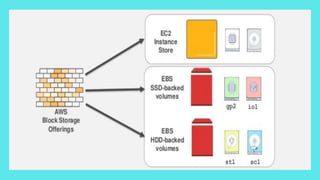
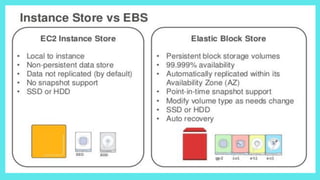
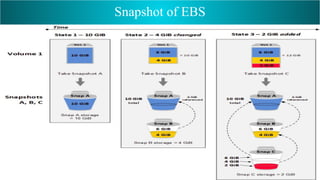
EBS (Elastic Block Store) provides block-level storage volumes for use with EC2 instances. EBS volumes behave like physical hard drives attached to instances and can persist independently from the life of an instance. EBS volumes are placed in Availability Zones and automatically replicated within the same zone for availability. Snapshots of EBS volumes can be taken and stored in S3 for backup and long-term data durability.