Embed presentation
Downloaded 12 times

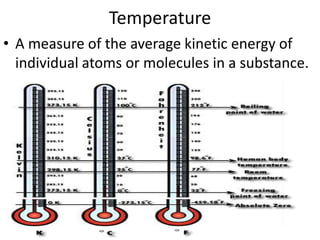
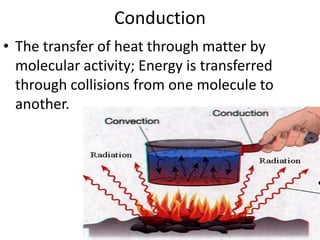
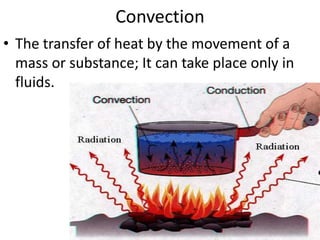
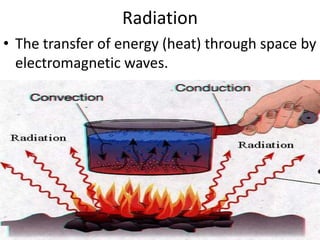


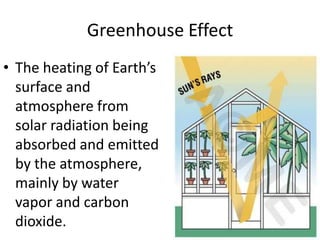


Conduction, convection, and radiation are the three major mechanisms of heat transfer. Conduction involves the transfer of heat through matter by molecular collisions. Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement of fluids. Radiation involves the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves in space. The greenhouse effect refers to the heating of the Earth's surface and atmosphere from solar radiation being absorbed and emitted by greenhouse gases like water vapor and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.










