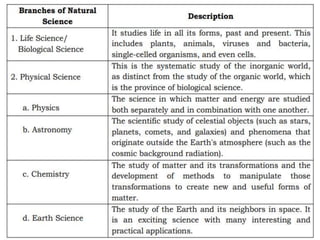
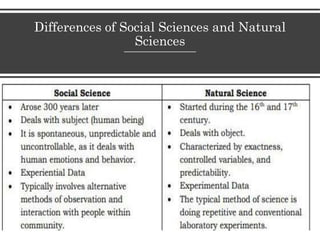
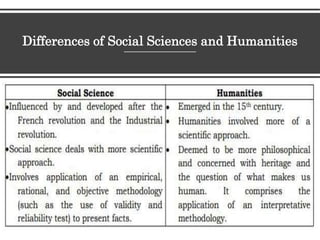
The document discusses the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. It defines social science as fields that study human group life and society, and lists its main disciplines as anthropology, economics, geography, history, political science, sociology, and psychology. Natural science is defined as using empirical methods to study natural laws. The humanities use analytical and critical methods to examine the human condition and include fields like history, literature, and philosophy. The document also compares social sciences to natural sciences and humanities, noting similarities and differences in their approaches and subjects of study.