The document discusses earthquakes, including what causes them, their effects, and how to prepare for and respond to them. Some key points include:
- Earthquakes are caused by movements of tectonic plates and can cause widespread damage and loss of life.
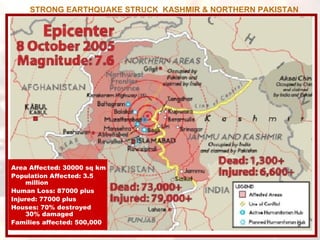
- Major historical earthquakes are described that caused extensive damage, such as in Kobe, Japan and Bhuj, India.
- Earthquakes can have secondary effects like tsunamis, land faults, fires, liquefaction, and epidemics.
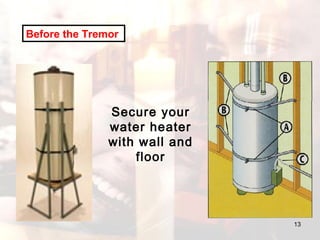
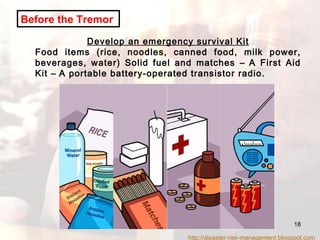
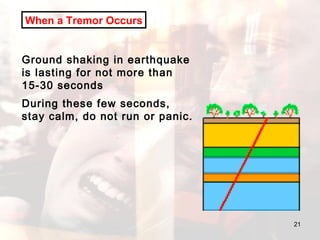
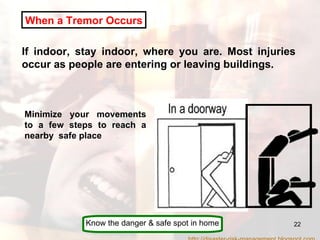
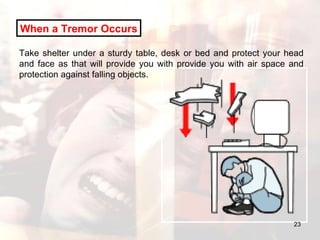
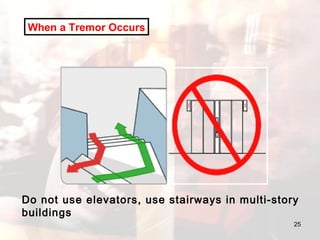
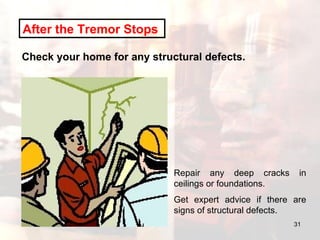
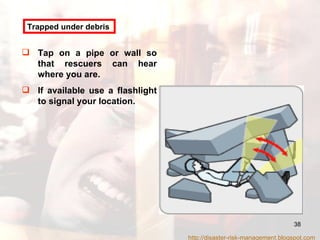
- Advice is provided on how to prepare for earthquakes and stay safe during and after shaking occurs.