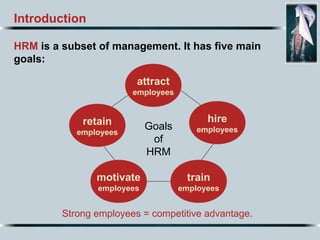
1. Human resource management (HRM) involves hiring, attracting, retaining, motivating and training employees to create a competitive advantage for organizations.
2. HRM must account for changing technologies, diverse workforces, globalization, and continuous improvement programs to empower employees.
3. Key HRM functions include staffing to recruit and select qualified employees, training and developing workers, motivating through performance reviews and compensation, and maintaining employee safety, communication and relations.