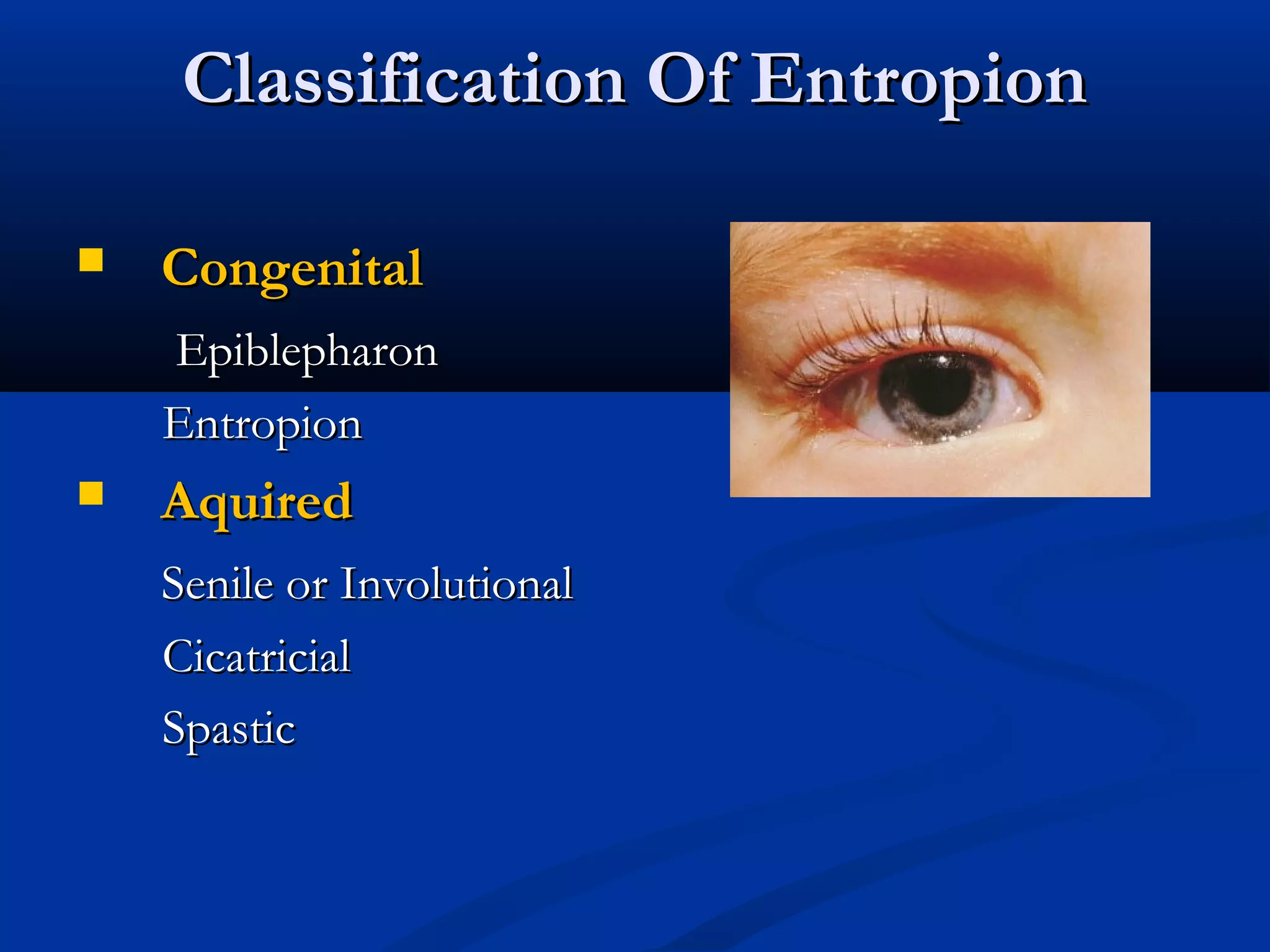
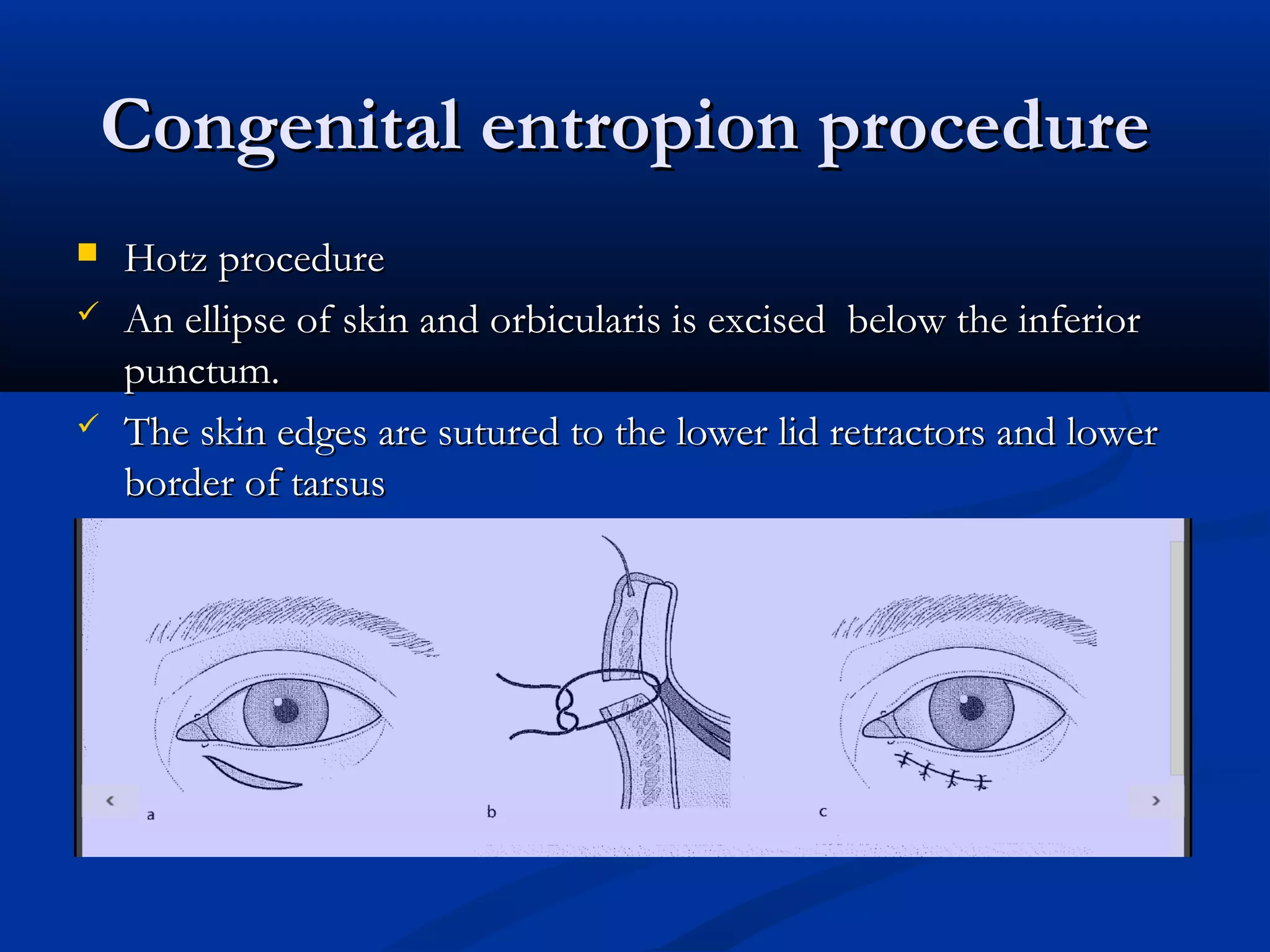
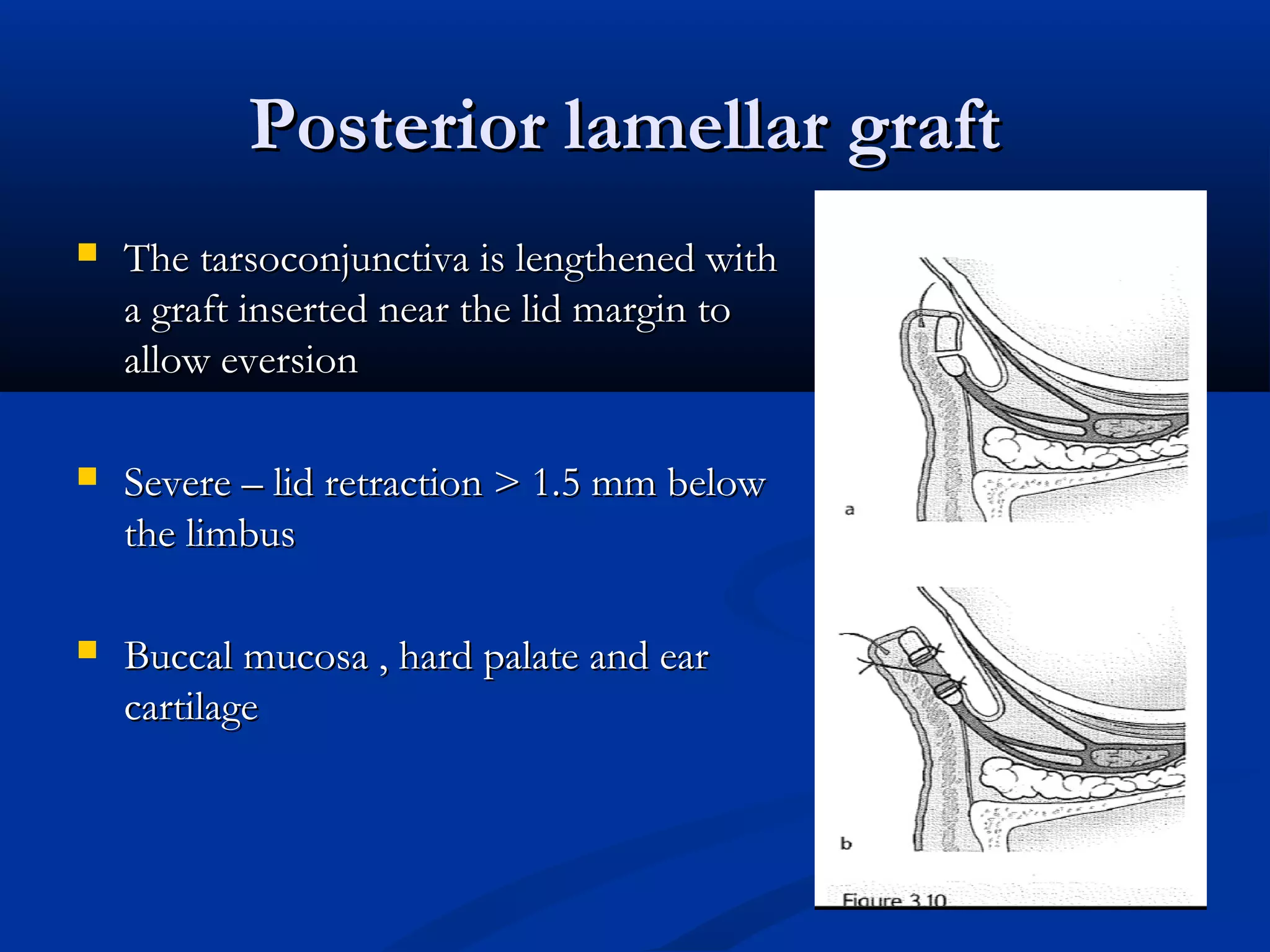
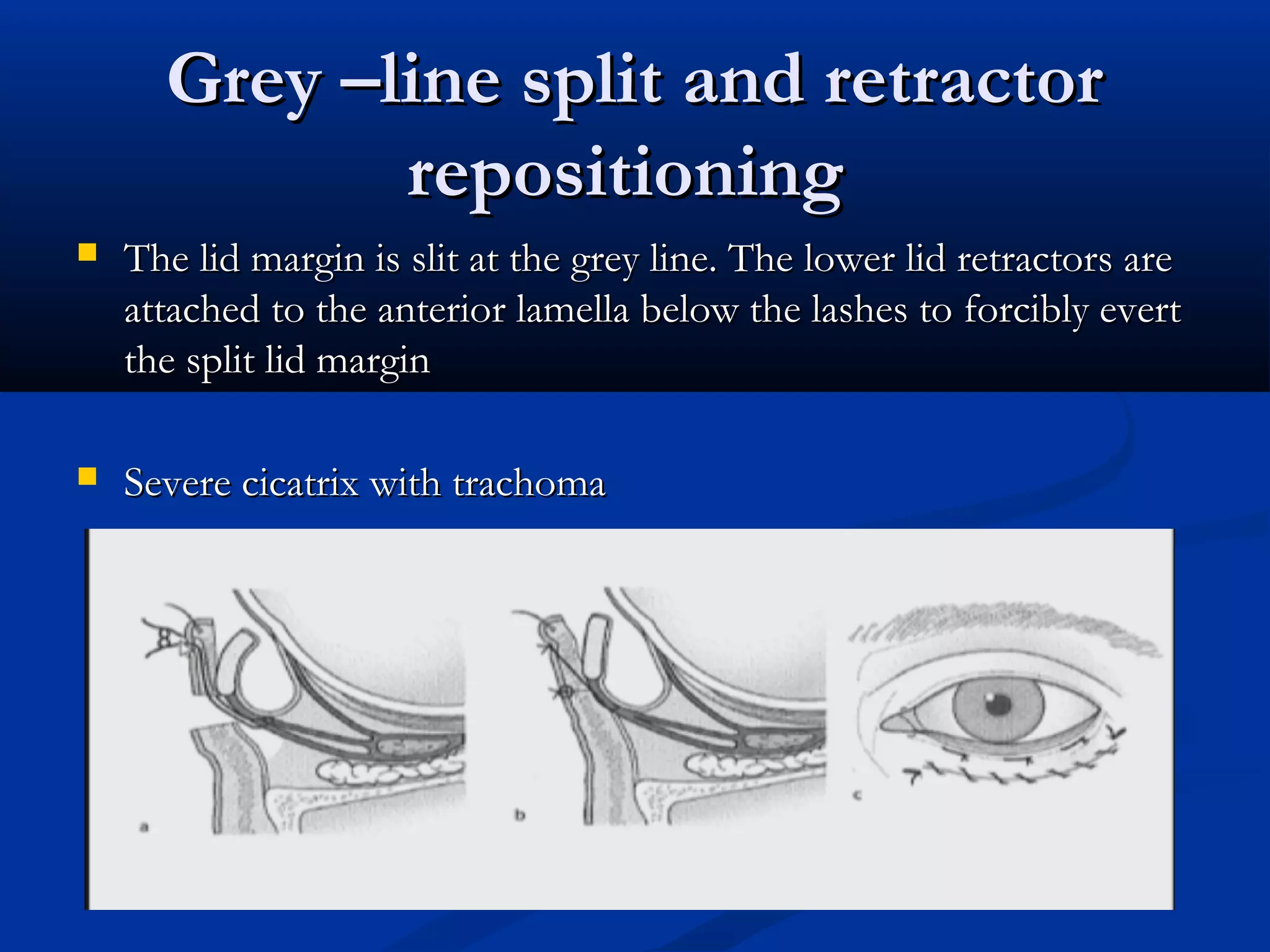
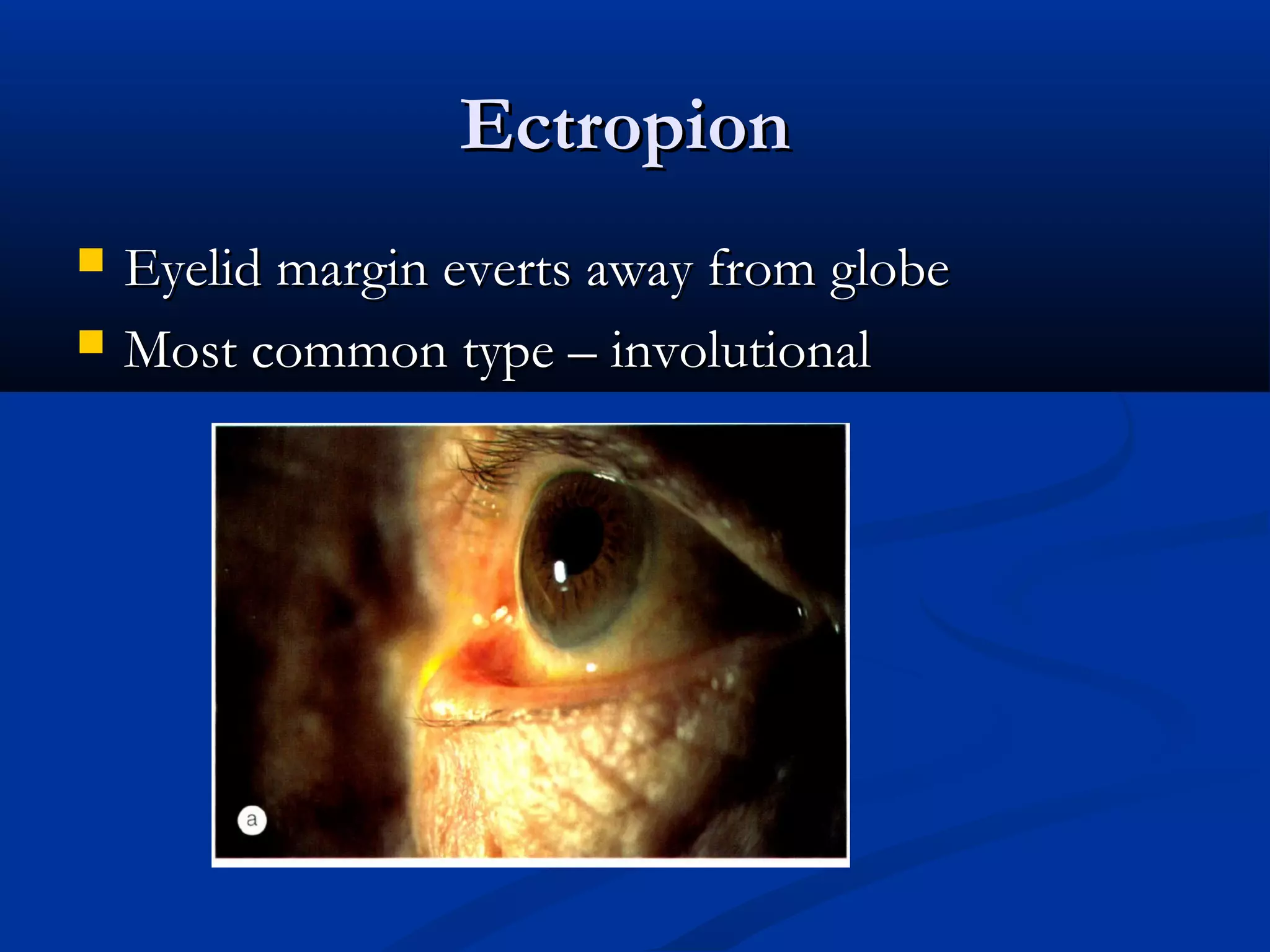
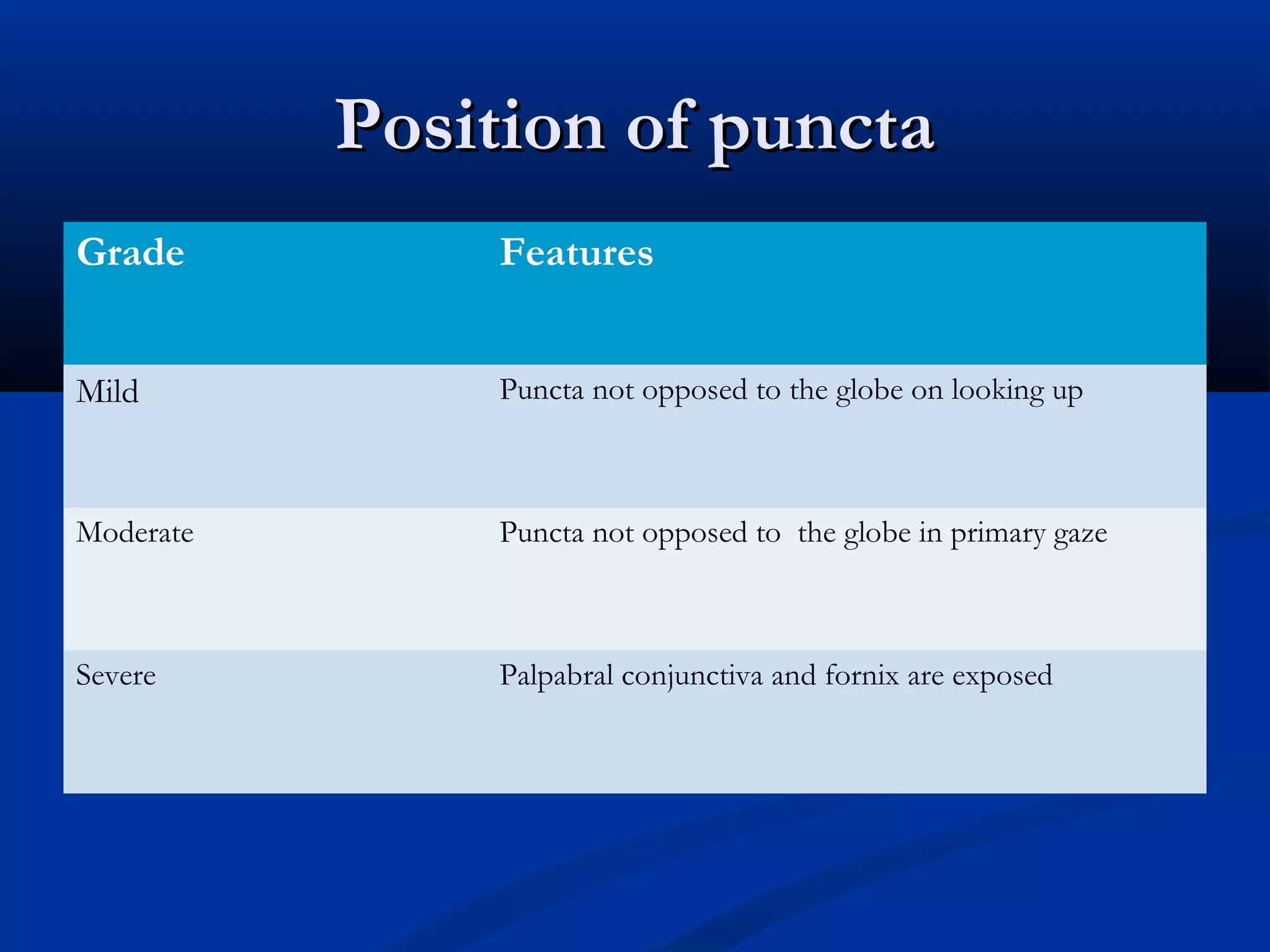
Entropion is the in-turning of the eyelid margin. It can be congenital or acquired, with the most common type being involutional/senile entropion caused by laxity of the eyelid tissues and weakness of the retractors. Examination involves assessing lid laxity, snap back test, and tendon laxity. Treatment depends on severity and includes sutures, transverse lid splits with everting sutures, horizontal lid shortening procedures, and lower lid retractor procedures. Ectropion is eyelid eversion away from the globe and can also be congenital or acquired, with involutional being most common. Examination tests for laxity and muscle weakness.