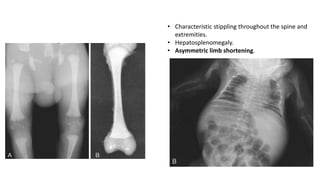
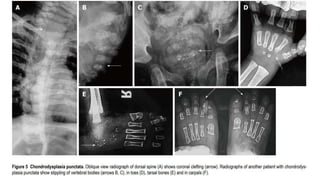
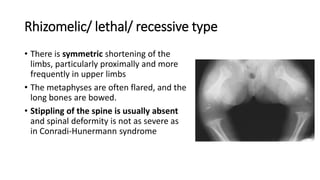
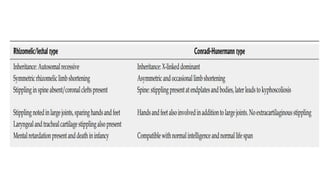
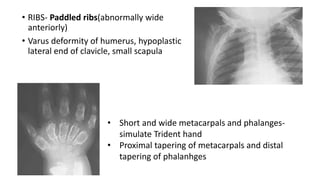
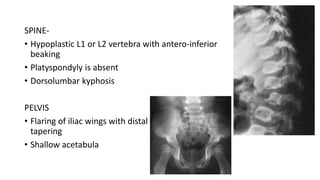
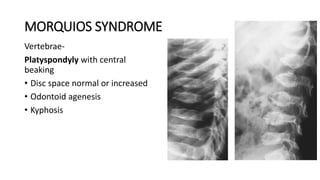
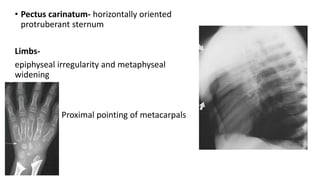
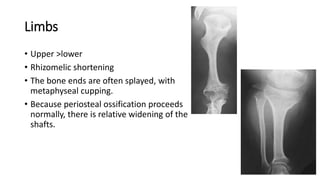
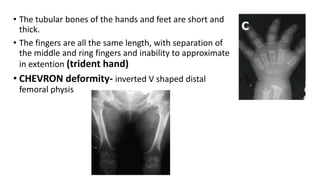
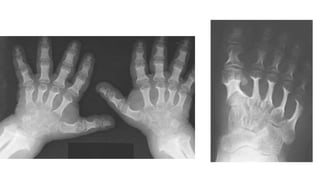
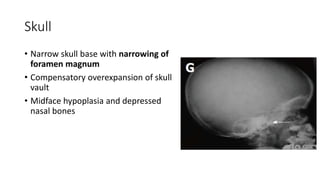
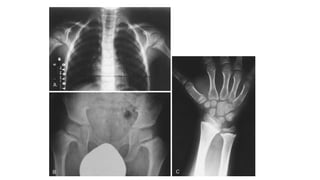
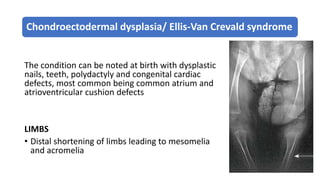
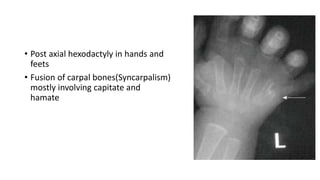
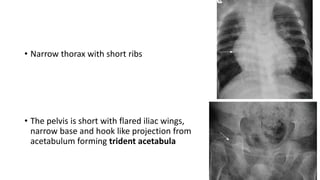
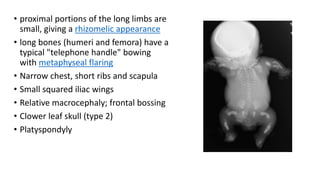
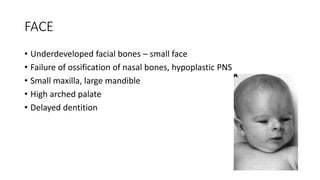
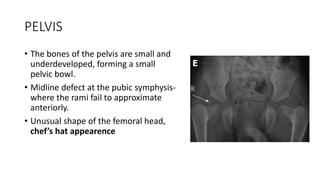
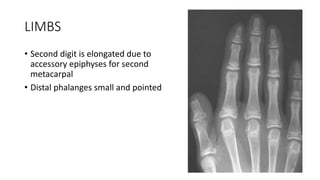
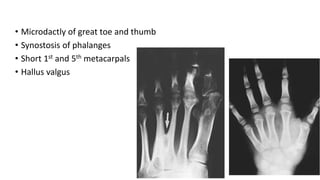
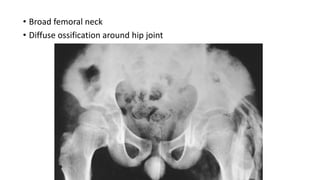
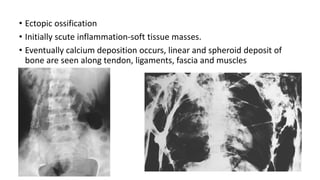
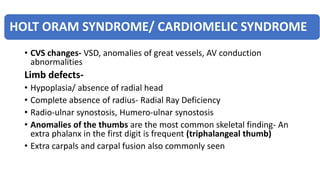
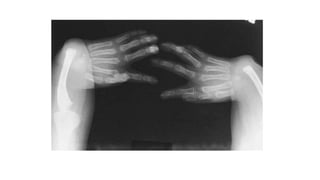
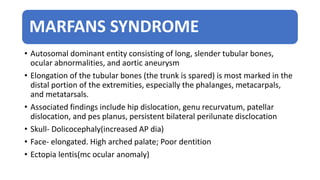
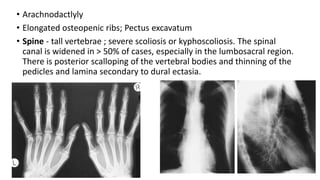
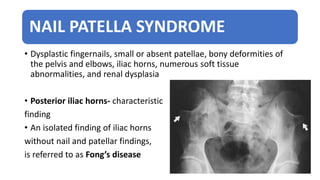
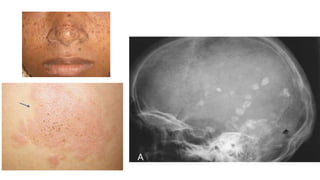
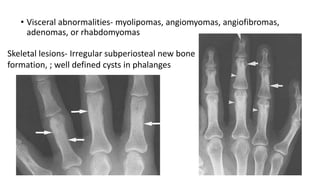
1. Skeletal dysplasias are abnormalities of bone and cartilage growth or texture that are evaluated using skeletal surveys and radiographs.
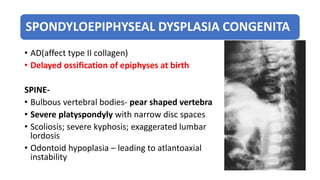
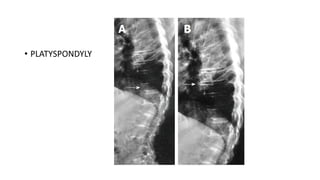
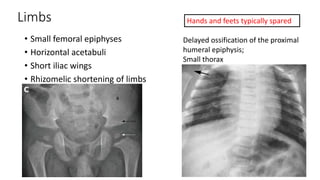
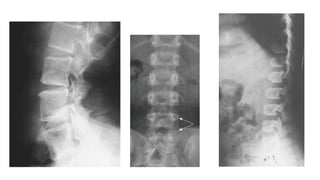
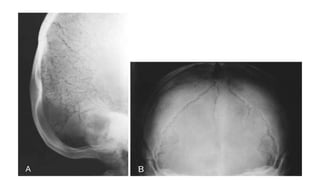
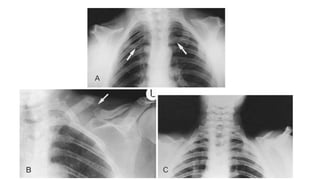
2. Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita is characterized by bulbous vertebral bodies, delayed ossification of epiphyses, and shortening of the limbs, especially proximally.
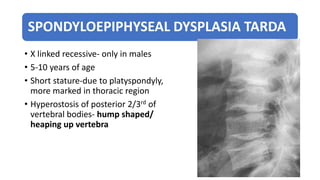
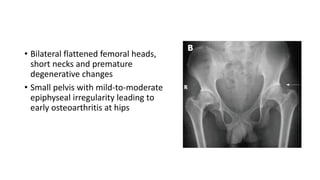
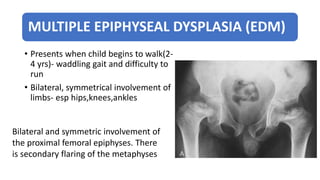
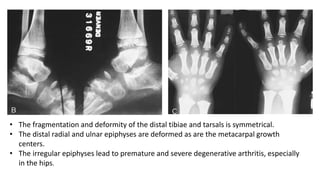
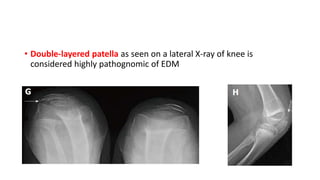
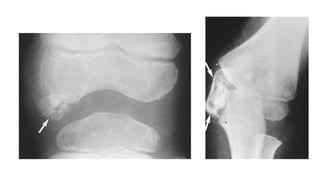
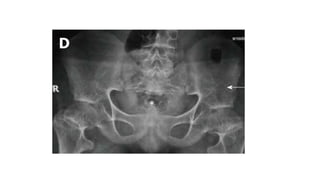
3. Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia presents in childhood with difficulty walking and running due to bilateral and symmetric involvement of the hips, knees, and ankles leading to premature osteoarthritis.