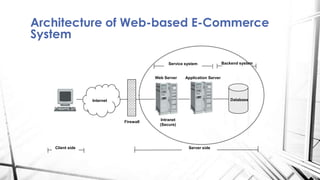
E-commerce refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over the Internet. It includes business-to-business transactions (B2B), business-to-consumer transactions (B2C), consumer-to-consumer transactions (C2C), and consumer-to-business transactions (C2B). E-commerce provides benefits like lower costs, larger catalogs, and improved customer interactions for businesses and greater access, selection, and convenience for consumers. However, it also faces limitations such as security issues, lack of standards, and threats to privacy.