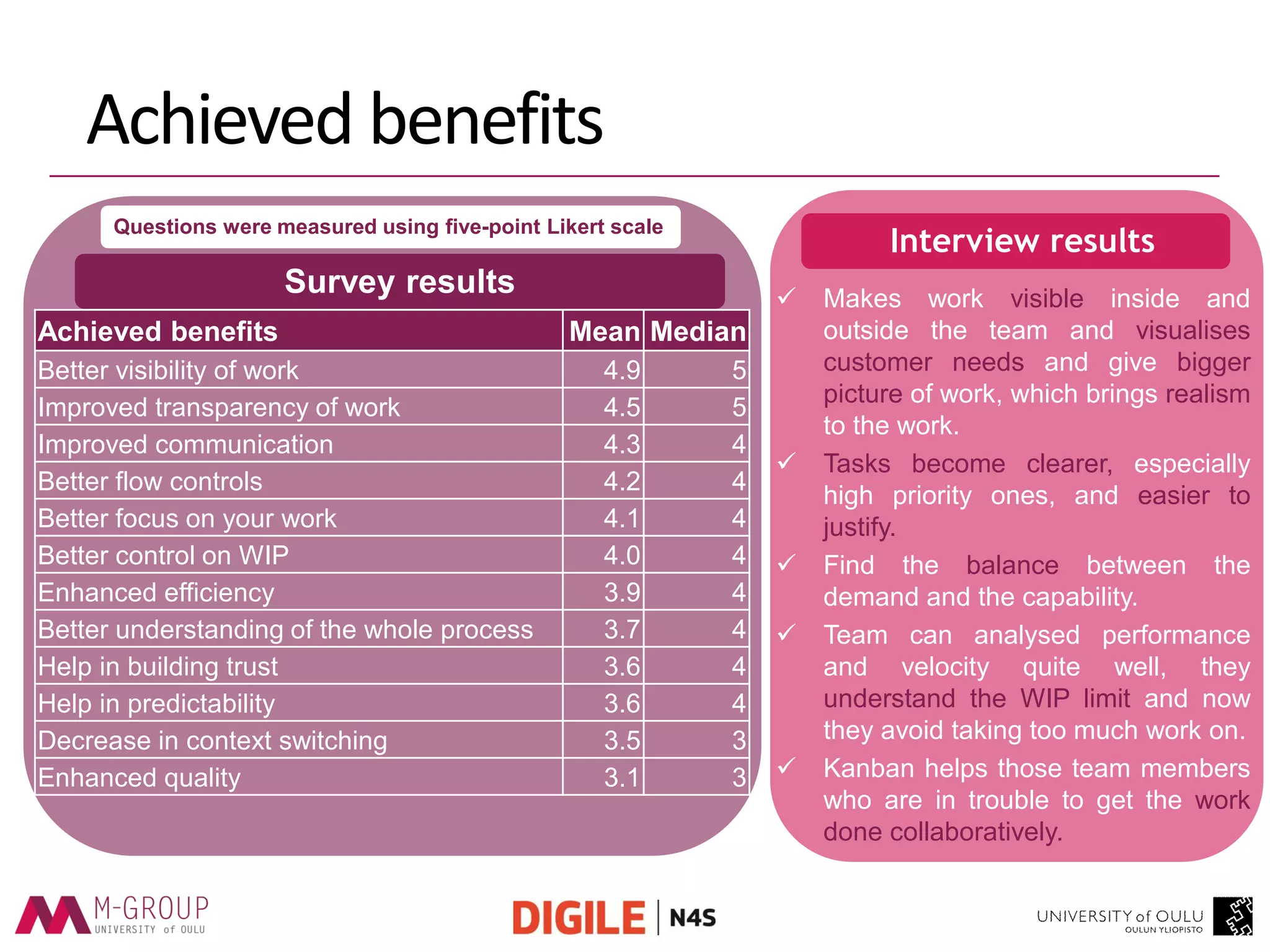
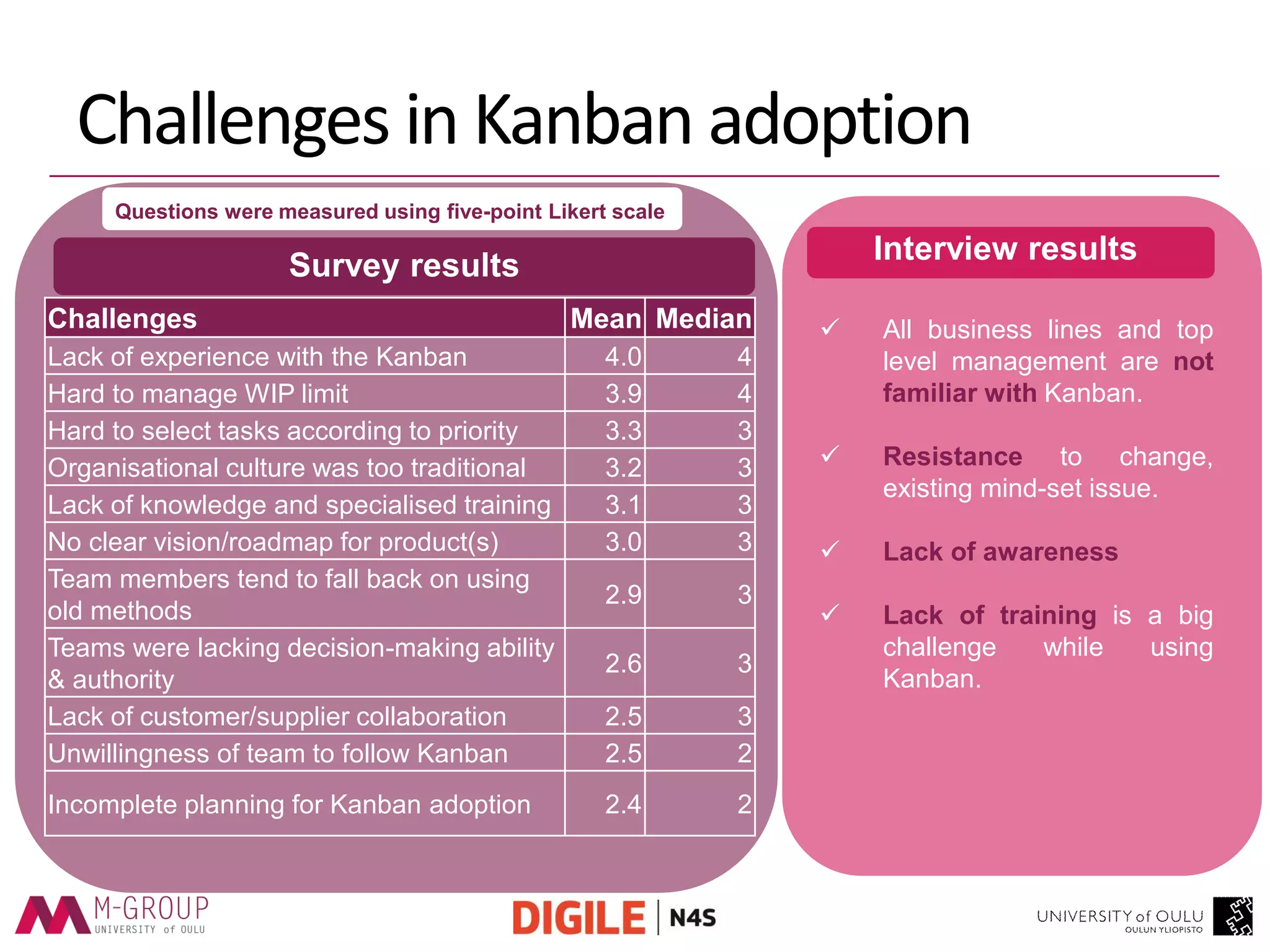
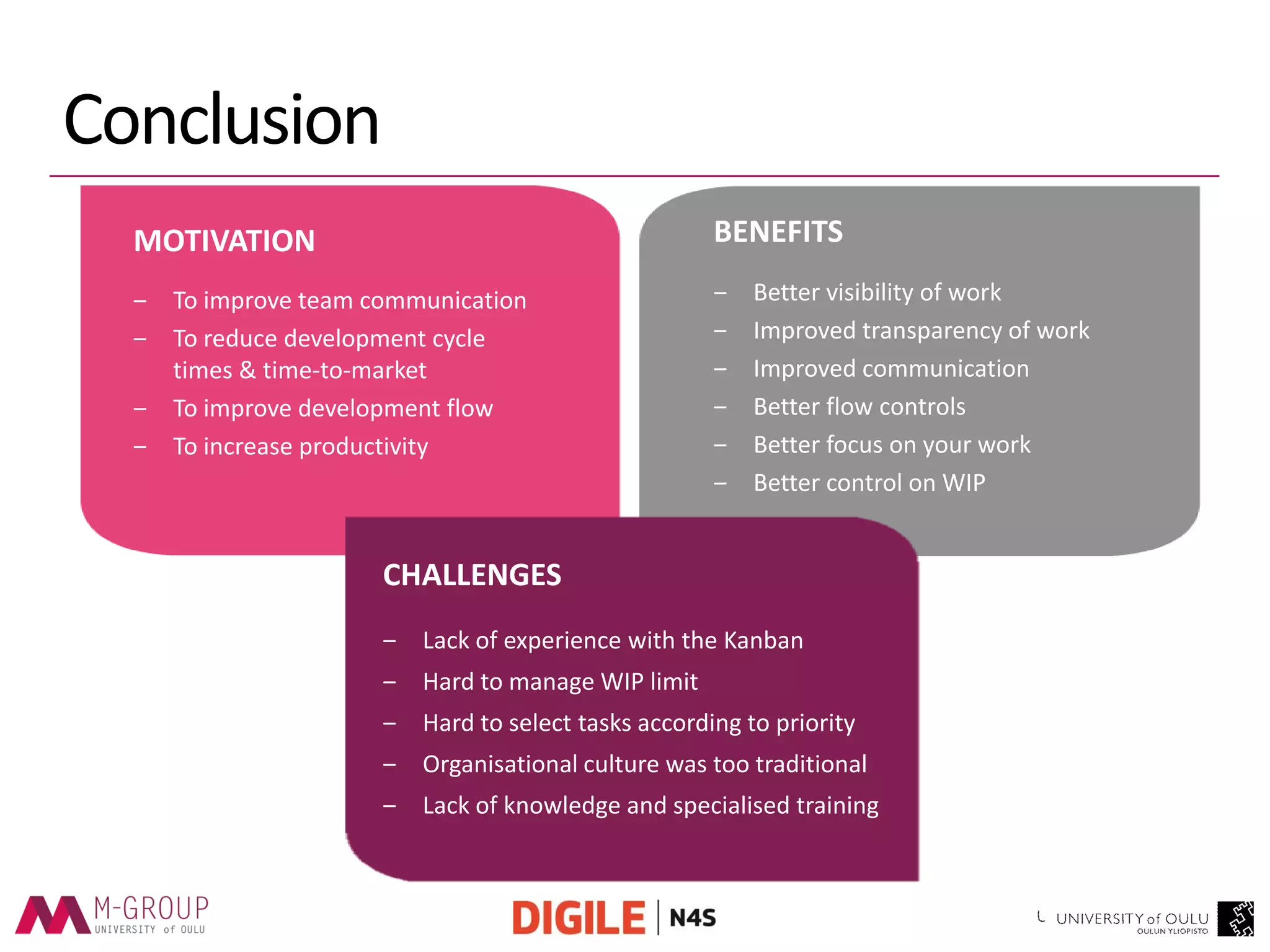
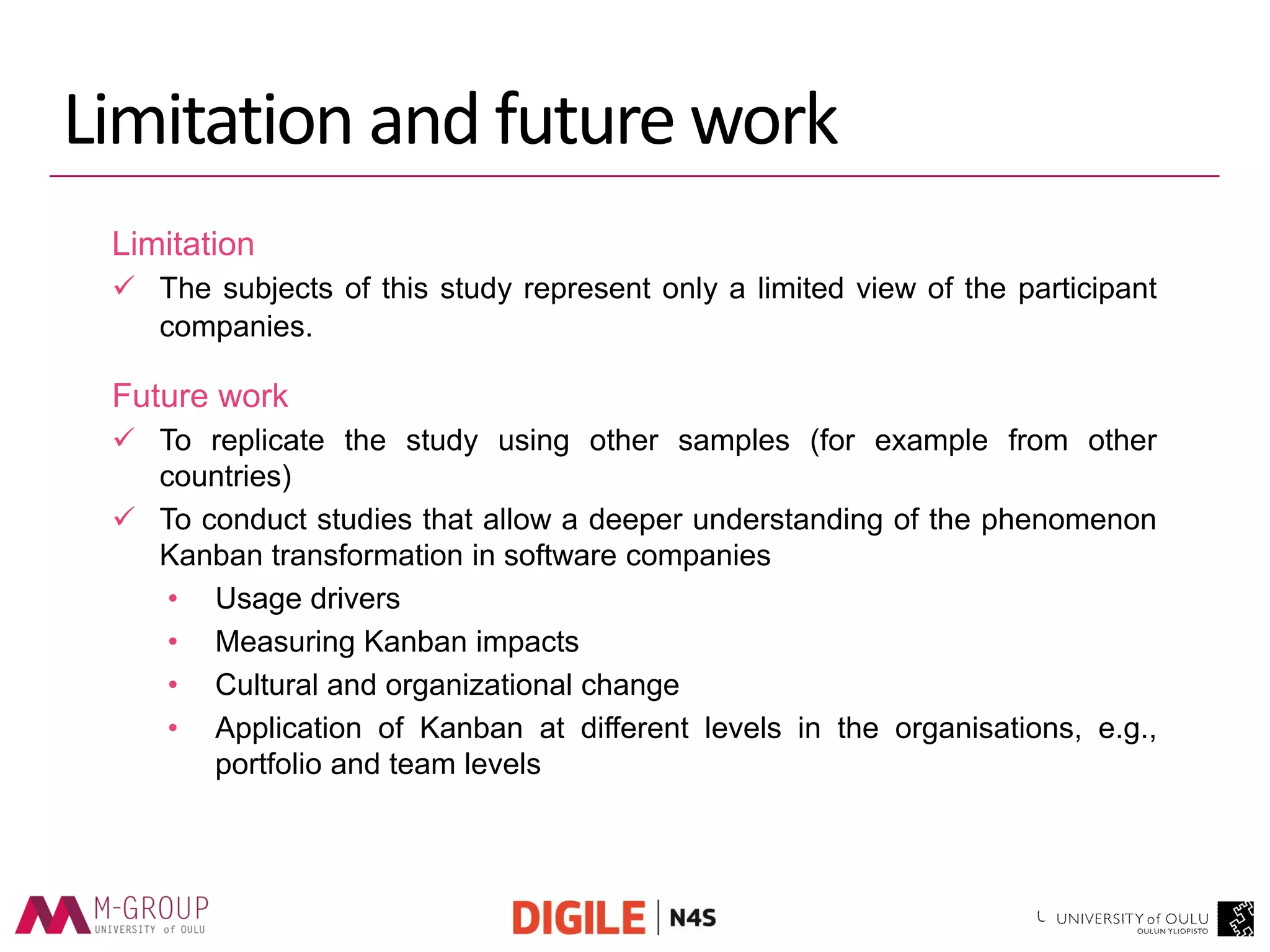
The document presents an empirical study on the usage of Kanban in software companies, highlighting its introduction, principles, and motivation for adoption. The research identifies benefits such as improved visibility, communication, and flow controls, as well as challenges like resistance to change and lack of training. Recommendations are provided to overcome these challenges, emphasizing the need for education and top-level management commitment for successful Kanban implementation.