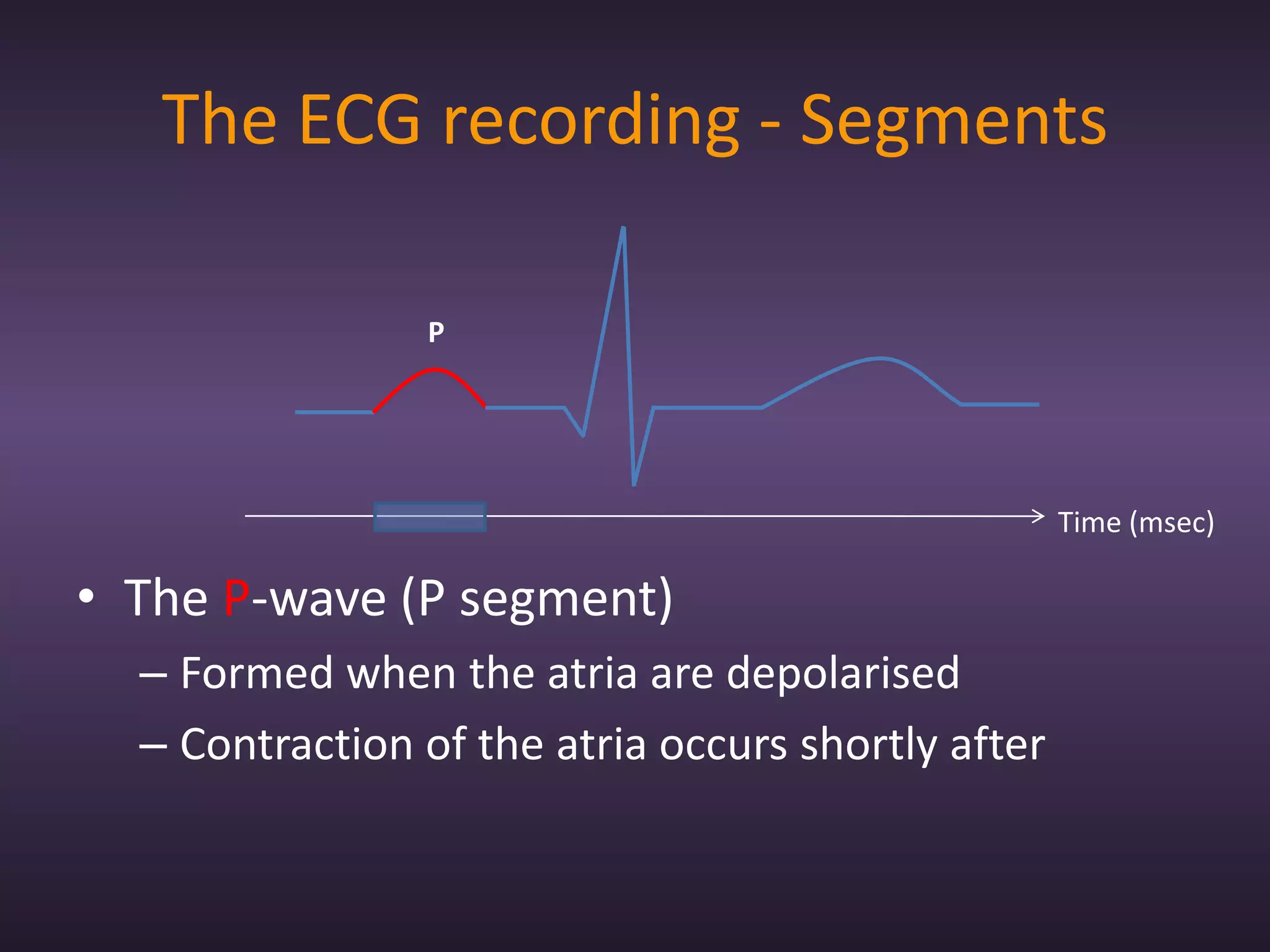
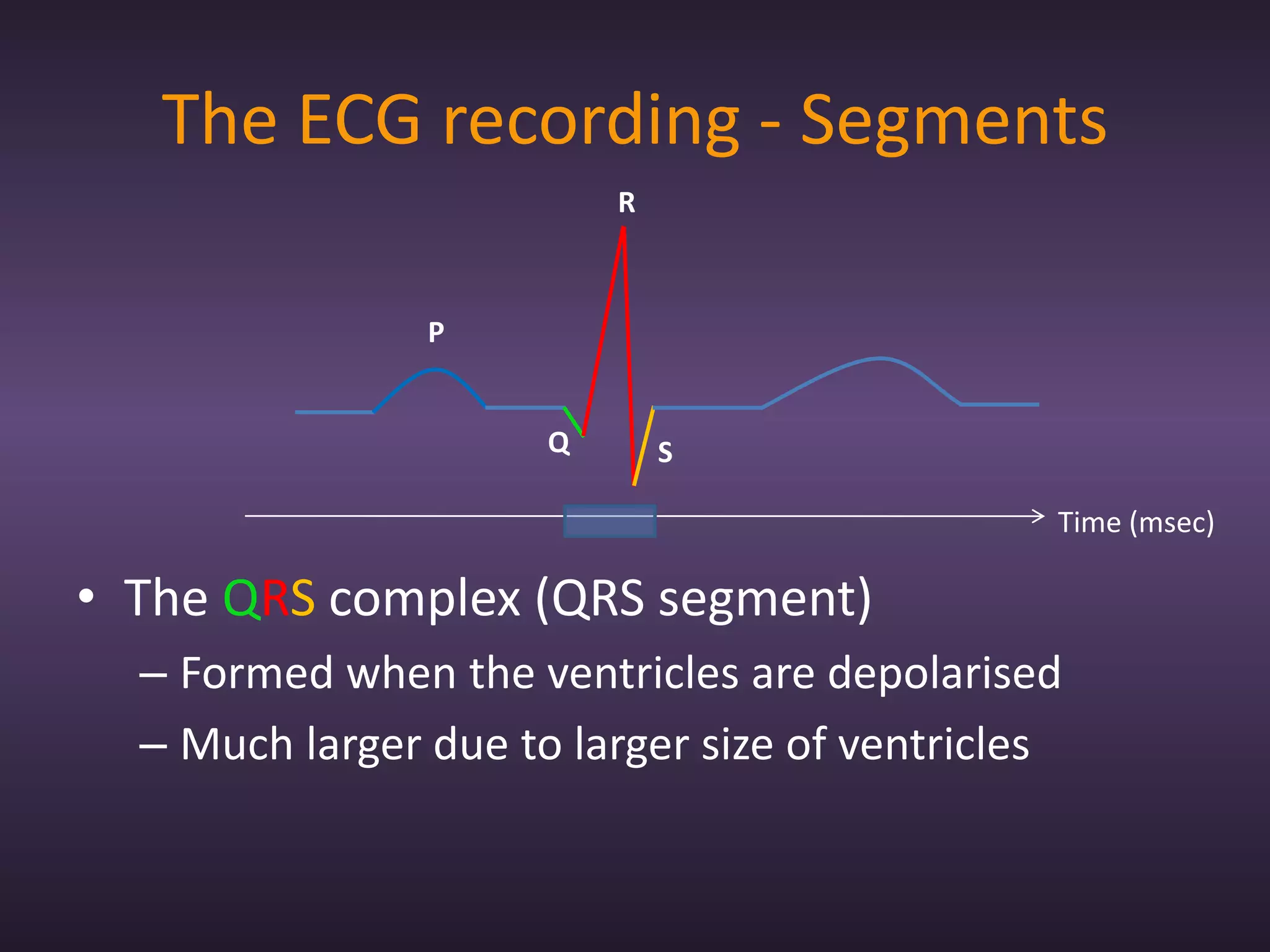
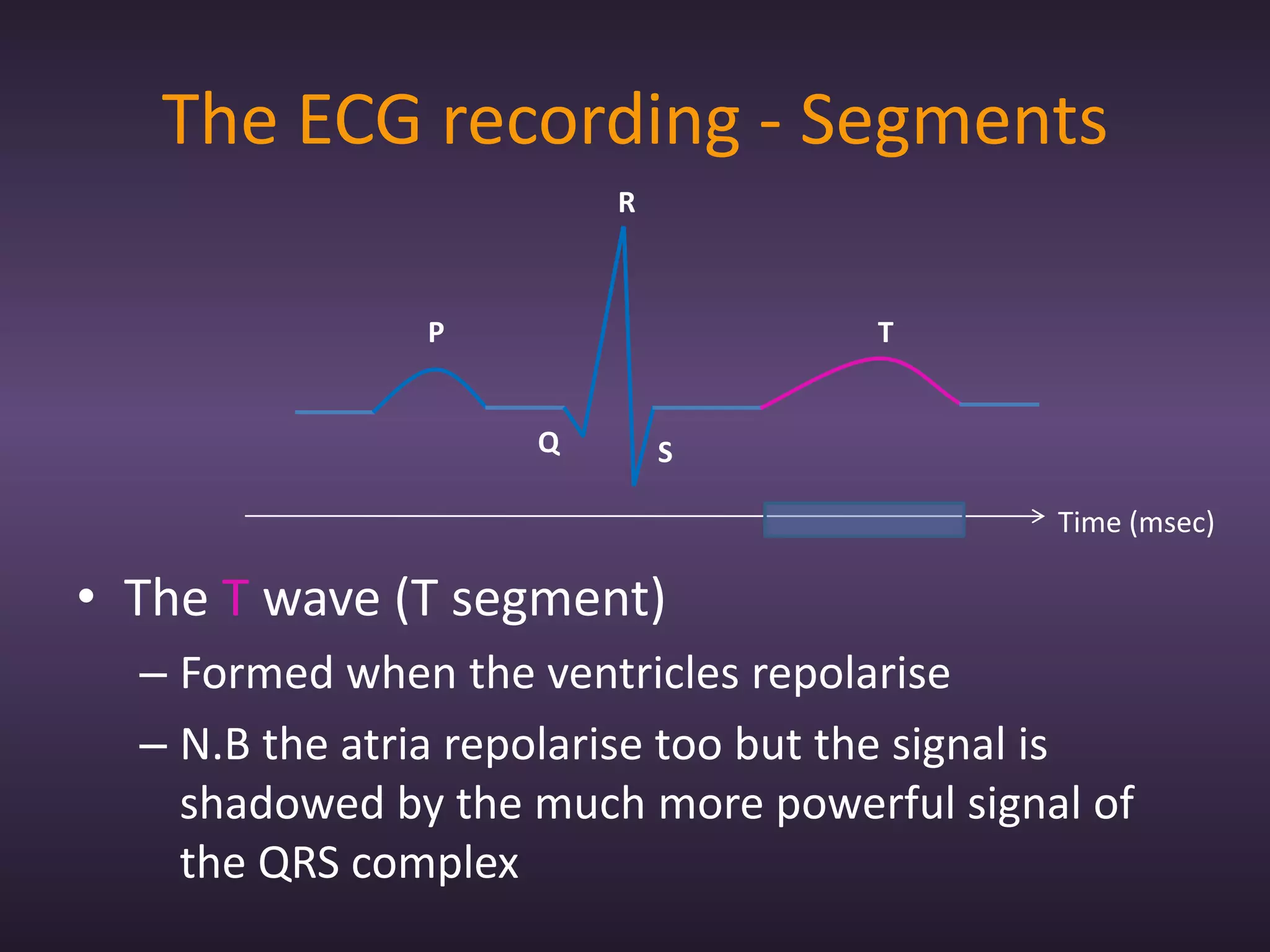
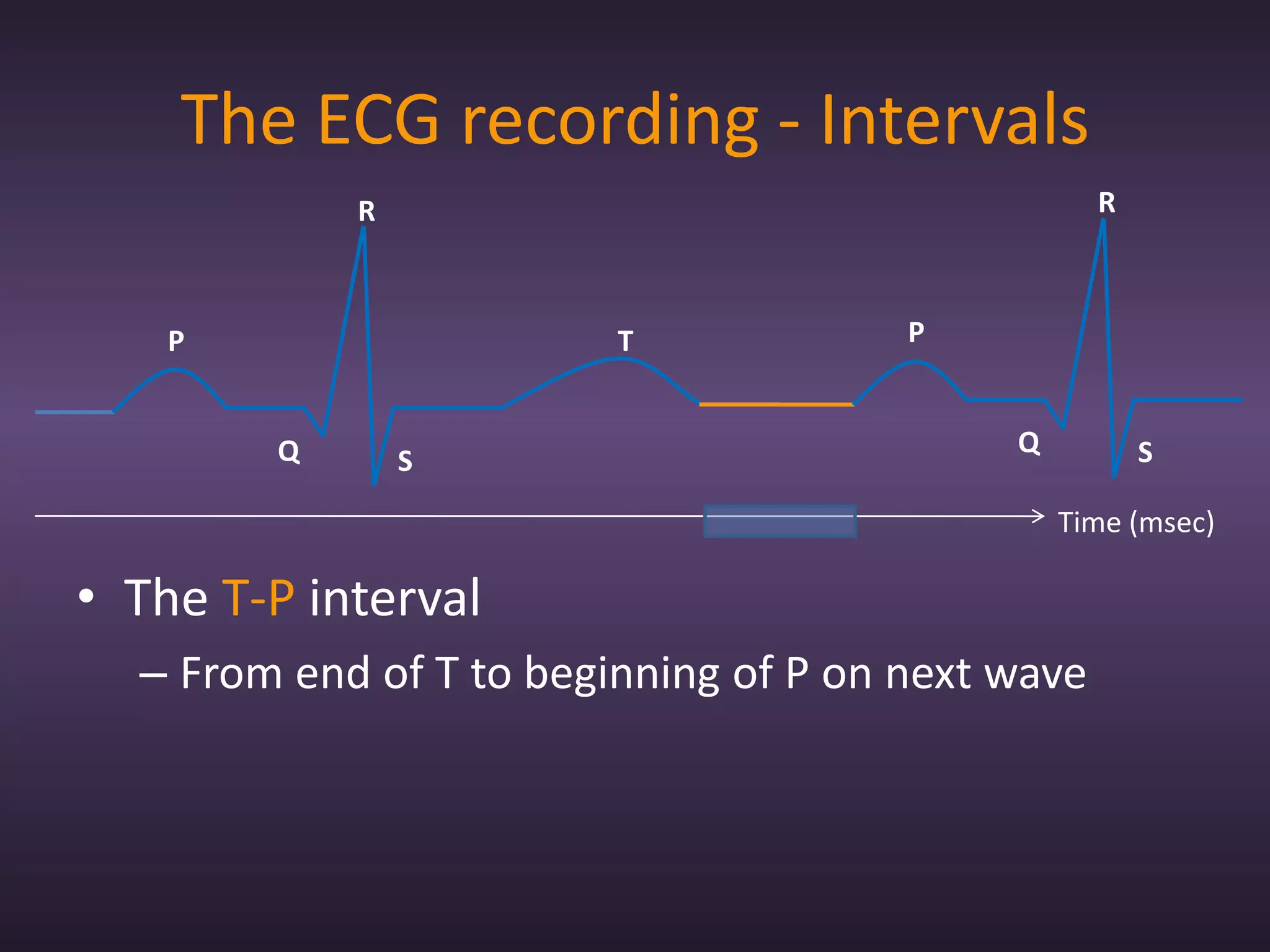
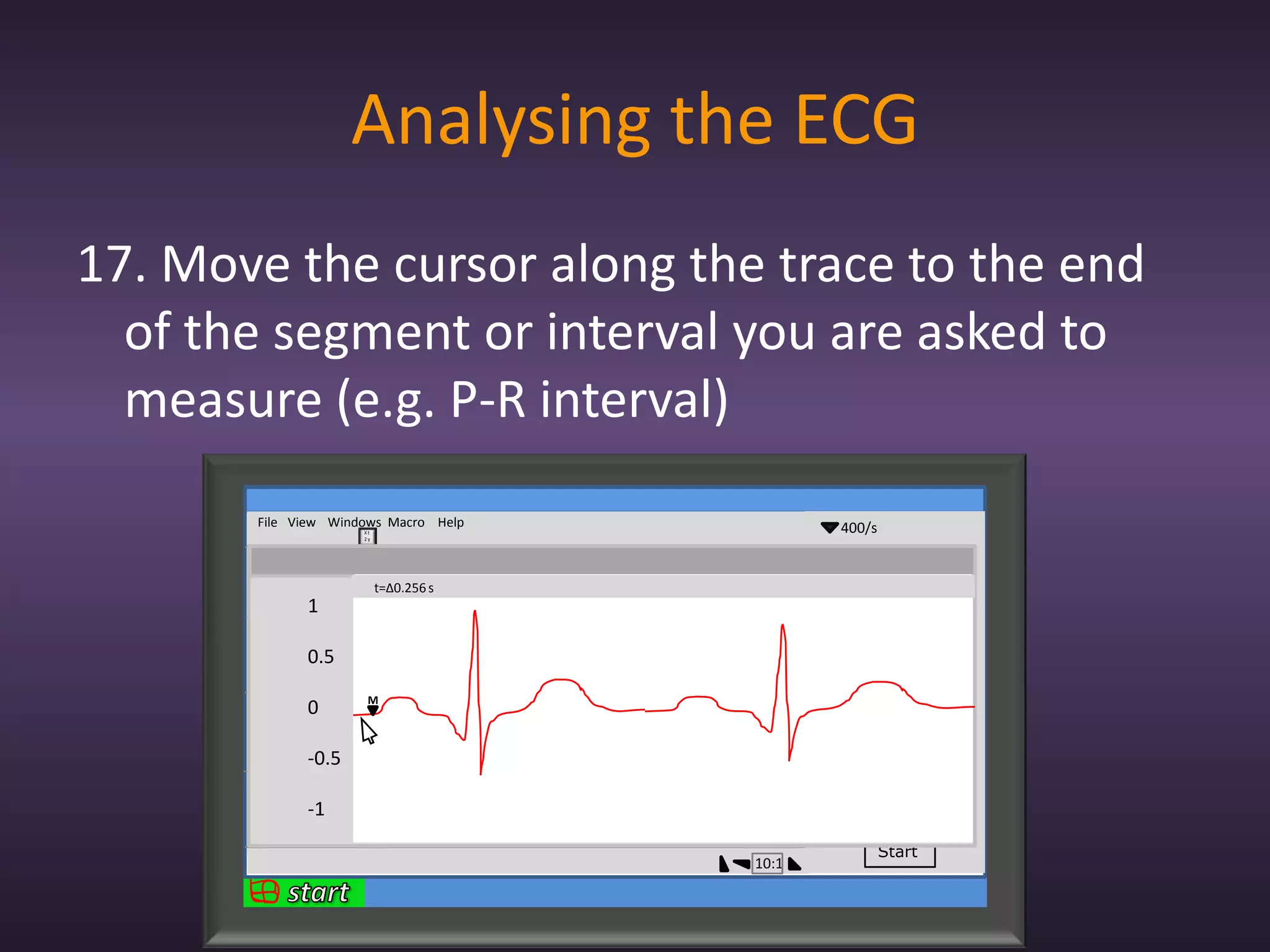
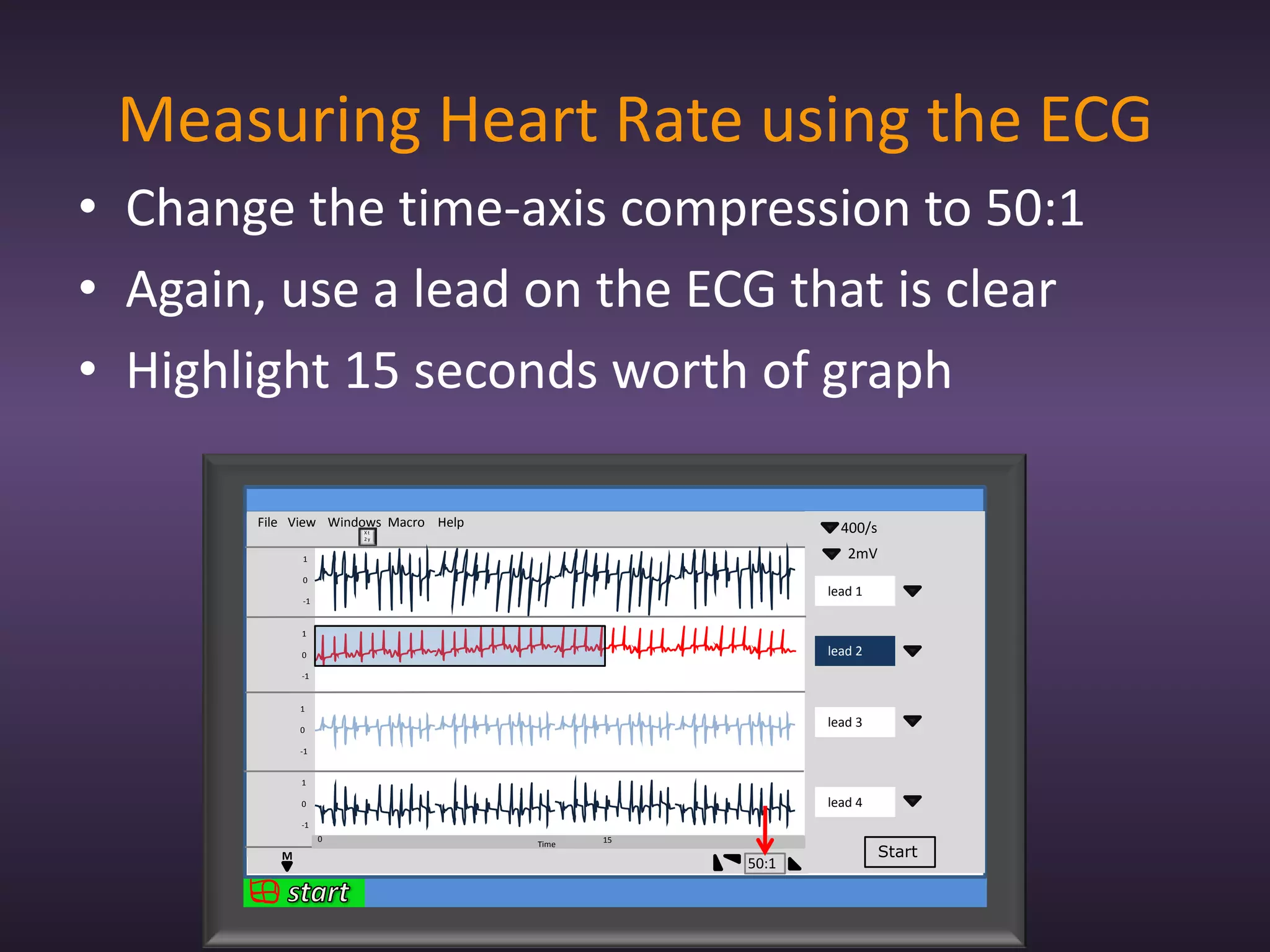
The document provides information about recording and interpreting an electrocardiogram (ECG). It describes how the ECG works by recording the heart's electrical activity. It outlines the 18 step procedure for performing an ECG exam, including preparing the patient, attaching electrodes, taking a recording, and analyzing segments and intervals. Key aspects like measuring heart rate using a 15 second recording at 50:1 compression are also covered. The document aims to prepare students for the ECG station of an OSCE exam.