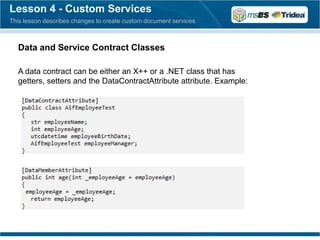
The document provides an overview of the Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Application Integration Framework (AIF), which has been renamed to 'services'. It outlines lessons on service groups, ports and adapters, infrastructure and deployment, custom services, web service consumption, data transformation, and using Office add-ins with Dynamics AX. Key improvements include enhanced configuration options, streamlined deployment processes, and integration capabilities with external web services.