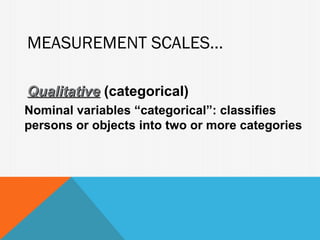
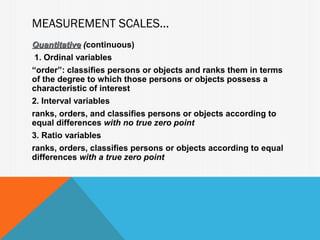
1. Educational instruments measure theoretical constructs like cognitive ability or attitudes that are not directly observable. There are three main types: cognitive, affective, and projective instruments.
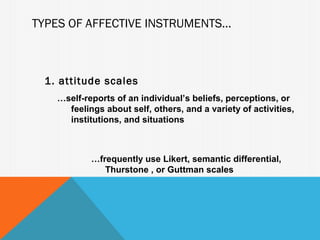
2. Cognitive instruments measure academic attainment through achievement and aptitude tests. Affective instruments assess feelings, values, and attitudes using scales and inventories. Projective instruments reveal responses to ambiguous stimuli.
3. Validity and reliability are important issues in using instruments. Validity indicates how well an instrument measures its intended construct, while reliability refers to an instrument's consistency in measurement.