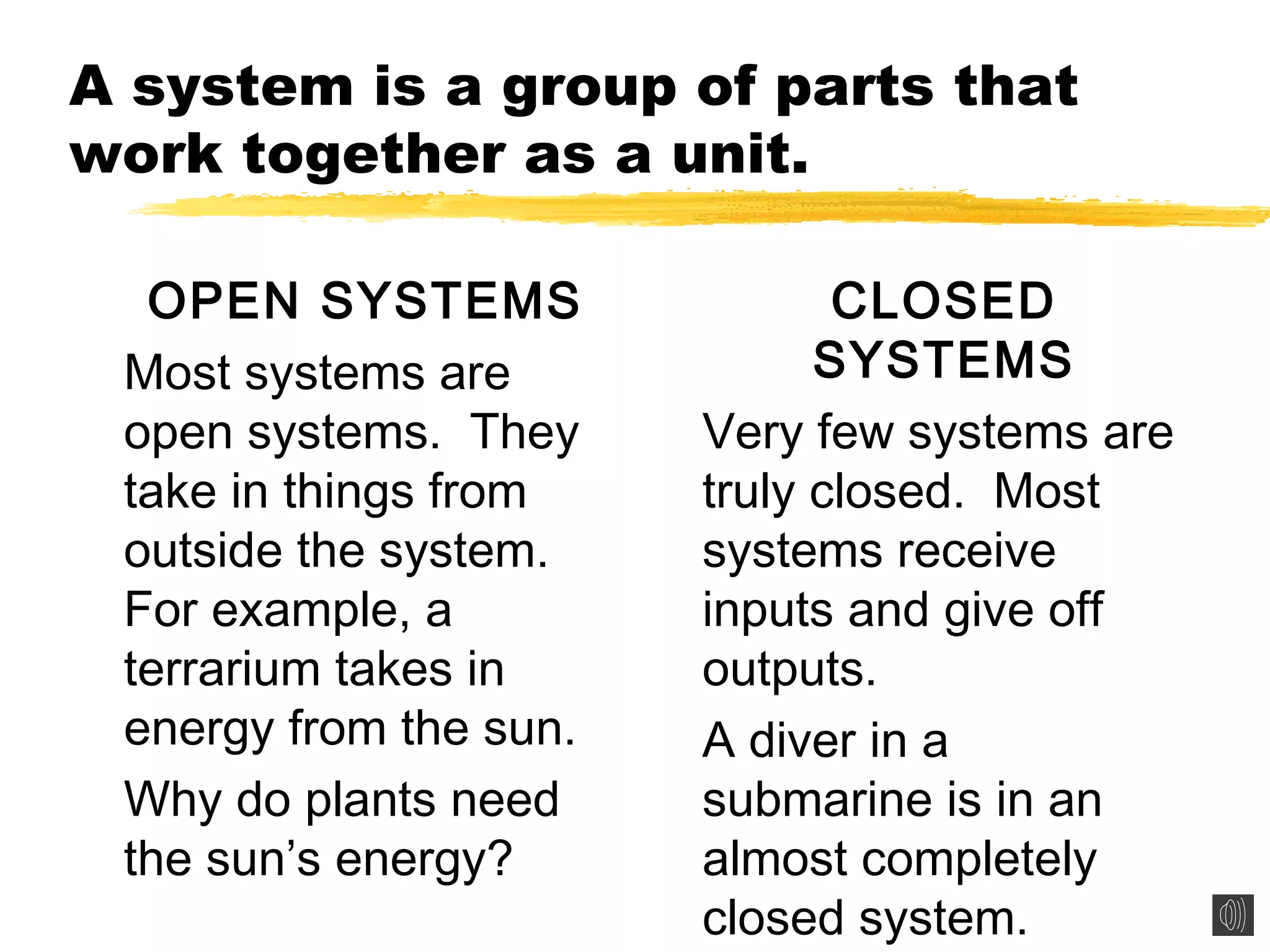
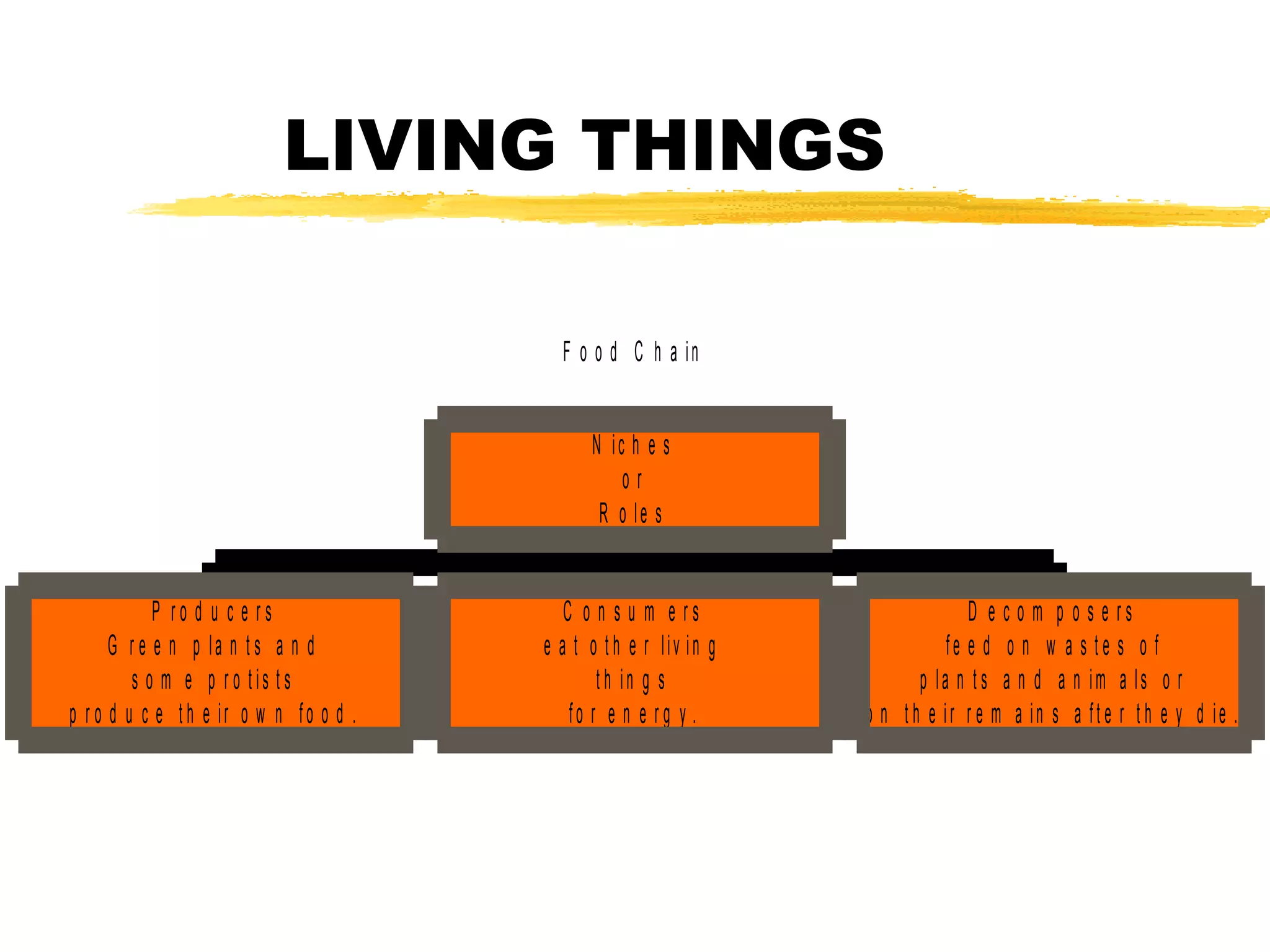
This document discusses ecosystems and their components. It defines a system as a group of parts that work together, and notes that most systems are open systems that take in inputs from outside. It explains that an ecosystem is a group of living things and their environment. Key parts of ecosystems include populations (groups of the same species), communities (all populations in an area), habitats (an organism's environment), and niches (an organism's role). Food chains and webs show how organisms fulfill different roles as producers, consumers, and decomposers within an ecosystem.