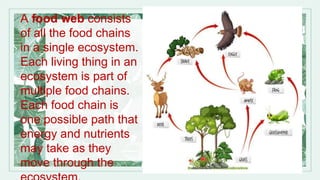
An ecosystem is a community of living things that interact with each other and their physical environment. It can include plants, animals, fungi, bacteria and other organisms as well as non-living elements like weather and landscape. Ecosystems provide environments for organisms to live and they maintain balance through complex interconnections between living and nonliving components. Examples of ecosystems discussed include deserts, tundra, rainforests, oceans, savannas and swamps.