Embed presentation
Downloaded 46 times
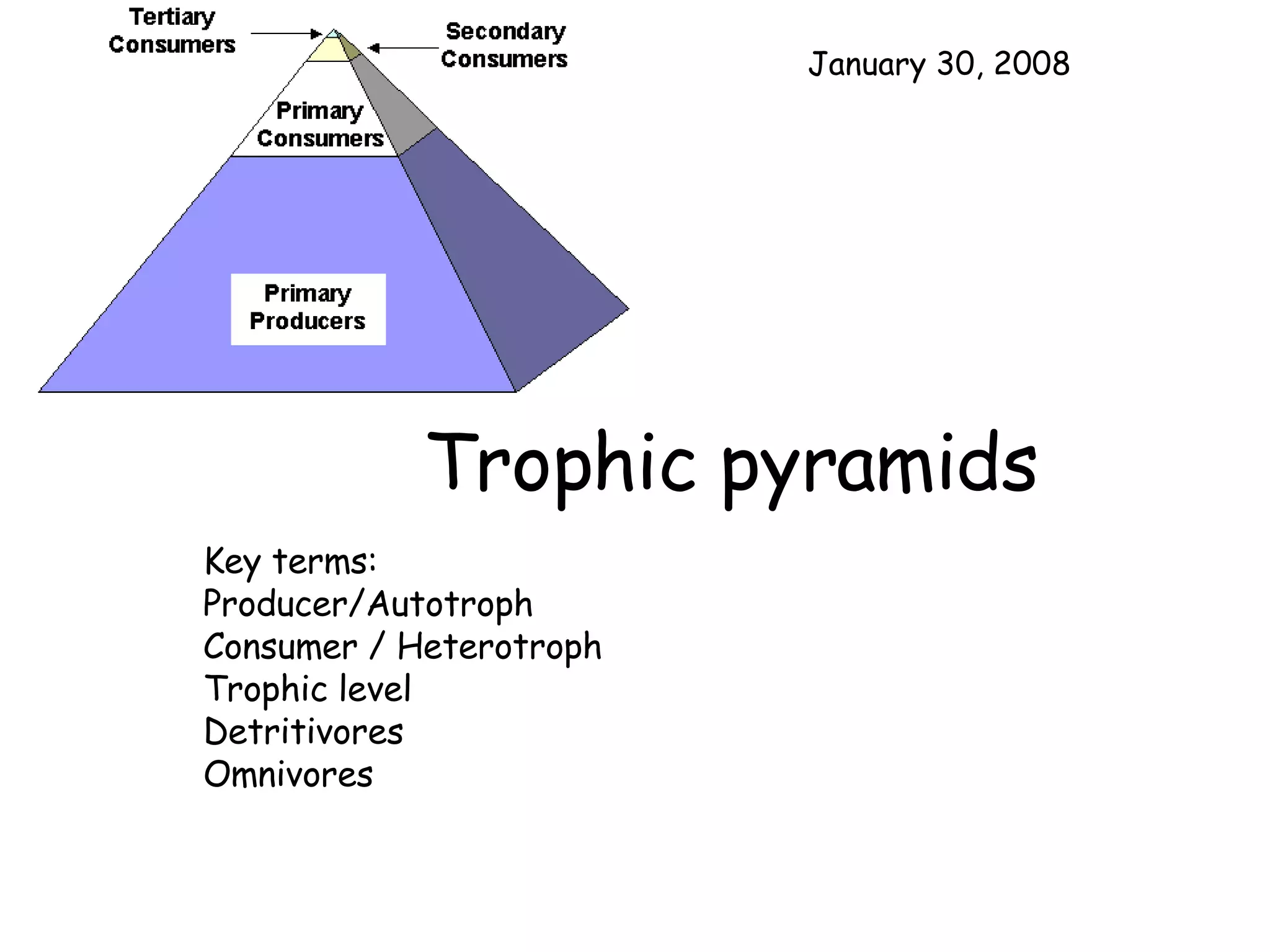
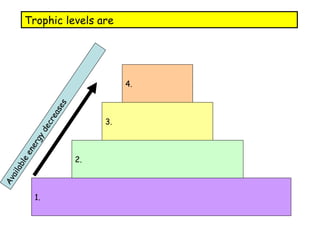
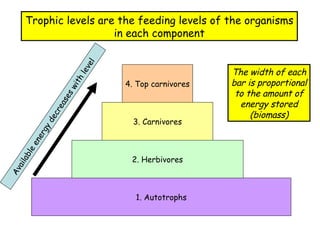
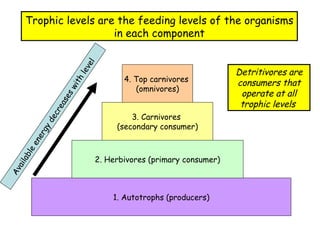

Trophic levels refer to the feeding positions that organisms occupy in a food chain or web. Producers such as plants are at the first trophic level. Herbivores that eat plants are at the second level. Carnivores that eat herbivores are at the third level. Top carnivores at the fourth level obtain energy by preying on other carnivores. Energy availability decreases at higher trophic levels as the energy from lower levels is used for metabolism and growth rather than being fully transferred up the food chain.





