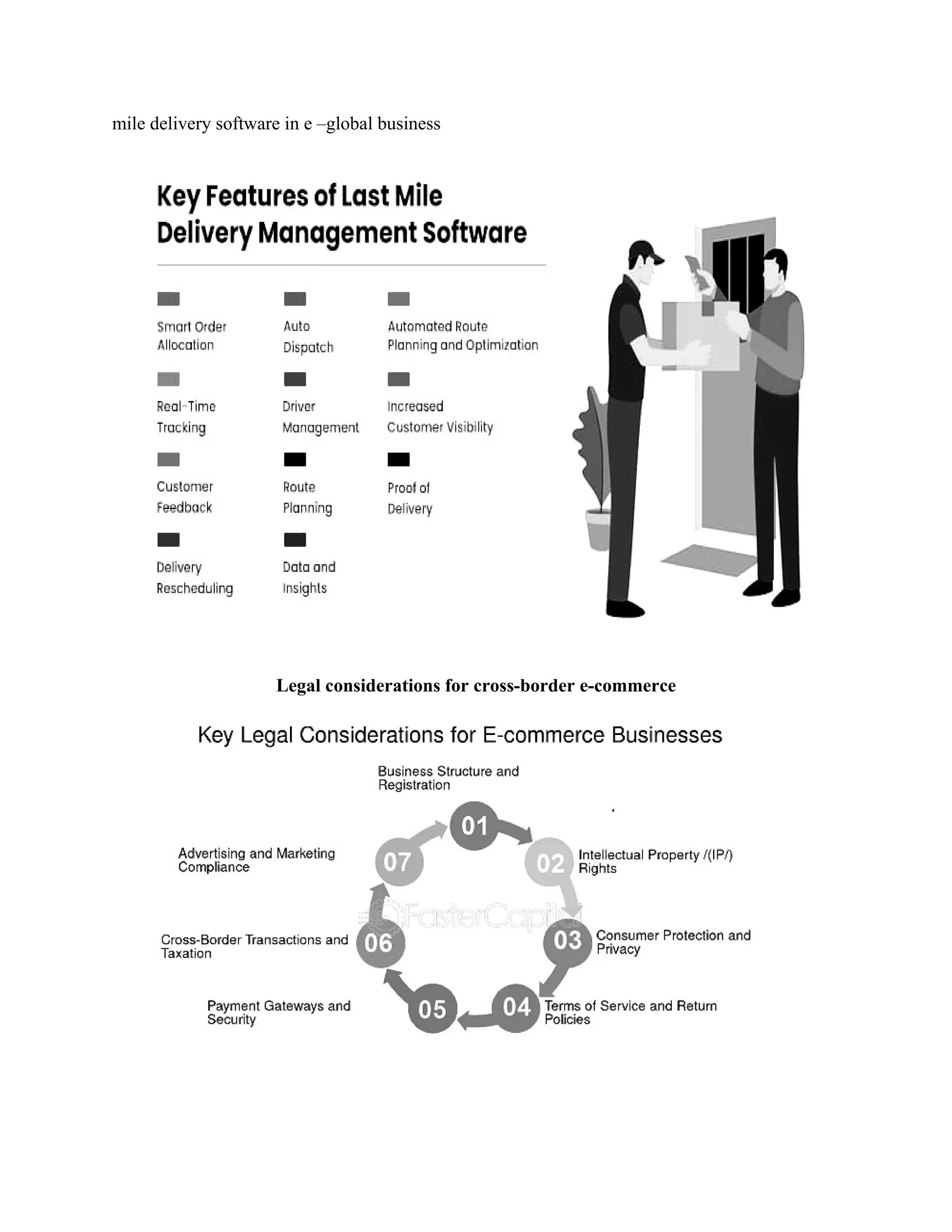
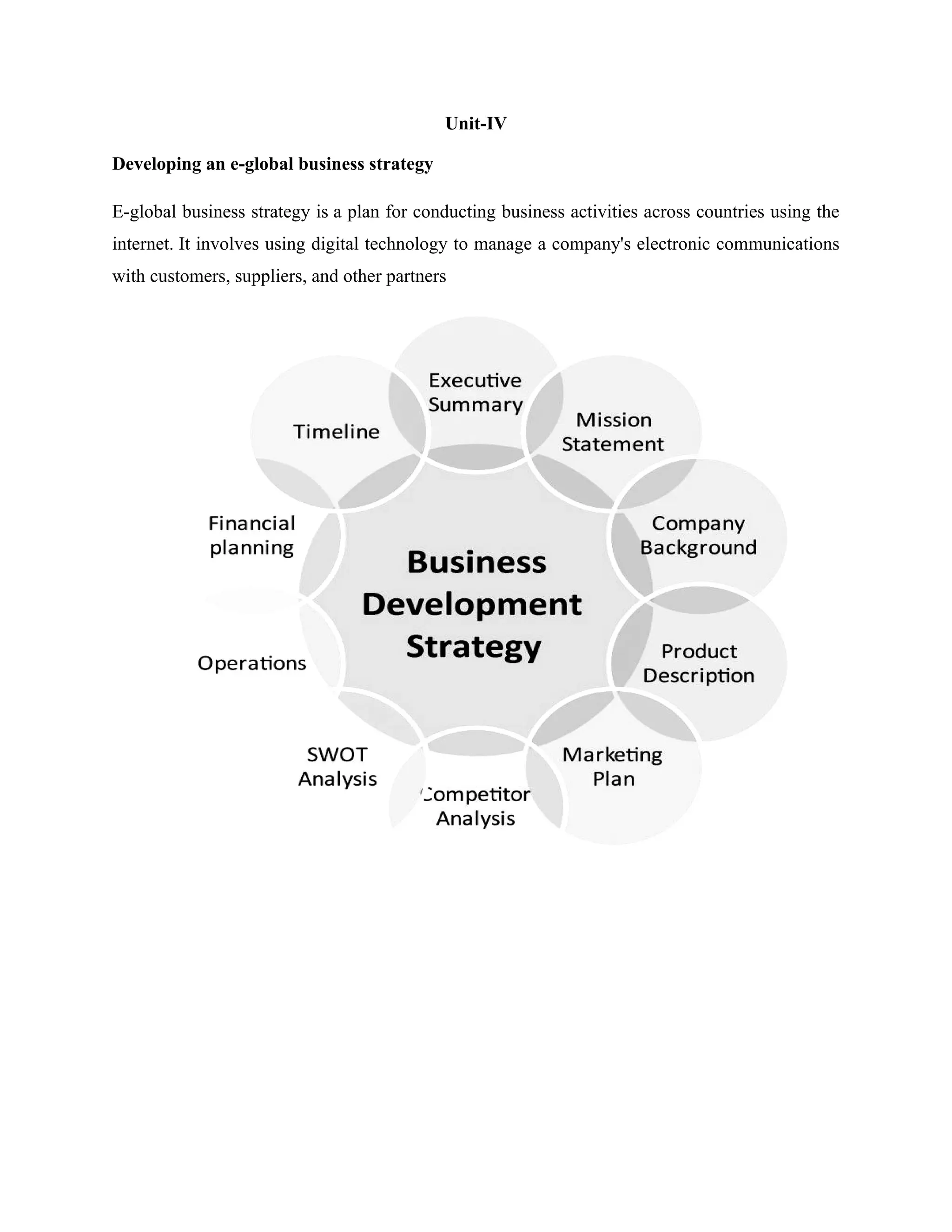
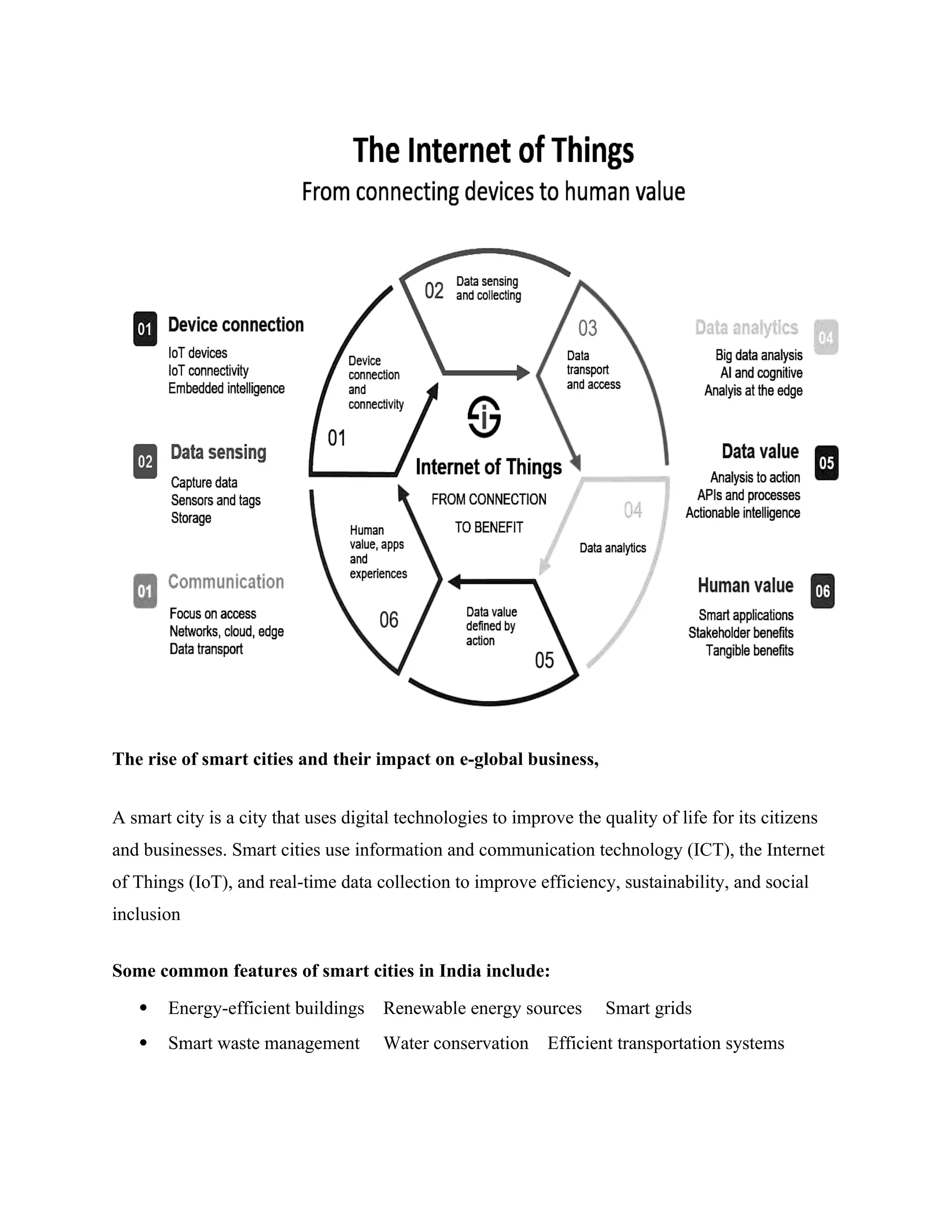
The document presents a comprehensive overview of e-global business, focusing on the fundamentals of e-commerce, its impact on global operations, and the integration of digital technologies in business practices. It outlines the legal requirements for e-commerce in India, innovations driving the industry, and the significance of customer engagement and digital marketing strategies. Additionally, it touches on challenges and the evolving landscape of cybersecurity and social media’s influence on business dynamics.






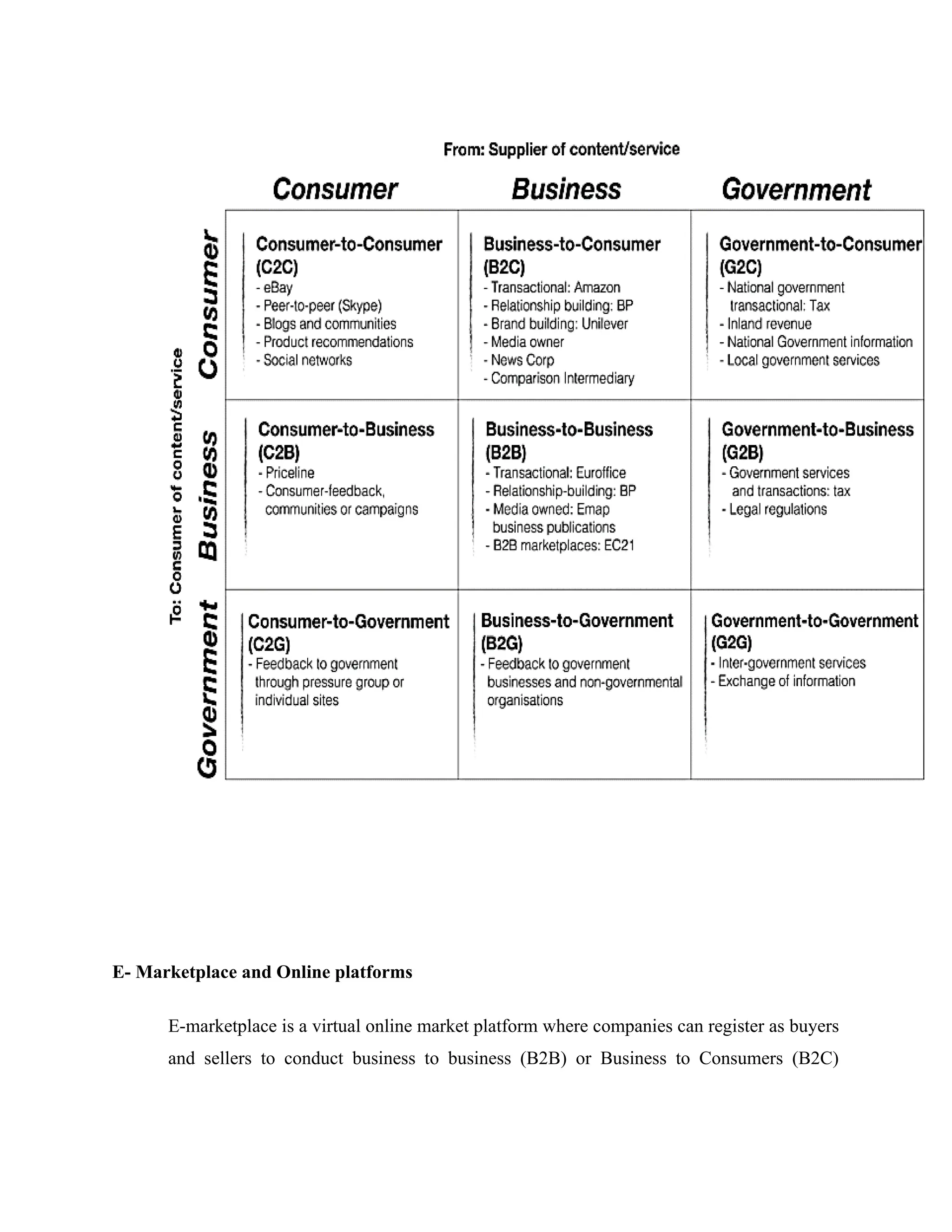
![Through electronic marketplaces, firms can collaborate effectively, forecast demand, and share
strategic information across companies. If firms want to participate in electronic marketplaces
fully, they must initially integrate internal and external supply chain activities
Role of artificial intelligence in e business
Artificial intelligence
What is artificial intelligence? Artificial intelligence (AI) is the ability of a computer or a robot
controlled by a computer to do tasks that are usually done by humans because they require
human intelligence and discernment
AI plays a crucial role in e-commerce by enabling businesses to analyze and understand
customer behavior patterns, enhance the shopping experience, and streamline various processes.
AI can help in product recommendations, chatbots, personalized promotions, fraud detection,
and more.
Legal Requirements of E-commerce business in India
Company or LLP Registration-[Limited liability partnership]
Every business is required to get registered with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs under the
applicable laws. Such a business shall either be incorporated under the (Indian) Companies Act,
2013 or a foreign company or an office, branch or an agency outside India and necessarily be
owned or controlled by an Indian resident. Such registration ensures that the bank account is
opened in the name of the company/ LLP which in return shall make the process of GST
registration convenient and quicker.
2. GST Registration
For a successful establishment of an E-commerce business, GST registration is mandatory. Every
E-commerce business irrespective of its turnover is required to be compulsorily registered under
the Central Goods & Service Tax (CGST) Act.
3. Bank Account
Opening a bank account in the name of the business is a convenient process. In case of a
Proprietorship firm, the first step is to obtain a GST registration in the name of the business in](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e-globalbusiness-finalnotes-241205103055-b1ac8f0e/75/Lecture-notes-for-the-subject-of-E-Global-Business-7-2048.jpg)


![3. AI-Powered Personalization Leads generated by AI are boosting sales by 50%. Top-rated
firms tailor their advertising with AI 28% of the time. Here are some benefits of AI.
4. Voice-Powered Shopping
Voice-powered shopping is an emerging trend in e-commerce. According to a study, 51% of
mobile buyers look up things using their voice assistants. Here’s how it can be advantageous –
5. Shopping using AR Technology-[Augmented Reality]
Enables customers to visualize products using their smartphones or tablets in a real-world
environment.
Shopping using AR technology is an emerging trend in e-commerce that has the potential
to revolutionize the way customers shop and interact with retailers.
6. Blockchain Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording
transactions and tracking assets in a business network. An asset can be tangible or intangible
8. Chatbots
A chatbot is a software application or web interface that aims to mimic human conversation
through text or voice interactions
9. Social Commerce
Social commerce (a subset of ecommerce) is the use of social media platforms like Facebook and
Instagram to market and sell products and services. This type of selling model lets customers
11. Remarketing
Remarketing is a powerful tool for e-commerce innovation that allows you to target customers
who have previously shown interest in your products or services.
12. Website Analytics
Web analytics is the collection, reporting, and analysis of website data.
13. E-wallet](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e-globalbusiness-finalnotes-241205103055-b1ac8f0e/75/Lecture-notes-for-the-subject-of-E-Global-Business-10-2048.jpg)









![ Free Lifetime Access to Basic Product or Service Plan
Collaborative consumption or sharing economy
Collaborative consumption is considered part of the sharing economy, Collaborative
consumption is the shared use of a good or service by a group. Collaborative
consumption differs from conventional consumption in that resources, goods, or services
are shared by a group rather than individuals. Ex: Airbnb, Airbnb,[Air Bed and
Breakfast,” is a service that lets property owners rent out their spaces to travelers looking
for a place to stay]and ride-sharing applications, car pooling
Benefits of the collaborative economy
Greater supply: Individuals who market goods and services increase options for people
looking to travel or buy items like household appliances, clothing and bicycles.
Savings: The items we find in collaborative consumption businesses are usually cheaper.
Sustainability: This exchange between consumers increases the useful life of the items
we buy. Because we reuse them, there’s no need to manufacture new things.
Care for the environment: Choosing services like collaborative transport and giving
new life to used items to prevent overproduction and use finite resources more efficiently
helps us care for the environment.
Digital marketing
Digital marketing, also called online marketing, is the promotion of brands to connect with
potential customers using the internet and other forms of digital communication. This includes
not only email, social media, and web-based advertising, but also text and multimedia messages
as a marketing channel.
Digital marketing strategies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e-globalbusiness-finalnotes-241205103055-b1ac8f0e/75/Lecture-notes-for-the-subject-of-E-Global-Business-22-2048.jpg)