1) A system is a group of parts that work together as a unit, with most systems being open systems that take in inputs from outside and provide outputs.
2) An ecosystem is a system made up of living things like plants and animals and their nonliving environment. Within an ecosystem, a population is a group of the same species that lives in the same area, while a community includes all the populations in an area that depend on each other.
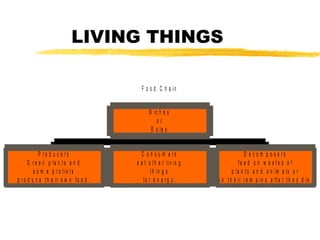
3) An organism's habitat is the environment that meets its needs, and its niche is its specific role within that habitat. As organisms fulfill their niches, they can impact both living and nonliving parts of the ecosystem.