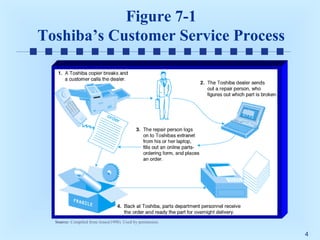
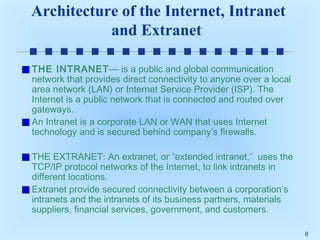
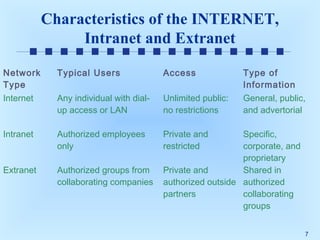
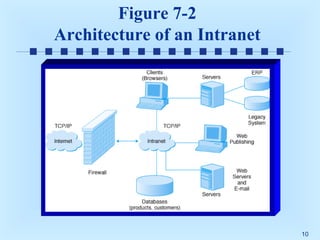
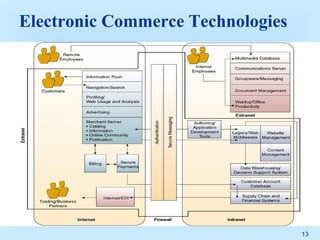
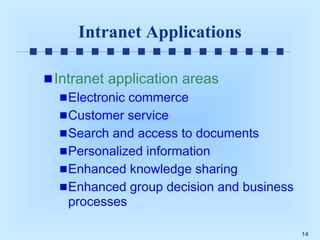
This document discusses intranets and extranets at Toshiba America and provides information on their architecture and applications. It describes how Toshiba created an online order system for its 300 dealers using an extranet/intranet to allow orders until 5pm for next-day delivery. It also explains that an intranet is a private network within a company that uses internet technology, while an extranet links intranets of different companies through a secured connection. The document outlines benefits of intranets and extranets like improved communication, productivity and cost reductions.