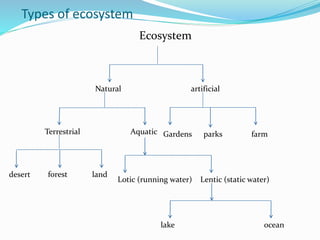
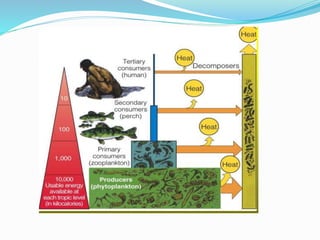
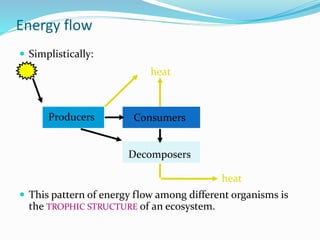
An ecosystem comprises both biotic (living organisms) and abiotic (non-living factors) components that interact to form a complex environment. It includes various types, such as terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, which function through energy flow, productivity, and biogeochemical cycling. Within these ecosystems, organisms are classified into producers, consumers, and decomposers, each participating in trophic levels that illustrate energy transfer and food relationships.