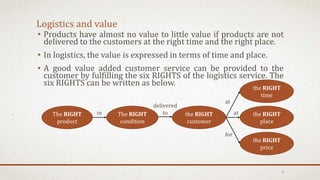
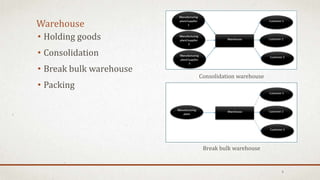
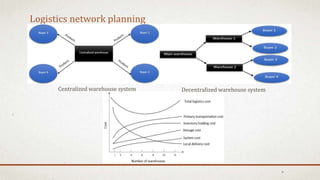
The document discusses logistics in manufacturing, highlighting its definitions, historical importance, and value in supply chain management. It examines in-house logistics and third-party logistics (3PL), detailing their benefits and drawbacks, as well as the functions and advantages of Transportation Management Systems (TMS). Furthermore, it emphasizes the significance of green logistics and the challenges faced in logistics management, concluding that effective logistics can significantly reduce costs and improve efficiency in manufacturing firms.