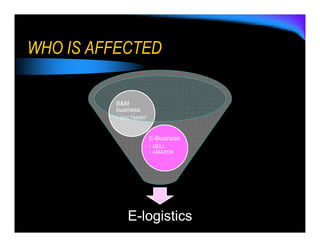
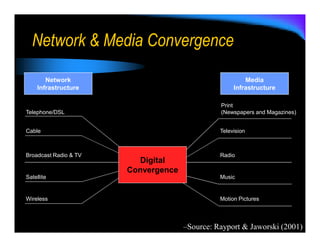
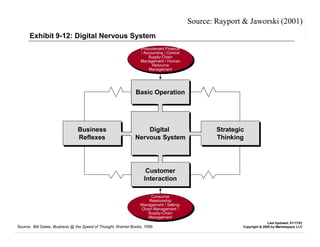
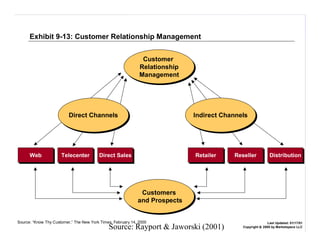
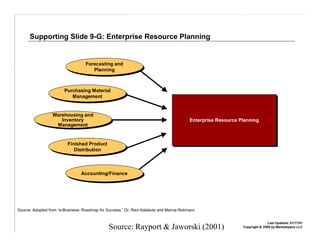
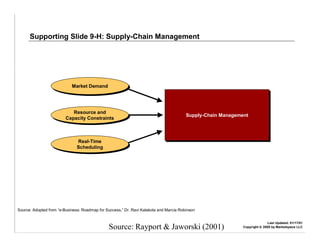
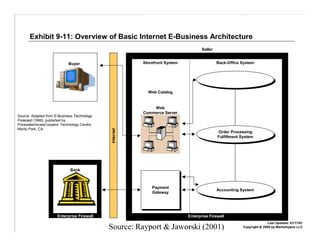
E-logistics combines the Internet and logistics. It allows for more integrated and efficient logistics processes through the use of Internet technologies. Key benefits include shorter order cycles, more reliable deliveries, and closer relationships between customers and logistics suppliers. E-logistics facilitates trends toward globalization, outsourcing, consolidation, and integration across the value chain in distribution and logistics.