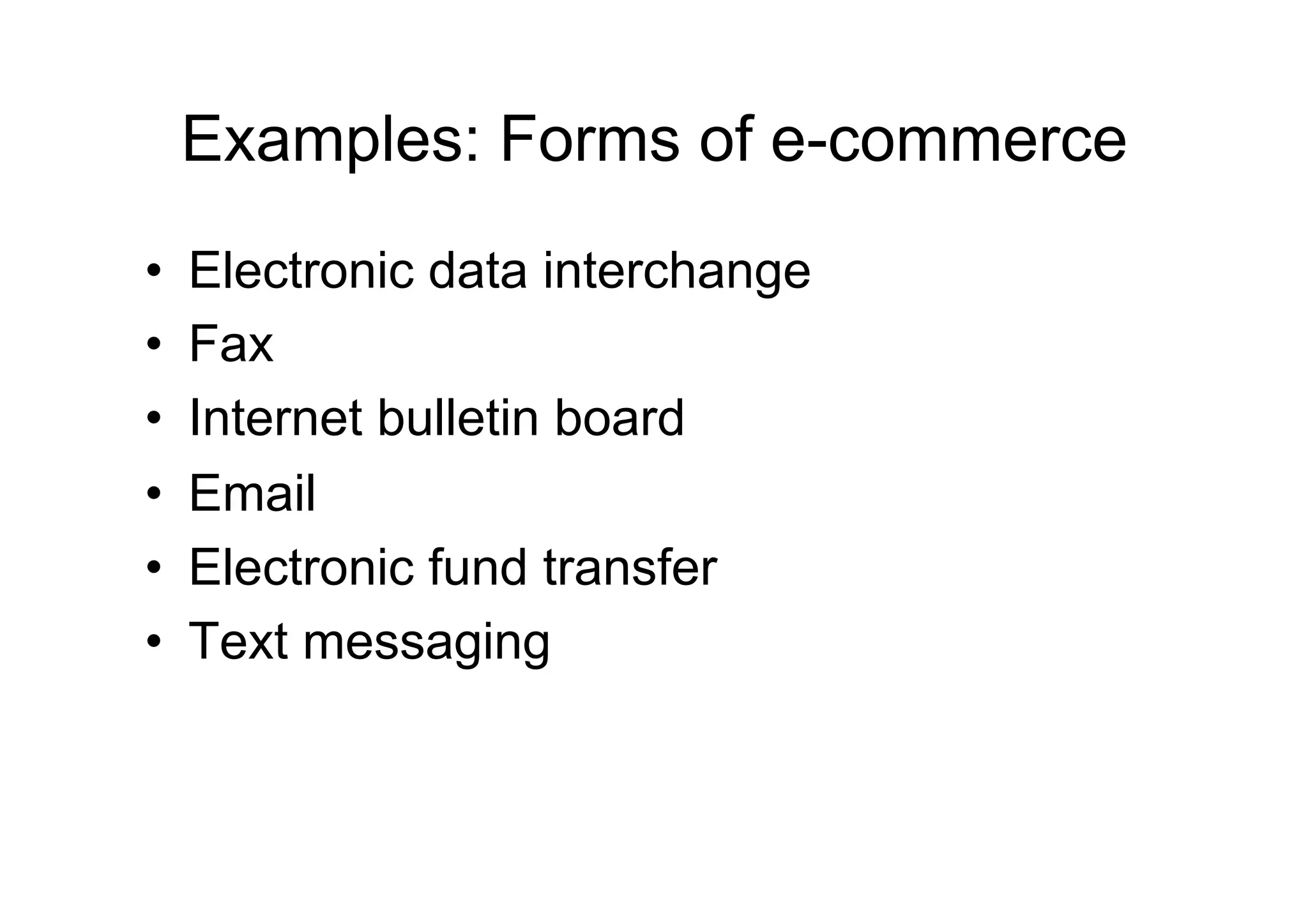
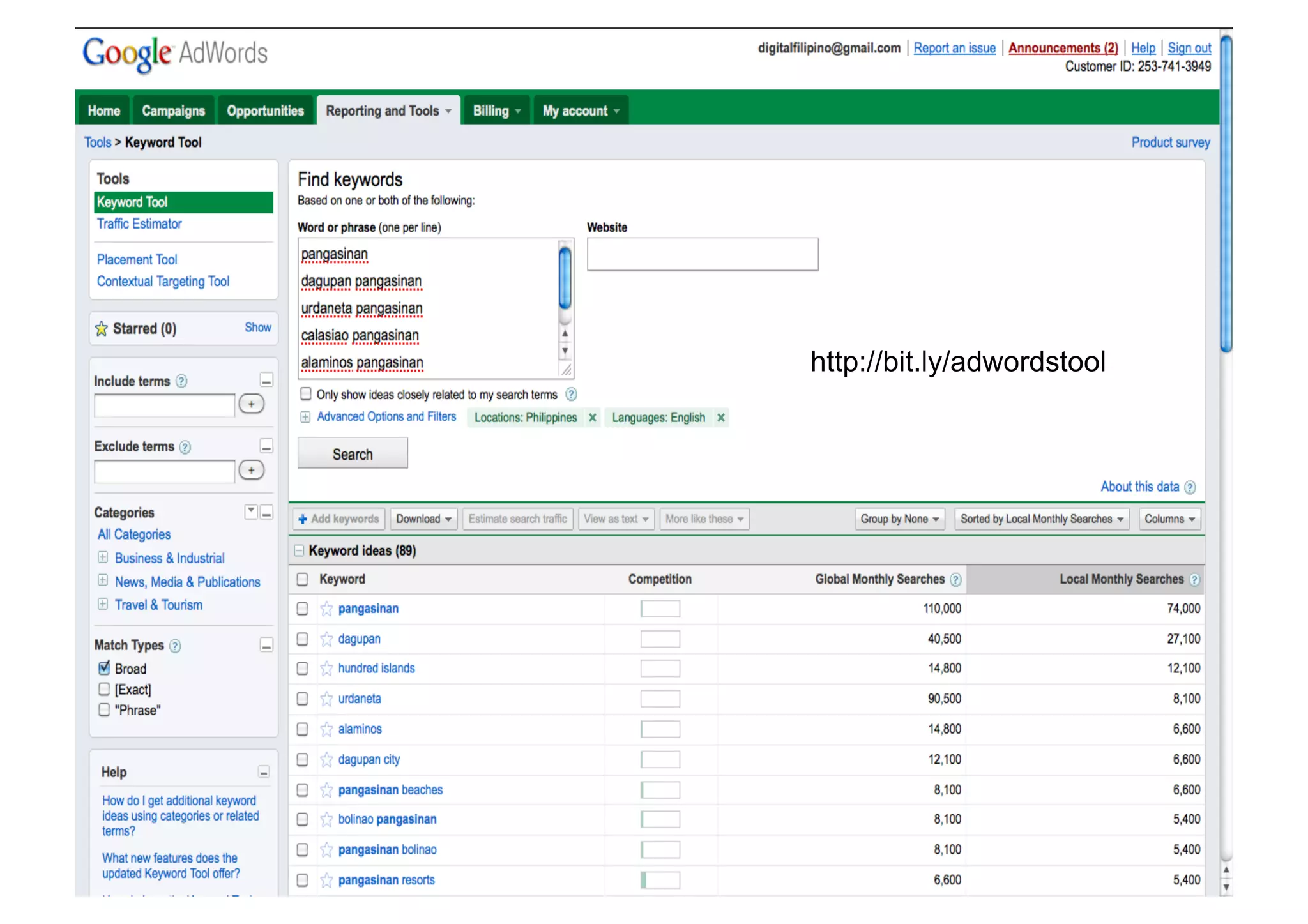
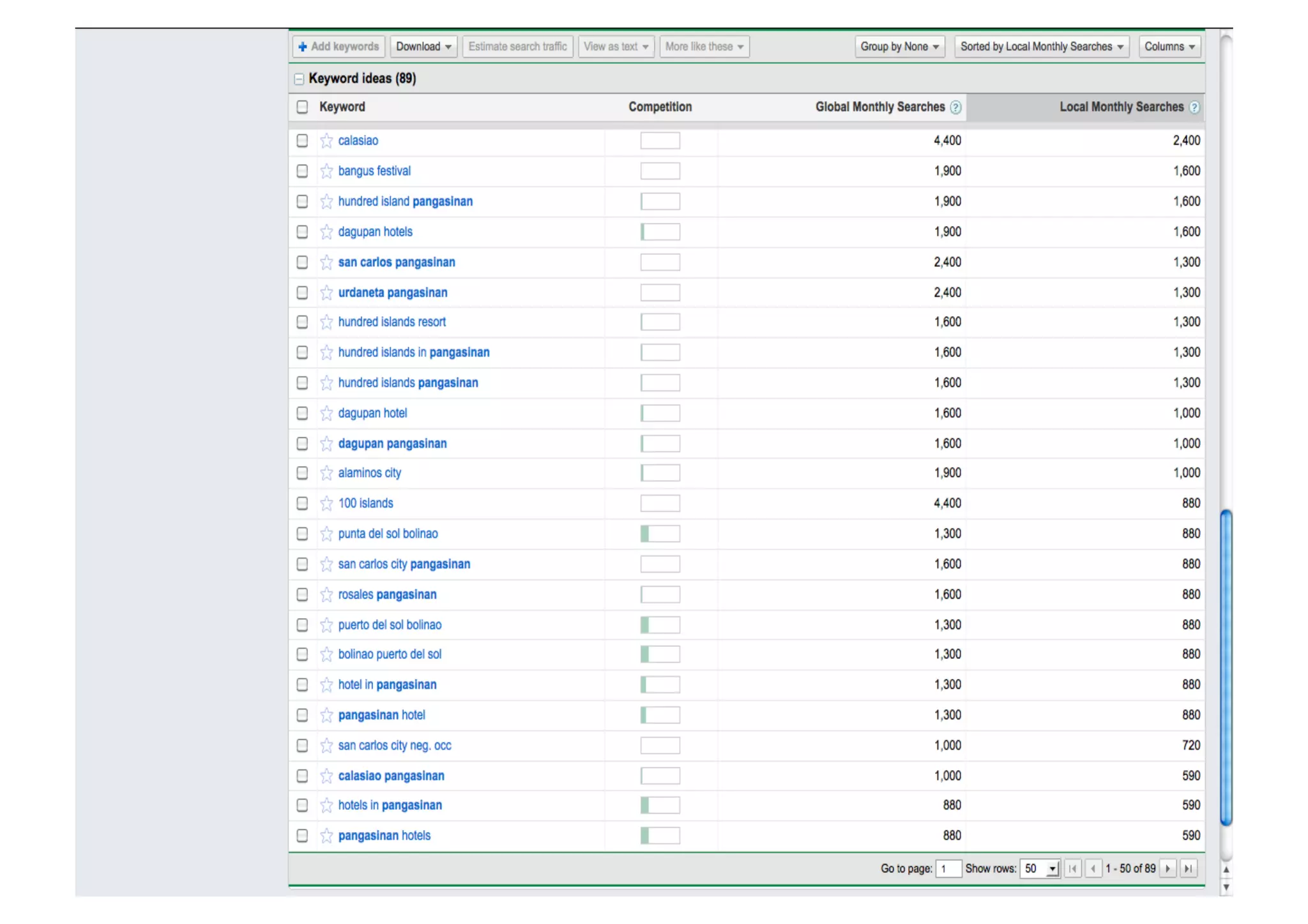
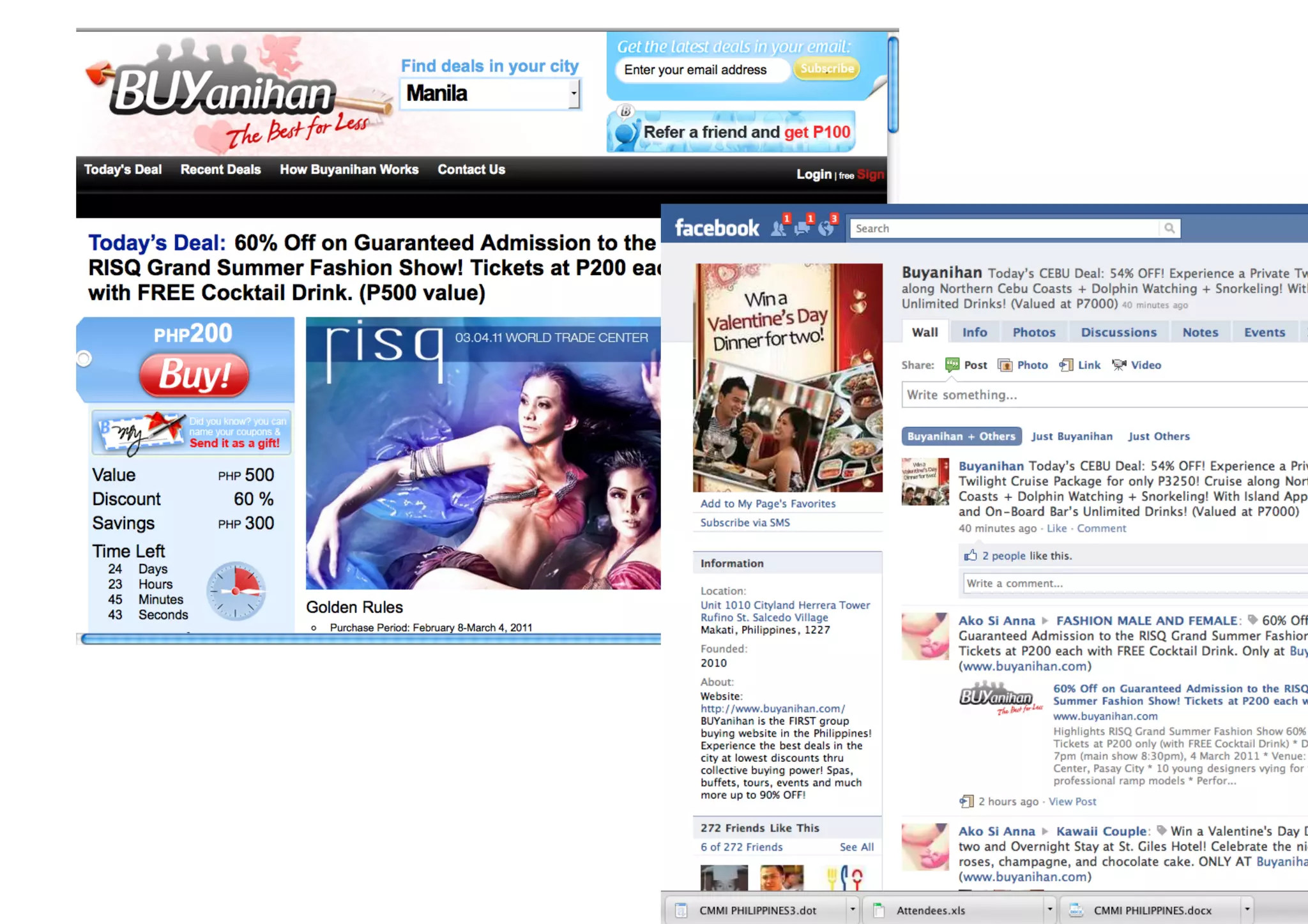
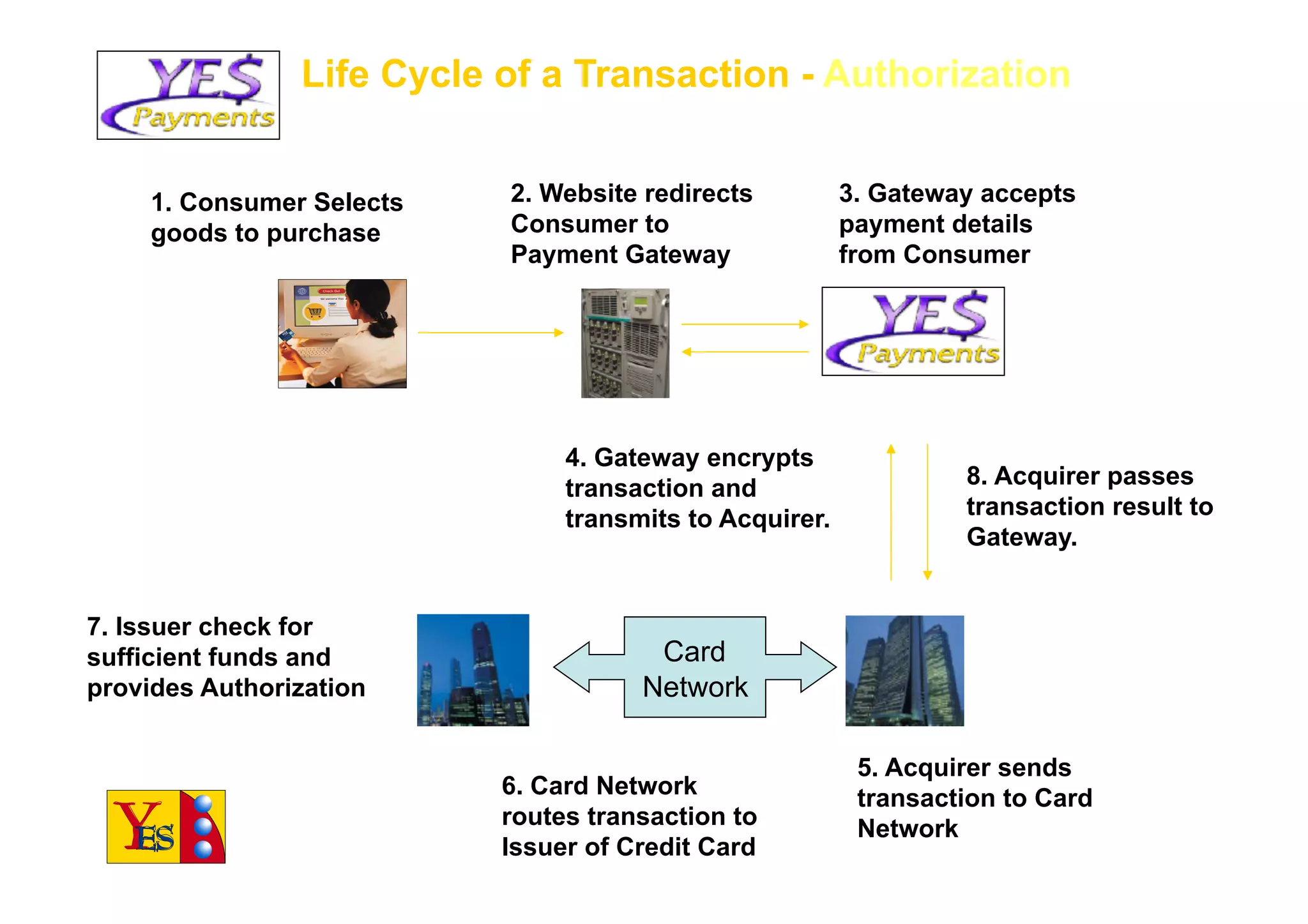
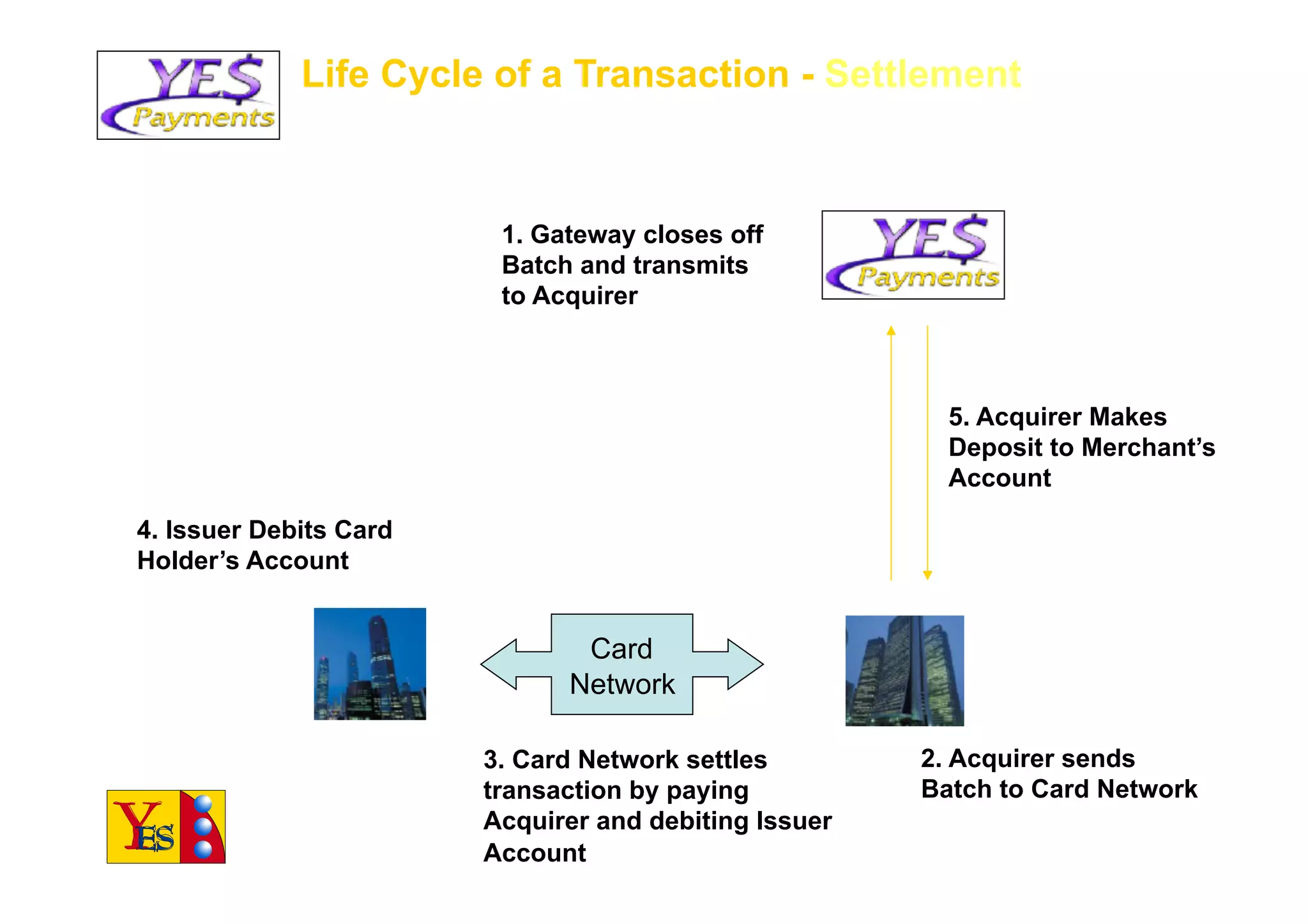
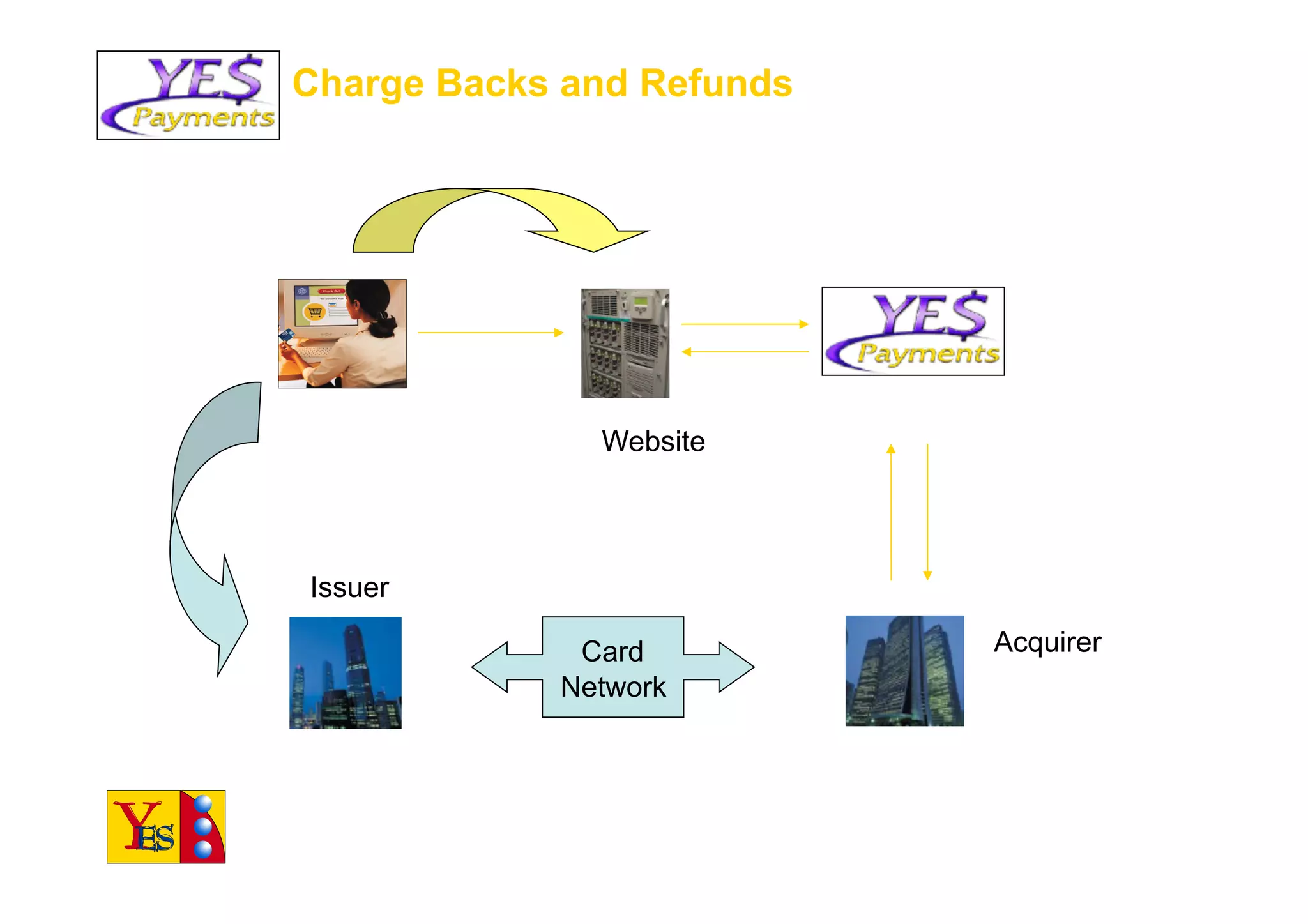
The document outlines the essentials of e-commerce in the Philippines, detailing its definition, legal framework, and types of transactions. It emphasizes the E-Commerce Law which provides legal recognition for electronic transactions and mandates government involvement in e-commerce development. Additionally, it discusses the rise of mobile commerce and provides insights into effective marketing strategies and consumer engagement within this digital landscape.